Crosspollination Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide To Genetic Diversity

Unveiling the Power of Cross-Pollination: Enhancing Genetic Diversity for a Thriving Garden

In the intricate dance of nature, the concept of genetic diversity holds immense importance, especially when it comes to the health and vitality of our gardens. Among the myriad strategies to achieve this diversity, cross-pollination stands out as a powerful tool, offering a plethora of benefits to both amateur and seasoned gardeners alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of cross-pollination, exploring its role, methods, and the profound impact it can have on the genetic makeup of your garden's flora.
Understanding the Significance of Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity is the lifeblood of any ecosystem, and gardens are no exception. It refers to the variety of genetic characteristics within a species, population, or ecosystem. In the context of plants, genetic diversity ensures resilience, adaptability, and vigor. It acts as a safeguard against diseases, pests, and environmental stresses, enabling plants to thrive and evolve over time.
A lack of genetic diversity can lead to a host of issues, including reduced yield, increased susceptibility to diseases, and a diminished ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions. On the other hand, a diverse gene pool equips plants with the tools to thrive, ensuring their survival and the survival of the ecosystem they are a part of.
The Art of Cross-Pollination: Unlocking Genetic Potential
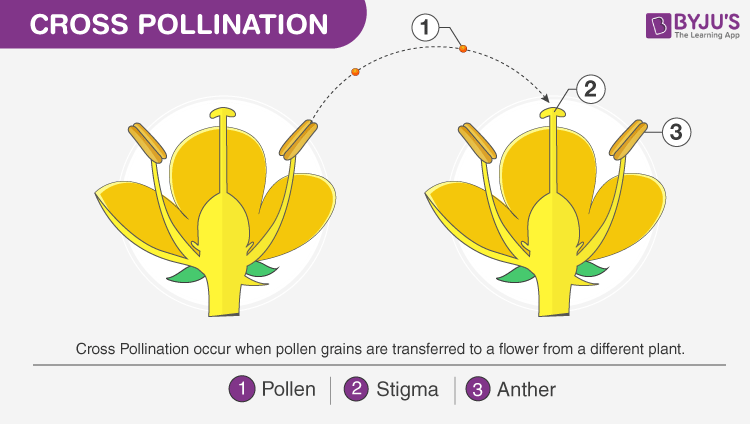
Cross-pollination is a natural process where the pollen from the male reproductive organ of one plant is transferred to the female reproductive organ of another plant. This transfer of genetic material between different individuals of the same species leads to the creation of offspring with unique genetic combinations.
This process is a fundamental aspect of plant reproduction and plays a crucial role in the evolution and adaptation of plant species. By introducing new genetic material, cross-pollination enhances the genetic diversity of a population, increasing its ability to withstand environmental challenges and evolve over time.
Natural Cross-Pollination: The Beauty of Nature's Design
In the wild, cross-pollination occurs naturally through various agents, such as wind, water, and most notably, animals. Birds, bees, butterflies, and other pollinators play a vital role in this process, carrying pollen from one plant to another as they feed on nectar or collect pollen for their nests.
For instance, consider the humble honeybee. As it flits from flower to flower, it inadvertently picks up pollen on its body, which is then transferred to the next flower it visits. This simple act of pollination has a profound impact on the genetic diversity of plant populations, ensuring the survival and evolution of countless species.
Human-Assisted Cross-Pollination: Taking Control of Genetic Destiny
While natural cross-pollination is a beautiful and intricate process, human intervention can play a significant role in enhancing genetic diversity, especially in controlled environments like gardens and agricultural settings.
Through various techniques, gardeners and farmers can facilitate cross-pollination, ensuring the creation of offspring with desirable traits. This process, known as "controlled cross-pollination," involves careful selection and management of parent plants to achieve specific genetic outcomes.
Methods of Cross-Pollination: A Gardener's Toolkit
There are several methods of cross-pollination that gardeners can employ to enhance the genetic diversity of their plants. These methods range from natural processes to more controlled and precise techniques.
Natural Cross-Pollination: Letting Nature Take its Course
As mentioned earlier, natural cross-pollination occurs through various agents, including wind and water. However, the most efficient and widespread method is through animal pollinators.
By creating a garden that attracts a diverse range of pollinators, you can encourage natural cross-pollination. This can be achieved by planting a variety of flowers that bloom at different times, providing a continuous source of nectar and pollen for visiting pollinators. Additionally, providing habitats and shelter for these beneficial insects can further enhance their presence in your garden.
Hand Pollination: Precision and Control
For a more controlled approach, hand pollination is a technique that allows gardeners to transfer pollen between specific plants with precision. This method is particularly useful for plants that are not naturally attractive to pollinators or for situations where natural cross-pollination is limited.
The process involves carefully collecting pollen from the male flower and transferring it to the female flower using a small brush or cotton swab. This technique requires a keen eye and a steady hand, but it offers the advantage of creating specific genetic combinations, allowing gardeners to select for desired traits.
Cross-Pollination through Grafting and Cloning
Grafting and cloning are advanced techniques used to create new plants with specific genetic traits. These methods involve taking parts of one plant and combining them with another, either through grafting (joining two plant parts together) or cloning (creating an exact genetic copy of a plant).
While these techniques may be more complex and require specialized knowledge, they offer a powerful way to introduce specific genetic traits into a population, enhancing its overall diversity and resilience.
The Impact of Cross-Pollination: Unlocking Genetic Potential

The benefits of cross-pollination are far-reaching and have a profound impact on the health and vitality of plant populations.
Increased Genetic Diversity
Perhaps the most significant impact of cross-pollination is the increase in genetic diversity within a population. By introducing new genetic material, cross-pollination creates offspring with unique combinations of traits, enhancing the overall diversity of the population.
This increased diversity has several advantages. It provides a wider range of genetic resources to draw from, allowing for better adaptation to changing environmental conditions. It also reduces the risk of diseases and pests, as diverse populations are less susceptible to widespread infections.
Improved Plant Vigor and Health
Cross-pollination can lead to the creation of offspring with improved vigor and overall health. By combining desirable traits from different parent plants, the resulting offspring may exhibit increased resistance to diseases, pests, and environmental stresses.
This enhanced health and vigor can lead to higher yields, better-quality produce, and a more robust and resilient garden ecosystem.
Enhanced Nutritional Value
The impact of cross-pollination extends beyond the realm of plant health and into the realm of human nutrition. Cross-pollination can lead to the creation of fruits and vegetables with enhanced nutritional value, as the genetic diversity introduced through cross-pollination can result in higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
This is particularly beneficial in the context of food security and nutrition, as it provides a more diverse and nutritious food source for both humans and animals.
The Future of Cross-Pollination: A Sustainable Approach
As we look to the future, the importance of cross-pollination and genetic diversity becomes even more apparent. In a world facing increasing environmental challenges, the ability of plants to adapt and thrive becomes crucial.
By embracing cross-pollination strategies, gardeners and farmers can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system. The increased genetic diversity achieved through cross-pollination can help plants withstand the challenges of climate change, such as increased temperatures, drought, and new pest and disease pressures.
Furthermore, the enhanced nutritional value of cross-pollinated crops can play a vital role in addressing global nutritional deficiencies and food security concerns.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Cross-Pollination
Cross-pollination is a powerful tool in the gardener's arsenal, offering a multitude of benefits to both the garden and its ecosystem. By understanding the significance of genetic diversity and employing various cross-pollination strategies, gardeners can create thriving, resilient, and diverse plant populations.
Whether through natural processes or human-assisted techniques, cross-pollination allows us to shape the genetic destiny of our gardens, ensuring their health, vitality, and long-term sustainability. So, let us embrace the beauty and power of cross-pollination, and together, we can cultivate a greener, more vibrant, and diverse world.
How can I attract more pollinators to my garden for natural cross-pollination?
+To attract more pollinators, consider planting a diverse range of flowers that bloom at different times, providing a continuous source of nectar and pollen. Create habitats and shelters for pollinators, such as bee houses or butterfly gardens. Additionally, avoid the use of pesticides that can harm beneficial insects.
What are some common plants that rely on cross-pollination for reproduction?
+Many fruit-bearing plants, such as apples, pears, and cherries, rely on cross-pollination for successful reproduction. Additionally, many vegetable crops, including squash, cucumbers, and melons, require cross-pollination to produce viable seeds.
Can cross-pollination lead to the creation of new plant species?
+While cross-pollination primarily leads to the creation of offspring with unique genetic combinations within the same species, it can occasionally result in the formation of new plant species. This occurs when two closely related species cross-pollinate, creating a hybrid offspring with distinct characteristics.



