15 Key Factors Impacting Life Expectancy

Life expectancy is a fundamental metric that reflects the health and well-being of populations worldwide. It is a complex and multifaceted concept influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from individual choices to global socioeconomic conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective public health strategies and policies aimed at improving the overall quality of life and longevity.
In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the 15 key factors that significantly impact life expectancy, exploring their mechanisms, global variations, and potential strategies for mitigation. By examining these factors through the lens of real-world examples and evidence-based research, we aim to provide a nuanced understanding of the intricate web of influences shaping life expectancy across the globe.
The Intricate Web of Factors Shaping Life Expectancy

Life expectancy, a critical indicator of a population’s health and vitality, is influenced by a complex interplay of biological, behavioral, environmental, and socioeconomic factors. While advancements in medical science and public health initiatives have contributed to significant increases in life expectancy over the past century, disparities persist across regions and demographic groups. Understanding these key factors is essential for developing targeted interventions and policies to promote healthy aging and reduce health inequalities.
1. Access to Quality Healthcare
Access to quality healthcare is a cornerstone of life expectancy. Populations with timely and equitable access to preventive care, diagnostics, and treatment options tend to experience better health outcomes and longer lifespans. Conversely, limited access to healthcare, often observed in low- and middle-income countries, contributes to higher mortality rates, particularly for treatable conditions like infectious diseases and maternal health complications.
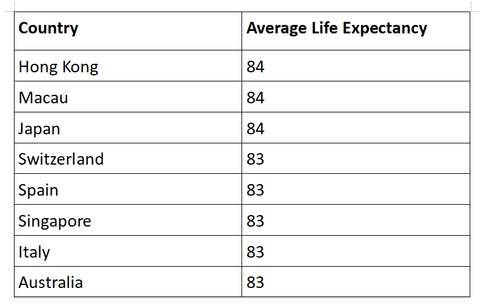
Case Study: Universal Healthcare in Japan
Japan boasts one of the highest life expectancies globally, with an average lifespan of 84.2 years. This longevity is attributed, in part, to the country’s universal healthcare system, which guarantees access to essential medical services for all citizens. The system emphasizes preventive care, early detection, and comprehensive treatment, contributing to lower mortality rates from chronic diseases and better management of age-related health issues.
2. Nutritional Status and Dietary Patterns
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in determining life expectancy. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall health, boosts the immune system, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. Conversely, malnutrition and dietary deficiencies can lead to weakened immune systems, increased susceptibility to infections, and a higher likelihood of developing non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
The Mediterranean Diet: A Recipe for Longevity
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by a high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats, has been associated with increased life expectancy and reduced risk of chronic diseases. This dietary pattern, observed in regions bordering the Mediterranean Sea, is believed to contribute to the lower rates of cardiovascular disease and certain cancers in these populations.
3. Physical Activity and Exercise
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of healthy aging. Exercise promotes cardiovascular health, strengthens muscles and bones, and improves mental well-being. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle is associated with an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers, all of which can significantly reduce life expectancy.
The Power of Physical Activity in Preventing Chronic Diseases
Research suggests that regular physical activity can reduce the risk of chronic diseases by up to 50%. For instance, moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, has been shown to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, while strength training can help prevent age-related muscle loss and improve bone density.
4. Smoking and Tobacco Use

Smoking and tobacco use are leading preventable causes of premature death worldwide. Tobacco smoke contains thousands of harmful chemicals, including nicotine and tar, which can damage nearly every organ in the body. Smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory conditions, significantly reducing life expectancy.
Global Tobacco Control: A Success Story
Global efforts to reduce tobacco use have led to significant declines in smoking rates and tobacco-related deaths. For instance, the implementation of comprehensive tobacco control policies, including smoke-free laws, increased tobacco taxes, and public awareness campaigns, has contributed to a 38% decrease in smoking prevalence in the United States since 1965. Similar successes have been observed in other countries, highlighting the effectiveness of evidence-based tobacco control strategies.
5. Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption, particularly excessive drinking, is associated with a range of health risks, including liver disease, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some health benefits, such as reduced risk of heart disease, excessive drinking can lead to organ damage, increased accident risk, and social and economic consequences, all of which can impact life expectancy.
Moderation is Key: The Benefits of Responsible Drinking
Moderate alcohol consumption, defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men, has been associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and certain types of stroke. However, it’s important to note that the benefits of moderate drinking are not observed in all populations, and the risks of excessive drinking far outweigh any potential benefits.
6. Air Quality and Environmental Factors
The quality of the air we breathe has a significant impact on life expectancy. Exposure to air pollutants, such as particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide, can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, increasing the risk of premature death. Additionally, environmental factors like water quality, sanitation, and exposure to toxic substances can also influence life expectancy.
The Impact of Air Pollution on Life Expectancy: A Global Concern
Air pollution is responsible for an estimated 7 million premature deaths worldwide each year. In highly polluted regions, such as certain cities in India and China, the average life expectancy can be reduced by up to 5 years due to the adverse health effects of air pollution. Efforts to improve air quality, such as implementing stricter emission standards and promoting clean energy sources, are crucial for mitigating these health risks.
7. Socioeconomic Status and Education
Socioeconomic status and education level are strongly correlated with life expectancy. Individuals with higher socioeconomic status and educational attainment tend to have better access to healthcare, healthier lifestyles, and reduced exposure to environmental risks. Conversely, lower socioeconomic status and limited education can lead to poorer health outcomes and reduced life expectancy.
The Impact of Education on Health and Longevity
Education plays a critical role in shaping health behaviors and outcomes. Individuals with higher levels of education are more likely to adopt healthy lifestyles, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and smoking cessation. Additionally, education can lead to better job opportunities and higher incomes, which are associated with improved access to healthcare and reduced exposure to environmental risks.
8. Mental Health and Well-being
Mental health and well-being are essential components of overall health and can significantly impact life expectancy. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and stress can increase the risk of physical health problems, including cardiovascular disease and immune system dysfunction. Additionally, mental health issues can lead to unhealthy behaviors, such as substance abuse and poor dietary choices, further reducing life expectancy.
The Link Between Mental Health and Physical Health
Research has consistently shown a strong association between mental health and physical health. For instance, individuals with depression are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, and those with anxiety disorders are more likely to experience respiratory conditions. Addressing mental health issues is crucial for promoting overall well-being and improving life expectancy.
9. Infectious Diseases and Immunization
Infectious diseases remain a significant threat to global health and can significantly impact life expectancy, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare and immunization programs. Vaccination is a highly effective strategy for preventing the spread of infectious diseases and reducing mortality rates, particularly for diseases such as measles, polio, and tetanus.
The Success of Global Immunization Programs
Global immunization programs have achieved remarkable success in reducing the burden of infectious diseases. For instance, the World Health Organization’s (WHO) Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI) has contributed to significant declines in mortality rates from vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles and polio. As a result, life expectancy has increased in many regions, particularly among children and vulnerable populations.
10. Maternal and Child Health
The health of mothers and children is a critical determinant of life expectancy. Adequate prenatal and postnatal care, access to family planning services, and early childhood nutrition and development programs are essential for ensuring healthy pregnancies, reducing maternal and infant mortality, and promoting long-term health and well-being.
The Impact of Early Childhood Nutrition on Life Expectancy
Nutrition during the first 1,000 days of life, from conception to a child’s second birthday, is critical for healthy growth and development. Adequate nutrition during this period can reduce the risk of stunting, improve cognitive development, and lay the foundation for a healthy and productive life. Interventions such as breastfeeding promotion, micronutrient supplementation, and early childhood development programs can have long-lasting impacts on life expectancy.
11. Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer, are leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Effective management of these conditions through lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular medical care can significantly improve life expectancy and quality of life. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and reducing mortality rates.
The Role of Lifestyle Modifications in Chronic Disease Management
Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking, are cornerstone strategies for managing chronic diseases. For instance, a heart-healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. Similarly, weight management and blood sugar control are essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications.
12. Healthcare Infrastructure and Capacity
The strength and capacity of a country’s healthcare infrastructure significantly impact life expectancy. Well-equipped and well-staffed healthcare facilities, coupled with a robust public health system, can provide timely and effective care for a wide range of health issues. Conversely, limited healthcare infrastructure and capacity can lead to delays in treatment, increased morbidity, and higher mortality rates.
The Impact of Healthcare Infrastructure on Maternal and Infant Mortality
Adequate healthcare infrastructure is particularly crucial for reducing maternal and infant mortality rates. Well-equipped maternity wards, skilled healthcare professionals, and access to emergency obstetric care can significantly improve outcomes for mothers and newborns. For instance, in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure, the risk of maternal and infant mortality is significantly higher due to delays in accessing emergency care and limited access to skilled birth attendants.
13. Gender and Biological Factors
Gender and biological factors play a role in determining life expectancy. On average, women tend to live longer than men, likely due to a combination of biological, behavioral, and social factors. Additionally, certain genetic and biological variations can influence an individual’s susceptibility to diseases and their response to treatment, impacting life expectancy.
The Gender Gap in Life Expectancy: Understanding the Differences
The gender gap in life expectancy is a complex phenomenon influenced by a range of factors. On average, women live longer than men due to a combination of biological factors, such as hormonal differences and a stronger immune system, as well as behavioral factors, such as lower rates of risky behaviors like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. However, the gender gap is narrowing in many countries due to improvements in healthcare and lifestyle factors, particularly among women.
14. Social Support and Community Engagement
Social support and community engagement are important determinants of life expectancy. Strong social networks, active community involvement, and positive social relationships can contribute to better mental health, reduced stress, and improved overall well-being. Conversely, social isolation and lack of community engagement can lead to increased health risks and reduced life expectancy.
The Power of Social Support in Promoting Healthy Aging
Research has shown that individuals with strong social support networks tend to have better health outcomes and longer lifespans. Social support can provide emotional comfort, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging, all of which can reduce stress and promote healthy behaviors. Additionally, community engagement can lead to increased physical activity, improved access to healthy foods, and a stronger sense of social cohesion, further contributing to healthy aging.
15. Public Health Interventions and Policy
Public health interventions and policies play a critical role in shaping life expectancy. Effective public health strategies, such as vaccination campaigns, tobacco control measures, and healthy lifestyle promotion, can significantly improve population health and reduce mortality rates. Additionally, policies that address social determinants of health, such as income inequality and access to education, can have long-lasting impacts on life expectancy.
The Success of Public Health Interventions: A Case Study
The success of public health interventions is well-illustrated by the case of tobacco control. Comprehensive tobacco control policies, such as those implemented in many high-income countries, have led to significant declines in smoking rates and tobacco-related deaths. These policies include smoke-free laws, increased tobacco taxes, public awareness campaigns, and restrictions on tobacco advertising. As a result, life expectancy has increased, particularly among populations previously heavily impacted by tobacco-related diseases.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex Web of Life Expectancy Factors
Life expectancy is a multifaceted concept influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from individual behaviors and social support to global healthcare systems and public health policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to promote healthy aging and reduce health disparities. By addressing these key influences through targeted interventions and policies, we can work towards a future where all individuals have the opportunity to lead long, healthy, and fulfilling lives.
How does access to healthcare impact life expectancy?
+Access to quality healthcare is a cornerstone of life expectancy. Populations with timely and equitable access to preventive care, diagnostics, and treatment options tend to experience better health outcomes and longer lifespans. Conversely, limited access to healthcare, often observed in low- and middle-income countries, contributes to higher mortality rates, particularly for treatable conditions like infectious diseases and maternal health complications.
What is the impact of nutrition on life expectancy?
+Nutrition plays a pivotal role in determining life expectancy. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall health, boosts the immune system, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. Conversely, malnutrition and dietary deficiencies can lead to weakened immune systems, increased susceptibility to infections, and a higher likelihood of developing non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
How does physical activity impact life expectancy?
+Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of healthy aging. Exercise promotes cardiovascular health, strengthens muscles and bones, and improves mental well-being. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle is associated with an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers, all of which can significantly reduce life expectancy.


