A Comprehensive Guide To Designing Effective Crosssectional Research

Cross-sectional research is a valuable method employed by researchers and data analysts to gather insights and make informed decisions. This research design involves collecting data from a diverse range of individuals or entities at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of the variables of interest. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of designing effective cross-sectional research, exploring its benefits, challenges, and best practices to ensure accurate and actionable findings.
Understanding the Power of Cross-Sectional Research
Cross-sectional research offers a unique perspective by capturing a wide range of data within a single study. Unlike longitudinal studies that track changes over time, cross-sectional research focuses on a single moment, making it an efficient approach for exploring various phenomena simultaneously. By comparing data from different groups or individuals, researchers can identify patterns, correlations, and trends that may not be apparent in isolated studies.
Key Advantages of Cross-Sectional Research
The design of cross-sectional research presents several advantages that make it a popular choice for researchers across various disciplines. Firstly, it allows for a quick and cost-effective data collection process, as researchers can gather information from multiple sources simultaneously. This efficiency is particularly beneficial when time and resources are limited.
Secondly, cross-sectional research provides a snapshot of the current state of affairs, making it ideal for studying phenomena that are rapidly changing or time-sensitive. Researchers can capture a moment in time and analyze the relationships between variables at that specific point, offering valuable insights into the dynamics of the subject matter.
Additionally, this research design enables the examination of a diverse range of variables and their interactions. By including multiple variables in the study, researchers can explore complex relationships and identify potential causes and effects. This flexibility makes cross-sectional research well-suited for exploring multifaceted issues and generating hypotheses for further investigation.
Challenges and Considerations
While cross-sectional research offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that researchers must navigate. One of the primary concerns is the risk of drawing conclusions based on a single snapshot of data. Without longitudinal data, it can be challenging to establish causality or understand the dynamics of change over time.
Another challenge lies in the potential for selection bias. Cross-sectional studies often rely on convenience sampling, which may not represent the entire population of interest. This can lead to biased results and limit the generalizability of the findings. Researchers must carefully consider the sampling strategy and ensure that the sample is representative of the target population to mitigate this risk.
Furthermore, cross-sectional research may not capture the full complexity of certain phenomena. Some variables may change over time, and capturing their dynamics requires a longitudinal approach. Researchers should be mindful of the limitations of cross-sectional data and consider complementing it with other research designs to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Designing an Effective Cross-Sectional Research Study

To ensure the success of a cross-sectional research study, careful planning and attention to detail are essential. Here are some key steps and considerations for designing an effective cross-sectional research project.
Define Research Objectives
Start by clearly defining the research objectives and questions you aim to address. Identify the specific variables of interest and the relationships you want to explore. A well-defined research question will guide the study design and data collection process, ensuring that the findings are relevant and meaningful.
Select an Appropriate Sample
Choosing the right sample is crucial for the validity and generalizability of your research. Consider the target population and determine the most appropriate sampling method. Random sampling, stratified sampling, or cluster sampling may be used, depending on the nature of your study and the characteristics of the population.
Ensure that the sample size is sufficient to provide reliable results. Use statistical methods to calculate the required sample size based on the desired level of precision and confidence. A larger sample size can increase the accuracy and representativeness of your findings.
Develop a Comprehensive Data Collection Plan
Design a comprehensive data collection plan that aligns with your research objectives. Determine the most suitable data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, observations, or secondary data analysis. Consider the advantages and limitations of each method and choose the ones that best fit your study’s needs.
Develop well-structured questionnaires or interview guides to ensure consistent data collection. Pilot test your instruments to identify and address any potential issues or ambiguities. This step is crucial for maintaining the validity and reliability of your data.
Implement Quality Control Measures
Implement quality control measures throughout the data collection process to ensure the accuracy and integrity of your data. Train data collectors or interviewers to follow standardized procedures and provide clear guidelines for data entry and management. Regularly monitor the data collection process to identify and address any issues promptly.
Consider using data validation techniques, such as cross-checking responses or conducting inter-rater reliability tests, to ensure the consistency and reliability of your data. These measures will enhance the overall quality of your research and reduce the risk of errors or biases.
Analyzing and Interpreting Cross-Sectional Data
Once you have collected your cross-sectional data, the next step is to analyze and interpret it effectively. Here’s a guide to help you navigate the data analysis process.
Data Cleaning and Preparation
Begin by cleaning and preparing your data for analysis. This involves identifying and handling missing values, outliers, or inconsistencies in the dataset. Use appropriate statistical methods to impute missing values or remove outliers that may skew the results. Ensure that your data is in a format suitable for the chosen analysis techniques.
Exploratory Data Analysis
Conduct exploratory data analysis to gain insights into the distribution, patterns, and relationships within your dataset. Visualize the data using charts, graphs, or summary statistics to identify any preliminary trends or correlations. This step helps you understand the data and identify potential areas of interest for further analysis.
Statistical Analysis Techniques
Choose the appropriate statistical analysis techniques based on your research objectives and the nature of your data. Common techniques used in cross-sectional research include descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing. Select the methods that best align with your research questions and the level of analysis required.
Consider the assumptions and limitations of each statistical technique and ensure that your data meets the necessary criteria. For example, regression analysis assumes a linear relationship between variables, so it may not be suitable for highly nonlinear data.
Interpretation and Reporting
Interpret the results of your statistical analysis carefully and draw meaningful conclusions. Consider the context of your study and the practical implications of your findings. Discuss the strengths and limitations of your research and provide suggestions for future studies or interventions based on your results.
Present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate tables, figures, and graphs to support your analysis. Ensure that your report is well-organized and easy to follow, allowing readers to understand the key takeaways and implications of your cross-sectional research.
Ethical Considerations in Cross-Sectional Research
Conducting ethical research is of utmost importance in any scientific endeavor, and cross-sectional research is no exception. Here are some key ethical considerations to keep in mind when designing and conducting your cross-sectional research study.
Informed Consent
Obtain informed consent from all participants involved in your study. Provide clear and detailed information about the purpose of the research, the procedures involved, and any potential risks or benefits. Ensure that participants have the right to refuse or withdraw from the study at any time without penalty.
Privacy and Confidentiality
Protect the privacy and confidentiality of your participants’ information. Implement appropriate data security measures to safeguard personal data and ensure that it is used only for the purposes of your research. Avoid sharing identifiable information without the explicit consent of the participants.
Avoid Harm and Minimizing Risk
Take steps to minimize any potential harm or risk to your participants. Assess the risks associated with your study and implement measures to mitigate them. Ensure that the benefits of the research outweigh any potential risks, and provide appropriate support or resources if participants experience any adverse effects.
Fair Treatment and Non-Discrimination
Treat all participants fairly and without discrimination. Ensure that your research design and data collection procedures do not disadvantage any specific groups or individuals. Strive for diversity and inclusivity in your sample to enhance the generalizability of your findings.
Future Directions and Implications

Cross-sectional research has a wide range of applications and can provide valuable insights across various fields. Here are some potential future directions and implications of this research design.
Policy and Decision-Making
Cross-sectional research can inform policy-making and decision-making processes by providing a snapshot of the current state of affairs. By identifying patterns and correlations, policymakers can develop evidence-based strategies and interventions to address societal issues or improve public services.
Healthcare and Public Health
In the field of healthcare and public health, cross-sectional research can be used to assess the prevalence of diseases, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, or identify risk factors for specific health conditions. By understanding the current health status of a population, researchers and healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions and improve health outcomes.
Market Research and Business
Cross-sectional research is widely used in market research and business to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. By analyzing cross-sectional data, businesses can make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and customer segmentation. This research design enables companies to stay ahead of the competition and adapt to changing market dynamics.
Social Sciences and Humanities
In the social sciences and humanities, cross-sectional research can explore a wide range of topics, including cultural trends, social norms, and human behavior. By comparing data from different groups or time periods, researchers can gain insights into the complexities of human society and develop theories to explain observed phenomena.
Conclusion
Designing effective cross-sectional research requires a thoughtful approach, careful planning, and attention to ethical considerations. By understanding the advantages and limitations of this research design, researchers can leverage its potential to generate valuable insights and inform decision-making across various disciplines. Whether it’s exploring societal trends, evaluating healthcare interventions, or understanding consumer behavior, cross-sectional research plays a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world around us.
How does cross-sectional research differ from longitudinal research?
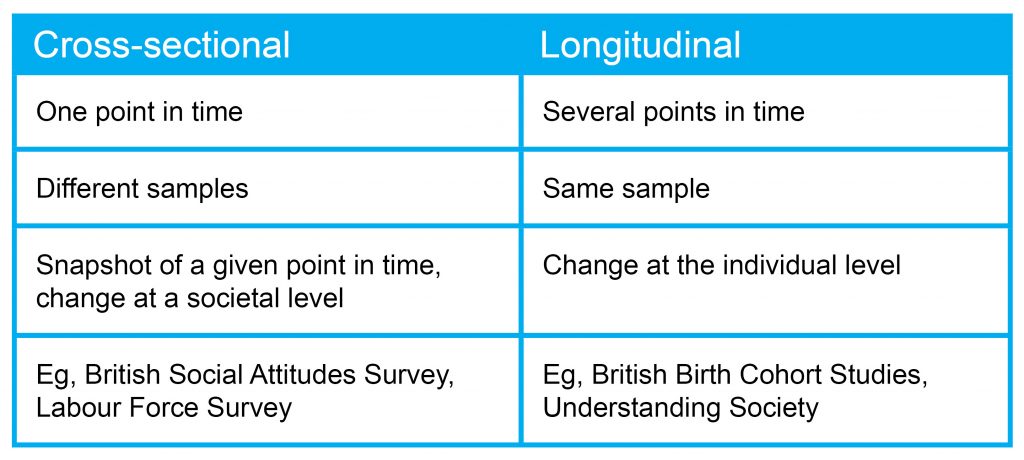
+Cross-sectional research focuses on collecting data from a diverse range of individuals or entities at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of the variables of interest. In contrast, longitudinal research involves tracking changes over time, often following the same individuals or groups over an extended period. While cross-sectional research offers a quick and efficient data collection process, longitudinal research provides a deeper understanding of the dynamics and changes over time.
What are the potential biases in cross-sectional research, and how can they be mitigated?
+Cross-sectional research may be susceptible to selection bias, as the sample may not represent the entire population of interest. To mitigate this, researchers should carefully consider the sampling strategy and ensure that the sample is diverse and representative. Additionally, researchers should be aware of response bias, where participants may provide biased responses due to social desirability or other factors. Implementing measures such as anonymity and confidentiality can help reduce response bias.
How can cross-sectional research be used to inform policy and decision-making?
+Cross-sectional research provides a snapshot of the current state of affairs, which can be valuable for policymakers and decision-makers. By identifying patterns, correlations, and trends, policymakers can develop evidence-based strategies and interventions. For example, cross-sectional research can assess the effectiveness of public health campaigns, evaluate the impact of policy changes, or identify areas where resources should be allocated to address specific societal issues.


