Derivative Of A Log
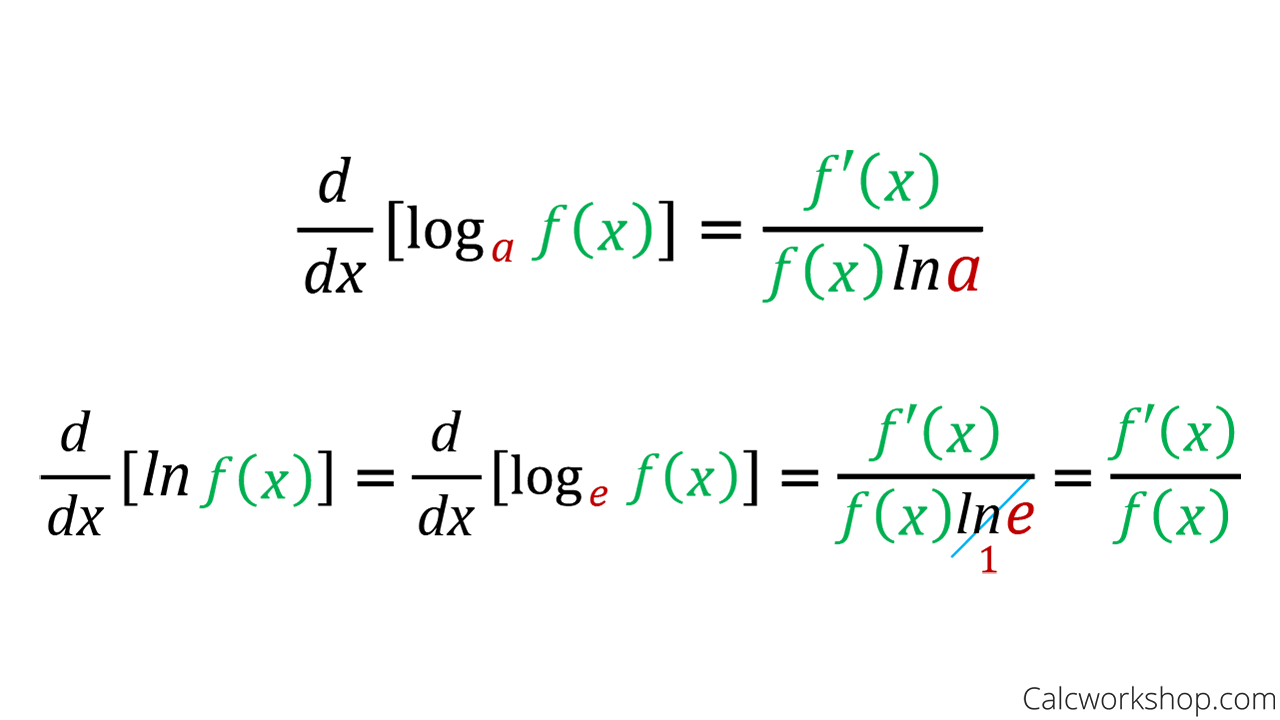
In the realm of mathematics, the concept of differentiation plays a pivotal role in understanding the rate of change of functions. Among the myriad of functions, the logarithmic function stands out as a cornerstone in calculus, and its derivative holds significant importance in various mathematical and scientific applications. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of the derivative of a log, exploring its definition, properties, and real-world implications.
Understanding the Derivative of a Logarithmic Function

The derivative of a logarithmic function, often denoted as f’(x) or dy/dx, represents the rate of change of the function with respect to its input variable x. In the context of logarithms, this derivative is particularly intriguing due to the unique properties of logarithmic functions.
Consider the natural logarithm, denoted as ln(x), which is the inverse of the exponential function e^x, where e is the base of the natural logarithm. The derivative of the natural logarithm function is given by the following expression:
f'(x) = 1/x
This simple yet powerful derivative reveals that the rate of change of the natural logarithm function is inversely proportional to the value of x. In other words, as x increases, the rate of change decreases, and vice versa.
Properties and Applications

The derivative of a log possesses several intriguing properties that make it a valuable tool in mathematical analysis.
Chain Rule and Composite Functions
When dealing with composite functions involving logarithms, the chain rule becomes essential. The chain rule allows us to find the derivative of a function composed of multiple functions. For instance, consider the function f(x) = ln(x^2). Applying the chain rule, we can find its derivative as follows:
f'(x) = (2x) / (x^2) = 2/x
This demonstrates how the derivative of a composite function involving a logarithm can be obtained by using the chain rule.
Logarithmic Differentiation
Logarithmic differentiation is a technique used to find the derivative of a function that is difficult to differentiate directly. By taking the natural logarithm of both sides of an equation and then differentiating, we can simplify the process. For example, let’s consider the function f(x) = x^x. Taking the natural logarithm of both sides, we get:
ln(f(x)) = x * ln(x)
Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we obtain:
f'(x) / f(x) = 1 + ln(x)
Solving for f'(x), we find:
f'(x) = f(x) * (1 + ln(x))
This technique is particularly useful for functions involving exponentials and logarithms.
Real-World Applications
The derivative of a log finds applications in various fields. In physics, it is used to analyze exponential decay processes, such as radioactive decay or the decay of a drug in the human body. In economics, it is employed to model exponential growth and decay in populations, prices, and other variables. Additionally, the derivative of a log plays a crucial role in information theory, where it is used to calculate the entropy of a probability distribution, a measure of the uncertainty or randomness in a system.
Examples and Exercises
Let’s explore some practical examples and exercises to reinforce our understanding of the derivative of a log.
Example 1: Differentiating a Simple Logarithmic Function
Find the derivative of the function f(x) = ln(3x).
Solution:
f'(x) = 3/x
Example 2: Chain Rule Application
Find the derivative of the function f(x) = ln(x^3 + 2).
Solution:
f'(x) = (3x^2) / (x^3 + 2)
Exercise 1: Logarithmic Differentiation
Find the derivative of the function f(x) = (x^2 + 1)^x using logarithmic differentiation.
Exercise 2: Composite Function
Find the derivative of the function f(x) = ln(sin(x)), where sin(x) is the sine function.
Conclusion
The derivative of a log is a fundamental concept in calculus, offering a deep understanding of the behavior of logarithmic functions. Its properties and applications extend across various scientific and mathematical disciplines, making it a valuable tool for mathematicians, scientists, and engineers alike. By mastering the derivative of a log, we unlock a powerful mechanism for analyzing and solving complex problems involving exponential and logarithmic functions.
What is the derivative of the natural logarithm function, and how is it derived?
+The derivative of the natural logarithm function, denoted as f’(x) or dy/dx, is given by 1/x. This derivative is derived by applying the definition of a derivative, which states that the derivative of a function f(x) at a point x is the limit of the difference quotient as h approaches zero. In the case of the natural logarithm, this involves evaluating the limit of (ln(x + h) - ln(x)) / h as h tends to zero.
How does the derivative of a log relate to exponential functions?
+The derivative of a log is closely tied to exponential functions due to the inverse relationship between logarithmic and exponential functions. The derivative of the natural logarithm function, 1/x, reflects the rate of change of the exponential function e^x with respect to x. This relationship is fundamental in calculus and is used in various applications, such as solving differential equations and analyzing exponential growth and decay.
Can the derivative of a log be used to solve real-world problems?
+Absolutely! The derivative of a log has numerous applications in real-world scenarios. For instance, it is used in physics to model exponential decay processes, such as radioactive decay or the decay of a drug in the body. In economics, it is employed to analyze exponential growth and decay in populations, prices, and other variables. Additionally, the derivative of a log plays a crucial role in information theory, where it is used to calculate the entropy of a probability distribution.