1099 Misc Forms: Understanding Your Tax Obligations

When it comes to navigating the world of freelance work and independent contracting, understanding your tax obligations is crucial. One of the key documents you'll encounter is the 1099-MISC form, which plays a vital role in reporting your income and fulfilling your tax responsibilities. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of the 1099-MISC form, exploring its purpose, who needs to file it, how to complete it accurately, and the potential tax implications it carries. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of your tax obligations as an independent contractor and be well-equipped to handle the 1099-MISC process with confidence.
Unraveling the 1099-MISC Form: A Comprehensive Guide
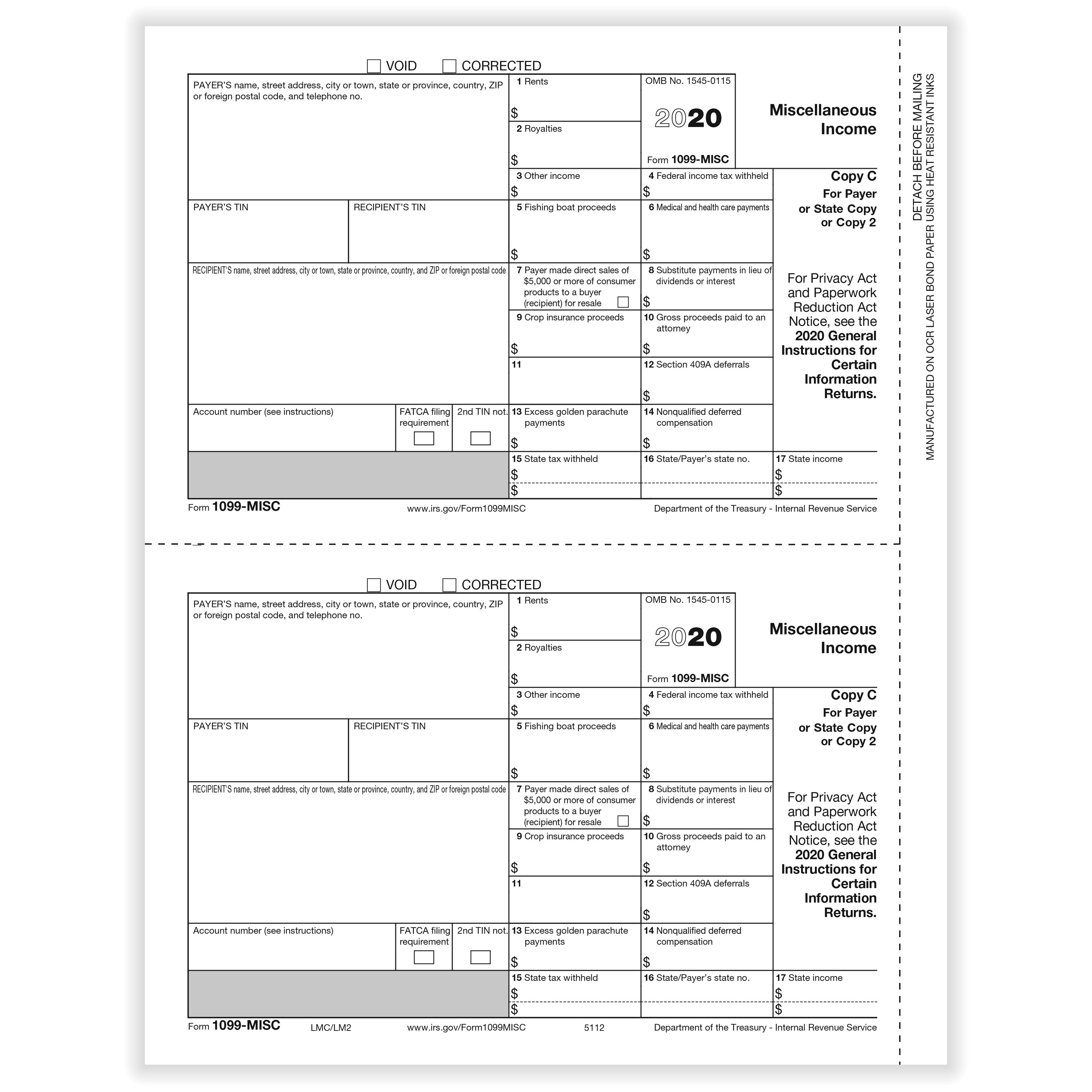
The 1099-MISC form, officially known as the "Miscellaneous Income" form, is a crucial tax document used by businesses and organizations to report various types of income paid to individuals who are not their employees. This form serves as a tool for the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to track and monitor income earned by independent contractors, freelancers, and other non-employee workers. Understanding the purpose and requirements of the 1099-MISC form is essential for both businesses and independent contractors to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Who Needs to File a 1099-MISC Form
The 1099-MISC form is a crucial tax document that affects both businesses and independent contractors. Here's a detailed breakdown of who needs to file this form and under what circumstances:
- Businesses and Organizations: Any business or organization that pays an independent contractor or freelancer for services rendered during the tax year must file a 1099-MISC form. This includes sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and other entities. The form is required when the total payments made to a single contractor exceed $600 during the tax year.
- Independent Contractors and Freelancers: As an independent contractor or freelancer, you are responsible for providing your business or client with your correct taxpayer identification number (TIN), typically your Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). This information is essential for the business to accurately report your income on the 1099-MISC form.
- Types of Income Reported: The 1099-MISC form is used to report various types of income, including rental income, royalties, prizes and awards, medical and health care payments, non-employee compensation, crop insurance proceeds, and fish purchases. Each type of income is reported in a specific box on the form, ensuring accurate reporting to the IRS.
- Exemptions and Exceptions: While the 1099-MISC form is a comprehensive reporting tool, there are certain exceptions and exemptions. For instance, payments made to corporations are generally not reported on the 1099-MISC form. Additionally, payments made to certain types of independent contractors, such as attorneys, may be exempt from reporting if the payments are for legal services and the attorney is a member of a law firm. It's important to consult with a tax professional or refer to IRS guidelines to understand these exemptions fully.
By understanding the criteria for filing a 1099-MISC form, businesses can ensure compliance with tax regulations, while independent contractors can anticipate the income reporting they will receive from their clients. This transparency and accuracy in reporting income are vital for maintaining a fair and accountable tax system.
Completing the 1099-MISC Form: A Step-by-Step Guide
Completing the 1099-MISC form accurately is essential to ensure compliance with tax regulations. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
- Obtain the Form: You can download the 1099-MISC form from the IRS website or obtain it from a tax preparation software provider. Ensure you are using the most recent version of the form to avoid any potential issues.
- Gather Necessary Information: Before filling out the form, gather the following information:
- Your business or organization's details, including name, address, and employer identification number (EIN)
- The independent contractor's or freelancer's name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN)
- The total amount of payments made to the contractor during the tax year
- The specific type of income being reported (e.g., rental income, non-employee compensation)
- Fill Out the Form: Carefully follow the instructions provided by the IRS for completing the 1099-MISC form. Here's a general overview of the key sections:
- Recipient's Information: Enter the contractor's name, address, and TIN in the designated fields. Ensure accuracy to avoid potential penalties.
- Payer's Information: Provide your business or organization's details, including your name, address, and EIN.
- Income Amounts: Report the total amount of payments made to the contractor in the appropriate box based on the type of income. For instance, non-employee compensation is reported in Box 7.
- Federal Income Tax Withheld: If federal income tax was withheld from the contractor's payments, enter the amount in Box 4.
- State Tax Withheld: If state income tax was withheld, enter the amount in Box 17.
- Sign and Date the Form: Once you have completed the form, sign and date it in the designated area. This step is crucial to validate the accuracy of the information provided.
- Provide Copies to the Contractor: Send a copy of the completed 1099-MISC form to the contractor by January 31st of the following year. This ensures they have the necessary information for their tax filing.
- File with the IRS: Submit the original 1099-MISC form to the IRS by the filing deadline, which is typically the end of February for paper filings and the end of March for electronic filings. Failure to file on time may result in penalties.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can ensure that the 1099-MISC form is completed accurately and submitted on time. Proper completion of this form is essential for both businesses and independent contractors to fulfill their tax obligations and maintain a transparent reporting system.
Tax Implications and Strategies for Independent Contractors
As an independent contractor, understanding the tax implications of the 1099-MISC form is crucial for effective financial planning. Here's a closer look at the tax obligations you may face and some strategies to navigate them:
Tax Obligations for Independent Contractors
When you receive a 1099-MISC form, it signifies that your client has reported your income to the IRS. This means you are responsible for paying taxes on that income. Here are some key tax obligations to keep in mind:
- Income Tax: You must pay income tax on the income reported on the 1099-MISC form. The tax rate and brackets will depend on your overall income and tax filing status.
- Self-Employment Tax: As an independent contractor, you are responsible for paying both the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. This is known as self-employment tax, and it can be a significant expense. It's important to set aside funds specifically for this tax obligation.
- Estimated Tax Payments: Since you don't have taxes withheld from your income like traditional employees, you may need to make estimated tax payments throughout the year. These payments help cover your income tax and self-employment tax liabilities. The IRS provides guidelines on how to calculate and pay estimated taxes.
Strategies for Managing Tax Obligations
To effectively manage your tax obligations as an independent contractor, consider the following strategies:
- Set Aside Funds for Taxes: Allocate a portion of your income specifically for tax payments. This will help you avoid any surprises come tax time and ensure you have the necessary funds to cover your tax liabilities.
- Use Tax Preparation Software: Invest in reputable tax preparation software that is tailored to independent contractors. These tools can help you calculate your tax obligations accurately and guide you through the filing process.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a tax professional who specializes in independent contractor taxes. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances and help you maximize deductions and credits.
- Keep Detailed Records: Maintain thorough records of your income, expenses, and any tax-related documents. This will make it easier to prepare your tax returns and support any deductions or credits you claim.
- Explore Tax-Efficient Business Structures: Consider incorporating or forming a limited liability company (LLC) to take advantage of potential tax benefits and liability protection. Consult with a tax advisor to determine the most suitable business structure for your situation.
By understanding your tax obligations and implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage your tax responsibilities as an independent contractor. Proper planning and record-keeping are essential to ensure compliance with tax regulations and minimize any potential tax liabilities.
Conclusion: Navigating the 1099-MISC Landscape

The 1099-MISC form is a critical component of the tax landscape for both businesses and independent contractors. By understanding the purpose, requirements, and implications of this form, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations and effectively manage your tax obligations. Whether you're a business owner issuing 1099-MISC forms or an independent contractor receiving them, accurate reporting and timely filing are essential to maintain a transparent and accountable tax system.
As the freelance and independent contractor workforce continues to grow, staying informed about tax obligations and best practices is more important than ever. By leveraging the insights and strategies outlined in this guide, you can navigate the 1099-MISC process with confidence and ensure a smooth tax experience.
What is the purpose of the 1099-MISC form?
+The 1099-MISC form is used to report various types of income paid to independent contractors, freelancers, and non-employees. It helps the IRS track income and ensure proper tax reporting.
Who is required to file a 1099-MISC form?
+Businesses and organizations that pay independent contractors or freelancers for services exceeding $600 during the tax year are required to file a 1099-MISC form.
What types of income are reported on the 1099-MISC form?
+The 1099-MISC form is used to report rental income, royalties, prizes and awards, medical and health care payments, non-employee compensation, crop insurance proceeds, and fish purchases.
What are the tax implications for independent contractors receiving a 1099-MISC form?
+Independent contractors are responsible for paying income tax and self-employment tax on the income reported on the 1099-MISC form. They may also need to make estimated tax payments throughout the year.