15 Ways To Master The Poisson Distribution Calculator
Unraveling the Poisson Distribution Calculator: 15 Essential Tips for Accurate Results
The Poisson distribution calculator is a powerful tool for statisticians, researchers, and data analysts, offering a means to model and understand various real-world phenomena characterized by independent events occurring at a constant rate. This article delves into 15 essential tips to help you master the Poisson distribution calculator, ensuring accurate and insightful results for your statistical analyses.
1. Understanding the Poisson Distribution

Before diving into the calculator, it's crucial to grasp the fundamentals of the Poisson distribution. This discrete probability distribution describes the probability of an event occurring in a given interval if these events occur with a known average rate and are independent of the time since the last event. In other words, the Poisson distribution is a powerful tool for modeling rare events that occur at a known average rate.
Mathematically, the Poisson distribution is defined by the equation:
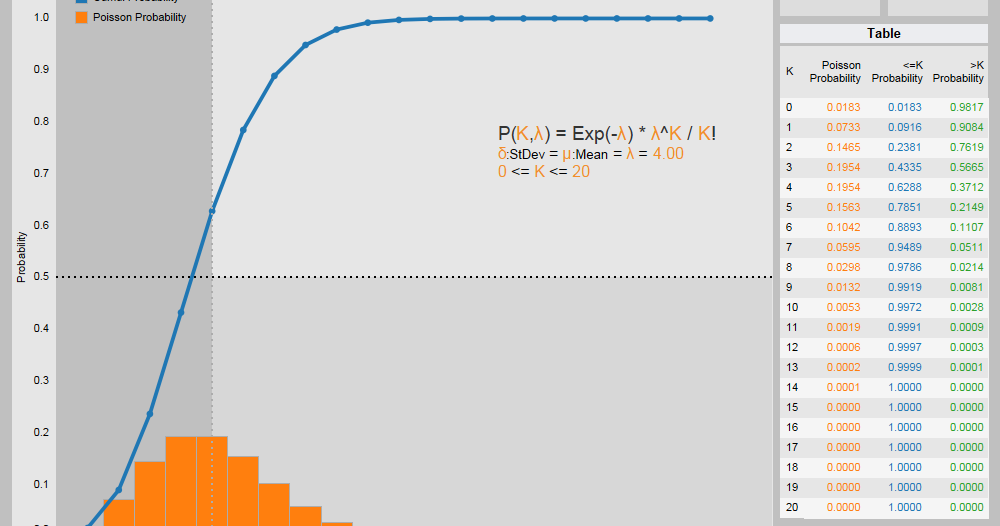
P(x; λ) = (e^-λ * λ^x) / x! where:
- P(x; λ) is the probability of x events occurring
- λ is the average rate of events
- e is the base of the natural logarithm
- x is the number of events
- x! is the factorial of x (x factorial)
Understanding this equation and its variables is key to using the Poisson distribution calculator effectively.
2. Choosing the Right Poisson Calculator
With numerous Poisson distribution calculators available online, it's essential to select one that suits your specific needs. Consider factors such as ease of use, the range of features offered, and the calculator's reputation for accuracy. Some calculators may offer additional functionalities, such as the ability to calculate cumulative probabilities or generate random numbers from a Poisson distribution.
3. Data Collection and Preparation
Accurate data collection and preparation are vital for reliable Poisson distribution calculations. Ensure that your data meets the assumptions of the Poisson distribution, such as independence of events and a constant average rate. Clean and preprocess your data to remove any outliers or anomalies that may skew your results.
For instance, if you're analyzing the number of customers entering a store per hour, ensure that your data represents a random sample and that the rate of customer entry remains relatively constant over time.
4. Specifying the Average Rate

The Poisson distribution calculator requires you to input the average rate of events, often denoted as λ (lambda). This value represents the expected number of events in a given interval. Ensure that your data supports the use of this rate, and consider the implications of choosing a specific value. For example, if you're modeling the number of car accidents per month, the average rate might vary based on factors like weather conditions or road conditions.
5. Understanding the Impact of Average Rate
The average rate of events in a Poisson distribution has a significant impact on the shape and characteristics of the distribution. A higher average rate will result in a higher probability of more events occurring, while a lower rate will shift the probability towards fewer events. Understanding how changes in the average rate affect the distribution is crucial for interpreting your results accurately.
6. Calculating Probabilities
One of the primary uses of the Poisson distribution calculator is to determine the probability of a specific number of events occurring. This can be particularly useful in fields like insurance, where the probability of claims can be modeled using the Poisson distribution. For example, an insurance company might use the calculator to determine the probability of receiving 5 claims in a given month, helping them set appropriate premiums.
7. Exploring Cumulative Probabilities
Cumulative probabilities provide a more comprehensive view of the Poisson distribution. These probabilities represent the likelihood of an event occurring or not occurring a certain number of times. A Poisson distribution calculator with cumulative probability functionality can be particularly useful for understanding the overall risk or likelihood of events.
8. Visualizing the Distribution
Visual representations of the Poisson distribution can greatly enhance your understanding of the data. Many Poisson distribution calculators offer the ability to generate histograms or bar charts, allowing you to see the distribution of events at a glance. This visual approach can help you identify patterns, outliers, or areas of interest in your data.
9. Sensitivity Analysis
Conducting sensitivity analysis is an important step in using the Poisson distribution calculator. This involves testing the calculator's results with different input values to understand how changes in the average rate affect the distribution. By performing sensitivity analysis, you can gain a deeper understanding of the stability and reliability of your results.
10. Comparing with Other Distributions
While the Poisson distribution is a powerful tool, it's not always the best fit for every dataset. Compare your results with those from other distributions, such as the normal distribution or the exponential distribution, to ensure that the Poisson distribution is the most appropriate model for your data. This comparative analysis can help you make more informed decisions about your statistical modeling.
11. Handling Large Datasets
When working with large datasets, the Poisson distribution calculator can be a valuable tool for analyzing subsets of your data. By selecting representative samples or subsets, you can efficiently calculate probabilities and explore the distribution without overwhelming your computational resources.
12. Validating Your Results
To ensure the accuracy of your Poisson distribution calculations, it's essential to validate your results. Compare your calculated probabilities with expected outcomes or known data. For example, if you're modeling the number of phone calls received by a call center per hour, compare your calculated probabilities with the actual number of calls received to ensure your model is accurate.
13. Interpreting Results in Context
The Poisson distribution calculator provides numerical results, but it's important to interpret these results in the context of your specific application. Consider the implications of your findings and how they align with your expectations or prior knowledge. For instance, if you're analyzing the number of defects in a manufacturing process, consider whether your calculated probabilities align with industry standards or previous data.
14. Communicating Your Findings
Effectively communicating your results is a critical aspect of using the Poisson distribution calculator. When presenting your findings, ensure that you explain the assumptions, methodologies, and limitations of your analysis. Visual aids, such as charts or graphs, can greatly enhance the clarity and impact of your communication.
15. Continuous Learning and Improvement
Mastering the Poisson distribution calculator is an ongoing process. Stay updated with the latest advancements in statistical methods and tools. Attend workshops, read relevant literature, and engage with other professionals in your field to continuously enhance your skills and knowledge. Continuous learning will ensure that you remain at the forefront of statistical analysis and interpretation.
What are some real-world applications of the Poisson distribution calculator?
+
The Poisson distribution calculator finds applications in various fields, including insurance (modeling claim probabilities), manufacturing (analyzing defect rates), telecommunications (predicting call volumes), and healthcare (modeling patient arrivals). Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for understanding and predicting rare events.
How can I ensure the accuracy of my Poisson distribution calculations?
+
To ensure accuracy, collect high-quality data, validate your results against known outcomes or expectations, and conduct sensitivity analysis to understand the impact of input variables. Regularly review and update your assumptions to maintain the integrity of your calculations.
What are some common challenges when using the Poisson distribution calculator?
+
Challenges may include selecting the appropriate average rate, handling large datasets efficiently, and interpreting results in complex scenarios. Additionally, ensuring the data meets the assumptions of the Poisson distribution can be a challenge, especially when dealing with non-independent events or non-constant rates.



