15+ Safe Injection Locations For Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone therapy, a treatment for low testosterone levels, is a vital medical intervention for many individuals. When administered correctly, it can significantly improve quality of life. However, the safety and effectiveness of this therapy largely depend on the injection site and technique used. In this article, we will explore over 15 safe injection locations for testosterone therapy, offering an in-depth guide to help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
Understanding Testosterone Therapy

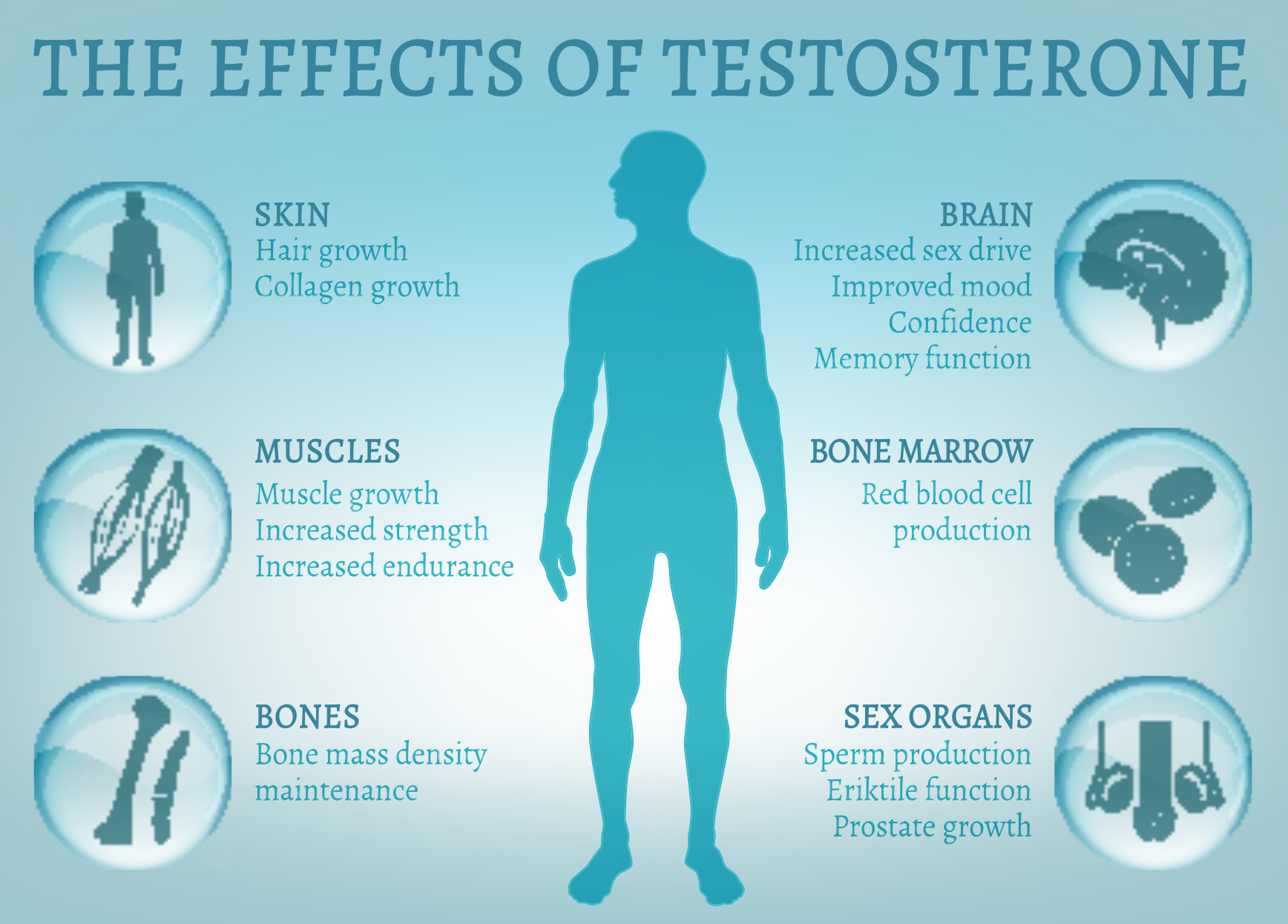
Testosterone, often referred to as the “male hormone,” plays a crucial role in various physiological functions in both men and women. It influences muscle mass, bone density, fat distribution, red blood cell production, and sexual health. When the body’s natural testosterone production is insufficient, medical intervention in the form of testosterone therapy may be recommended.
Testosterone therapy involves the administration of synthetic testosterone, typically via injections, to restore hormone levels to a normal range. This treatment is commonly prescribed for conditions such as hypogonadism, delayed puberty, and menopause symptoms. While the benefits of testosterone therapy are well-documented, it's essential to ensure safe and effective administration to avoid potential complications.
Safe Injection Locations for Testosterone Therapy

Selecting the right injection site is crucial for the success and safety of testosterone therapy. Here are over 15 safe and effective injection locations, each with its own advantages and considerations.
1. Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle, located in the upper arm, is a popular choice for testosterone injections due to its ease of access and quick absorption. It’s an excellent option for individuals who prefer a quicker release of testosterone into the bloodstream.
2. Vastus Lateralis
The vastus lateralis, a muscle in the thigh, is another commonly used injection site. This location is particularly beneficial for individuals who prefer a slower release of testosterone, as the muscle’s size and blood supply allow for a more gradual absorption.
3. Ventrogluteal Muscle
The ventrogluteal muscle, located in the upper outer quadrant of the buttock, is a safe and effective injection site. It’s preferred by many healthcare providers due to its low risk of nerve and blood vessel damage.
4. Dorsogluteal Muscle
The dorsogluteal muscle, found in the upper outer quadrant of the buttock, is a traditional injection site. However, due to the risk of injury to nearby nerves and blood vessels, it’s less preferred than the ventrogluteal site.
5. Rectus Femoris
The rectus femoris, a muscle in the front of the thigh, is a viable injection location. It offers a good balance between ease of access and absorption rate.
6. Biceps Femoris
The biceps femoris, located in the back of the thigh, is another option for testosterone injections. This muscle provides a large area for injection and is often used for individuals with smaller deltoid or vastus lateralis muscles.
7. Semimembranosus
The semimembranosus, a deep muscle in the back of the thigh, is a less commonly used but safe injection site. It’s suitable for individuals who prefer a deeper injection location.
8. Tensor Fasciae Latae
The tensor fasciae latae, a muscle in the outer thigh, is a viable option for testosterone injections. It’s easily accessible and provides good absorption rates.
9. Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat
For individuals who prefer a less invasive approach, injecting testosterone into the subcutaneous abdominal fat just below the navel can be an option. This method is typically used for testosterone esters that are designed for subcutaneous administration.
10. Subcutaneous Upper Arm
Similar to the abdominal fat, the upper arm’s subcutaneous fat can be used for testosterone injections. This location is often chosen for its ease of access and comfort.
11. Subcutaneous Thigh
The subcutaneous fat in the thigh is another option for testosterone therapy. It provides a large area for injection and is suitable for individuals who prefer a less painful approach.
12. Subcutaneous Hip
The hip’s subcutaneous fat can be used for testosterone injections, offering a less painful alternative to muscle injections.
13. Gluteal Fold
The gluteal fold, the crease between the buttock and thigh, is a safe injection site. It’s often chosen for its convenience and ease of access.
14. Subcutaneous Buttock
The subcutaneous fat in the buttock can be used for testosterone injections, providing a larger area for administration.
15. Subcutaneous Calf
The subcutaneous fat in the calf is a less commonly used but safe injection location. It’s suitable for individuals who prefer a lower-body injection site.
16. Subcutaneous Upper Back
For individuals who find it challenging to reach other injection sites, the subcutaneous fat in the upper back can be an option. However, this location may be less comfortable for some.
Performance Analysis and Best Practices
When administering testosterone therapy, it’s crucial to consider several factors to ensure optimal performance and safety. These include the type of testosterone prescribed, the patient’s medical history, and their preference for injection sites.
Testosterone esters, such as testosterone cypionate and testosterone enanthate, are commonly used for intramuscular injections. These esters have a longer half-life, allowing for less frequent injections. On the other hand, testosterone propionate, with its shorter half-life, may require more frequent administration.
The patient's medical history, especially any history of bleeding disorders or blood clotting issues, should be carefully considered. Individuals with such conditions may benefit from subcutaneous injections, which carry a lower risk of bleeding complications.
Patient preference plays a significant role in choosing the injection site. Some individuals may prefer a less painful approach, while others may prioritize convenience or the speed of absorption. Healthcare providers should work closely with patients to determine the most suitable injection location and technique.
Future Implications and Research
As the field of testosterone therapy continues to evolve, research is ongoing to improve the safety and effectiveness of treatment. One area of focus is the development of new testosterone delivery methods, such as transdermal patches and oral medications, which may offer alternative administration routes for individuals who prefer non-injection methods.
Additionally, ongoing research aims to optimize the dosing and timing of testosterone therapy to achieve the best possible outcomes. This includes studying the impact of different injection sites on testosterone absorption and distribution throughout the body.
Another crucial aspect of future research is the long-term safety of testosterone therapy. While short-term studies have shown its effectiveness and safety, long-term studies are needed to fully understand the potential risks and benefits of this treatment.
Conclusion

Testosterone therapy is a vital treatment option for individuals with low testosterone levels. By understanding the various safe injection locations and their advantages, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions to ensure the success and safety of this therapy. As research continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in testosterone therapy, offering even better outcomes for patients.
How often should testosterone injections be administered?
+The frequency of testosterone injections depends on the type of testosterone prescribed and the patient’s individual needs. Typically, injections are given every 1 to 4 weeks, with the exact schedule determined by a healthcare professional.
Are there any side effects associated with testosterone therapy?
+Yes, like any medical treatment, testosterone therapy may have side effects. Common side effects include acne, increased red blood cell count, and changes in cholesterol levels. More serious but rare side effects include liver damage and cardiovascular issues. It’s essential to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider before starting therapy.
Can women undergo testosterone therapy?
+Yes, testosterone therapy can be prescribed to women with low testosterone levels, typically as part of hormone replacement therapy for menopause symptoms or other conditions. However, the dosage and administration may differ from male patients.



