A Comprehensive Ipa Guide: Mastery And Evaluation Strategies
Welcome to the ultimate guide on IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) mastery and evaluation strategies. The IPA is a powerful tool for linguists, language learners, and anyone interested in the science of speech. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of IPA, explore its applications, and provide expert tips for mastering this essential phonetic system. Whether you're a language enthusiast or a professional in the field, this guide will enhance your understanding and proficiency with IPA.
Understanding the IPA: A Global Language of Sounds

The International Phonetic Alphabet is a standardized system of symbols used to represent the sounds of spoken languages. It was developed by the International Phonetic Association to provide a consistent and universal means of transcribing speech sounds. With over 100 symbols and diacritics, the IPA offers a comprehensive framework for describing the intricate nuances of human speech.
One of the key advantages of the IPA is its ability to transcend language barriers. Regardless of the native language, IPA symbols remain consistent, allowing linguists and language enthusiasts to communicate and study the phonetics of any language with precision. This universality makes the IPA an invaluable tool for cross-cultural communication and language documentation.
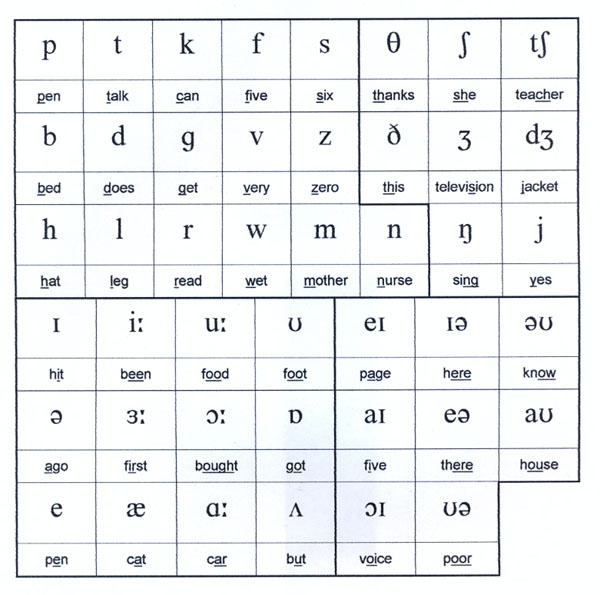
The IPA Symbol Set: A Comprehensive Overview

The IPA symbol set is divided into several categories, each representing a specific aspect of speech production. Let’s explore the primary categories and their significance:
Consonants
Consonants are produced by partially or completely obstructing the airflow in the vocal tract. The IPA provides symbols for various types of consonants, including stops, fricatives, nasals, and more. Each symbol represents a specific manner and place of articulation, ensuring accurate transcription.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| /p/ | Voiceless bilabial stop |
| /b/ | Voiced bilabial stop |
| /t/ | Voiceless alveolar stop |
| /d/ | Voiced alveolar stop |
| /k/ | Voiceless velar stop |
| /g/ | Voiced velar stop |

Vowels
Vowels are produced without any obstruction in the vocal tract, allowing for a free flow of air. The IPA utilizes a two-dimensional vowel chart to represent the different qualities of vowels. The chart positions vowels based on their tongue height and backness, providing a visual representation of their acoustic properties.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| /i/ | Close front unrounded vowel |
| /e/ | Mid-close front unrounded vowel |
| /a/ | Open front unrounded vowel |
| /u/ | Close back rounded vowel |
| /o/ | Mid-close back rounded vowel |
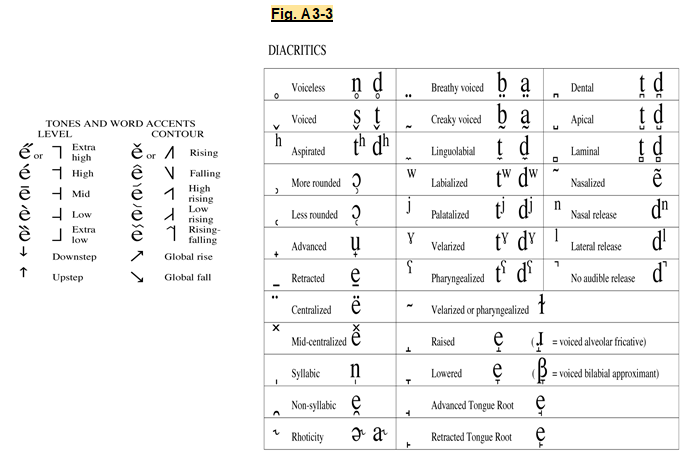
Suprasegmentals
Suprasegmentals refer to features of speech that extend beyond individual segments or phonemes. This category includes elements such as stress, tone, and intonation. The IPA provides symbols and diacritics to mark these suprasegmental features, allowing for a comprehensive description of speech patterns.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| ' | Primary stress marker |
| ˈ | Secondary stress marker |
| ˌ | Unstressed syllable marker |
| ̌ | Rising tone |
| ˥ | High tone |
Mastering IPA: Strategies for Effective Learning
Mastering the IPA requires a systematic approach and consistent practice. Here are some expert strategies to enhance your proficiency with this phonetic system:
Start with the Basics
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the IPA symbol set and its categories. Understand the basic principles of articulation and how each symbol represents a specific sound. Start with the consonants and vowels, as they form the foundation of speech production.
Practice Transcription
Transcription is a crucial skill for IPA mastery. Practice transcribing spoken words and phrases into IPA symbols. Start with simple words and gradually increase the complexity. Focus on accuracy and precision, ensuring that your transcriptions accurately reflect the spoken sounds.
Explore Phonetic Transcription Resources
Utilize online resources, textbooks, and phonetic dictionaries to enhance your IPA knowledge. These resources often provide extensive examples, exercises, and audio recordings to help you understand and practice phonetic transcription. Engage with interactive platforms and mobile apps designed specifically for IPA learning.
Study Language-Specific IPA Applications
Different languages have unique phonetic characteristics, and the IPA is adapted to represent these variations accurately. Study the IPA applications for specific languages you are interested in. Explore the phonetic differences between languages and how the IPA accommodates these variations.
Join IPA Communities and Forums
Engage with online communities and forums dedicated to IPA and linguistics. These platforms provide a wealth of knowledge, resources, and support from fellow IPA enthusiasts and experts. Participate in discussions, share your experiences, and seek guidance when needed.
Evaluating IPA Proficiency: Assessment and Certification
Assessing your IPA proficiency is essential for self-improvement and professional recognition. Here are some strategies for evaluating your skills and obtaining certifications:
Self-Assessment Tools
Utilize online self-assessment tools and quizzes to gauge your IPA knowledge. These tools often cover various aspects of IPA, including symbol recognition, transcription accuracy, and phonetic concepts. Regularly assess your progress to identify areas that require further study.
IPA Proficiency Exams
Consider taking IPA proficiency exams offered by reputable organizations. These exams evaluate your understanding of the IPA symbol set, phonetic transcription, and linguistic concepts. Passing such exams provides a credible validation of your IPA skills and can enhance your professional profile.
Seek Feedback and Peer Review
Share your IPA transcriptions and phonetic analyses with peers and experts in the field. Constructive feedback and peer review can help identify areas of improvement and provide valuable insights into your IPA proficiency. Engage in collaborative learning and seek guidance from experienced linguists.
Applications of IPA: Unlocking Language Potential
The IPA is a versatile tool with numerous applications across various fields. Let’s explore some of the key areas where IPA plays a crucial role:
Language Documentation and Preservation
The IPA is invaluable for documenting and preserving endangered languages. Linguists use IPA to create precise phonetic representations of spoken languages, ensuring that their unique sounds and structures are accurately recorded for future generations.
Language Teaching and Learning
IPA is widely used in language teaching and learning materials. It provides a standardized framework for describing the pronunciation of words and phrases, aiding learners in developing accurate speech patterns. IPA-based phonetic transcriptions are particularly beneficial for language learners aiming to master a new language’s pronunciation.
Speech Therapy and Rehabilitation
In the field of speech therapy, the IPA is a powerful tool for assessing and treating speech disorders. Therapists use IPA to analyze and diagnose speech impairments, develop treatment plans, and monitor progress. The precise representation of speech sounds in IPA facilitates targeted interventions and improved communication skills.
Linguistic Research and Analysis
Linguists rely on the IPA for detailed phonetic analysis and research. The IPA’s standardized symbols and diacritics enable researchers to compare and contrast the phonetics of different languages, study language evolution, and explore the intricate relationships between sounds and meaning.
Future Prospects: The Evolution of IPA
The IPA continues to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of linguistics and language studies. As our understanding of phonetics deepens and new languages are discovered, the IPA remains a dynamic and evolving system. Here are some future prospects and developments to watch for:
Expansion of the IPA Symbol Set
The International Phonetic Association periodically revises and expands the IPA symbol set to accommodate new phonetic discoveries and language variations. Stay updated with the latest IPA revisions and additions to ensure your phonetic knowledge remains current and comprehensive.
Integration of Technology
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing the way we interact with and learn the IPA. Interactive IPA apps, virtual reality (VR) experiences, and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are enhancing the learning process, making IPA more accessible and engaging for a wider audience.
Global Collaboration and Standardization
As the world becomes more interconnected, the need for a universal phonetic system becomes increasingly evident. The IPA serves as a powerful tool for global collaboration and standardization in language studies. Linguists, language enthusiasts, and researchers from diverse backgrounds can come together to further refine and promote the IPA as a global language of sounds.
How is the IPA used in language teaching and learning?
+The IPA is widely used in language teaching materials to provide a standardized representation of pronunciation. It helps learners develop accurate speech patterns and improves their language acquisition skills.
What are some common challenges in mastering the IPA?
+Challenges may include understanding the complex symbol set, recognizing subtle phonetic differences, and accurately transcribing speech. Consistent practice and engagement with phonetic resources can help overcome these challenges.
Are there any online resources for learning the IPA?
+Yes, there are numerous online platforms, websites, and apps dedicated to IPA learning. These resources often provide interactive exercises, audio recordings, and comprehensive guides to enhance your IPA proficiency.



