Flat Earth Theory: A New Perspective On Celestial Events
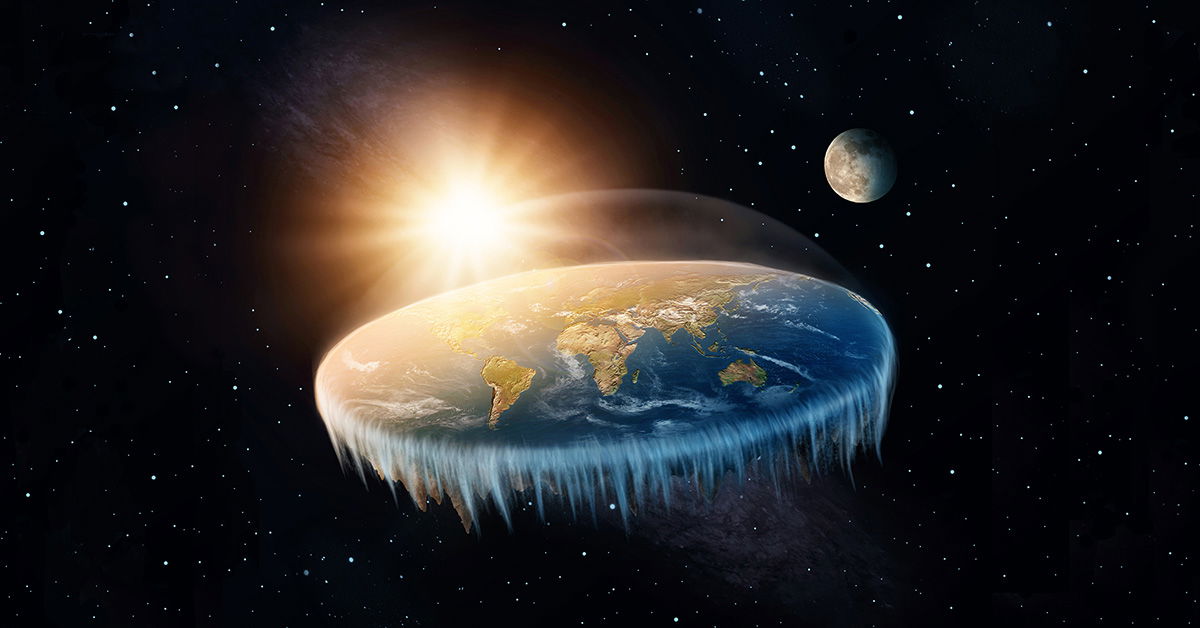

The Flat Earth Theory, a controversial and intriguing concept, has sparked curiosity and debate among individuals fascinated by the unknown. While widely regarded as a fringe belief, it presents an alternative perspective on celestial events, challenging conventional wisdom and offering a unique lens through which to interpret the cosmos. This article delves into the intricacies of the Flat Earth Theory, exploring its origins, key principles, and the impact it has on our understanding of celestial phenomena.
Unveiling the Flat Earth Theory

The Flat Earth Theory posits that the Earth is not a spherical globe but rather a flat plane. Proponents of this theory argue that the evidence we perceive as supporting a spherical Earth is either misinterpreted or part of a grand illusion. This theory has gained attention in recent years, with online communities and individuals advocating for a reevaluation of our understanding of the cosmos.
Key Principles of the Flat Earth Theory
The Flat Earth Theory is built upon several fundamental principles, each challenging conventional scientific understanding:
- Flat Earth Geometry: The theory asserts that the Earth is a flat, circular plane with the North Pole at its center and a surrounding ice wall, known as Antarctica, preventing access to the outer regions.
- Celestial Mechanics: Flat Earth proponents argue that the Sun and Moon are smaller than traditionally believed and move in circular patterns above the flat Earth. They also suggest that stars are fixed points on a celestial sphere.
- Gravity and Motion: Contrary to the laws of physics, the theory proposes that gravity is an illusion and that objects fall due to a “downward momentum” caused by the Earth’s flat surface.
- Conspiracy Theories: Many Flat Earth believers subscribe to conspiracy theories, claiming that governments and scientific institutions have conspired to hide the truth about the Earth’s shape to maintain control and manipulate public perception.
Celestial Events through a Flat Lens

When viewed through the lens of the Flat Earth Theory, celestial events take on a new and often contradictory interpretation. Here’s how some key celestial phenomena are explained within this framework:
Sunrise and Sunset
According to Flat Earth theorists, the Sun and Moon are small, luminous objects that move in circular paths above the flat Earth. Sunrise and sunset are explained as the result of these celestial bodies moving into and out of view, with the Sun’s apparent movement being caused by its circular motion rather than the Earth’s rotation.
Eclipses
Lunar and solar eclipses are attributed to the alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth, with the Moon occasionally blocking the Sun’s light from reaching the Earth. This explanation differs from the conventional understanding of eclipses, which involves the Earth’s shadow falling on the Moon or the Moon passing between the Sun and Earth.
Seasons and Weather Patterns
The Flat Earth Theory attributes seasonal changes to variations in the angle of the Sun’s path across the sky. Proponents suggest that the Sun’s path is influenced by factors such as the tilt of the Earth’s axis and the Earth’s position relative to the Sun. Weather patterns, on the other hand, are believed to be caused by air currents and the movement of moisture, rather than the Earth’s rotation and tilt.
Star Constellations and Navigation
Flat Earth believers argue that stars are fixed points on a celestial sphere, which explains their apparent fixed positions in the night sky. This belief system also influences navigation, with some proponents suggesting that ancient sailors used the stars to navigate based on their fixed positions rather than the Earth’s rotation.
Challenges and Criticisms
The Flat Earth Theory faces numerous challenges and criticisms from the scientific community and even from within its own ranks. Some of the key criticisms include:
- Scientific Evidence: The theory contradicts a vast body of scientific evidence, including satellite imagery, space exploration, and numerous experiments that have confirmed the Earth's spherical shape and its position in the solar system.
- Geographical Observations: The Flat Earth model struggles to explain various geographical phenomena, such as the curvature of the Earth's horizon, the visibility of distant objects, and the behavior of shadows and light.
- Internal Inconsistencies: The theory itself is riddled with inconsistencies, as different proponents offer varying explanations for the same celestial events, leading to a lack of coherence within the Flat Earth community.
- Conspiracy Theories: The belief in widespread conspiracies to hide the truth about the Earth's shape has led to skepticism and ridicule from the general public and even from those who hold other unconventional beliefs.
Impact and Implications
Despite the challenges and criticisms, the Flat Earth Theory has had a notable impact on popular culture and has influenced various fields. Here are some of the key implications:
- Popular Culture: The theory has gained significant attention online, with numerous YouTube videos, podcasts, and social media posts dedicated to exploring and discussing Flat Earth beliefs. This has led to a resurgence of interest in alternative theories and a broader conversation about the nature of truth and knowledge.
- Conspiracy Culture: The Flat Earth Theory has become a symbol of conspiracy culture, with its proponents often aligning themselves with other conspiracy theories and anti-establishment beliefs. This has led to a deeper exploration of the role of power, control, and manipulation in society.
- Scientific Literacy: The debate surrounding the Flat Earth Theory has sparked discussions about scientific literacy and the importance of critical thinking. It has encouraged individuals to question their assumptions, seek evidence-based explanations, and engage in rational discourse.
- Education and Outreach: The theory has prompted educators and science communicators to develop new strategies for engaging with the public and addressing misconceptions. This has led to a more inclusive and accessible approach to science education, aiming to bridge the gap between scientific understanding and public perception.
Conclusion
The Flat Earth Theory presents a unique and challenging perspective on celestial events, offering an alternative lens through which to view the cosmos. While it faces significant criticism and lacks scientific support, its impact on popular culture, conspiracy culture, and scientific literacy cannot be ignored. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the universe, the Flat Earth Theory serves as a reminder of the power of curiosity, the importance of evidence-based reasoning, and the ongoing quest for a deeper understanding of our place in the cosmos.
What is the primary evidence cited by Flat Earth theorists to support their claims?
+Flat Earth theorists often cite observations such as the apparent flatness of the horizon, the inability to see distant objects due to the Earth’s curvature, and the behavior of shadows and light as evidence for their theory. They also point to historical accounts and ancient texts that describe the Earth as flat.
How do Flat Earth believers explain satellite imagery and space exploration that contradicts their theory?
+Flat Earth believers often argue that satellite imagery and space exploration are part of a grand conspiracy to maintain the illusion of a spherical Earth. They suggest that these images and data are manipulated or that the spacecraft themselves are hoaxes.
Are there any scientific experiments or observations that support the Flat Earth Theory?
+No, there are no scientific experiments or observations that conclusively support the Flat Earth Theory. The vast majority of scientific evidence, including data from satellites, space probes, and experiments conducted on the ground, confirms the Earth’s spherical shape and its position in the solar system.



