How Did La Fire Start
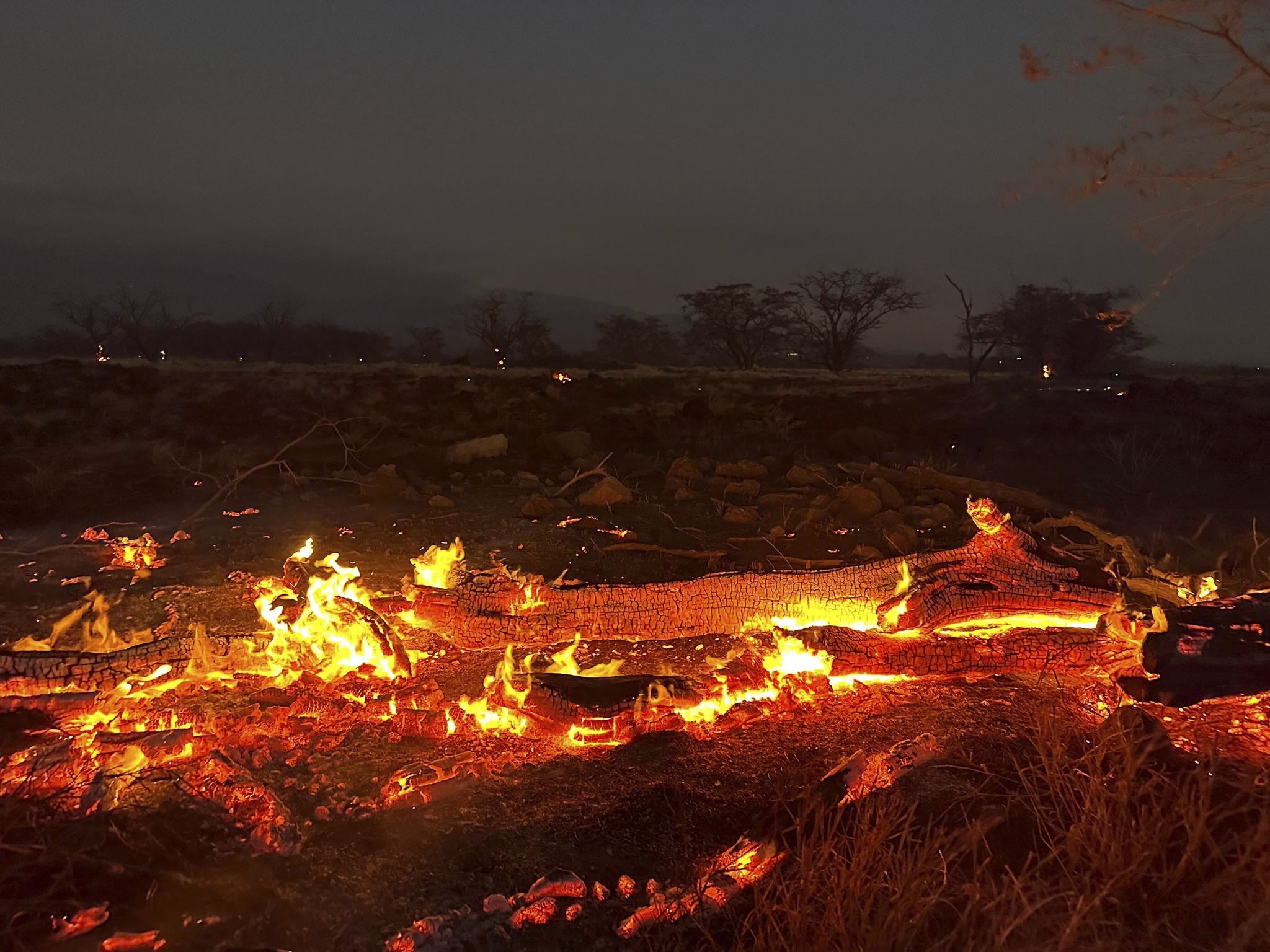

The devastating La Fire, which ravaged the California landscape in 2020, serves as a stark reminder of the unpredictable nature of wildfires and the urgent need for effective wildfire management strategies. This article delves into the origins of the La Fire, exploring the factors that contributed to its rapid spread and the challenges faced by emergency responders in containing it. By examining the specific circumstances that led to this catastrophic event, we can gain valuable insights into wildfire behavior and develop more robust prevention and mitigation measures.
Unveiling the Origins of the La Fire
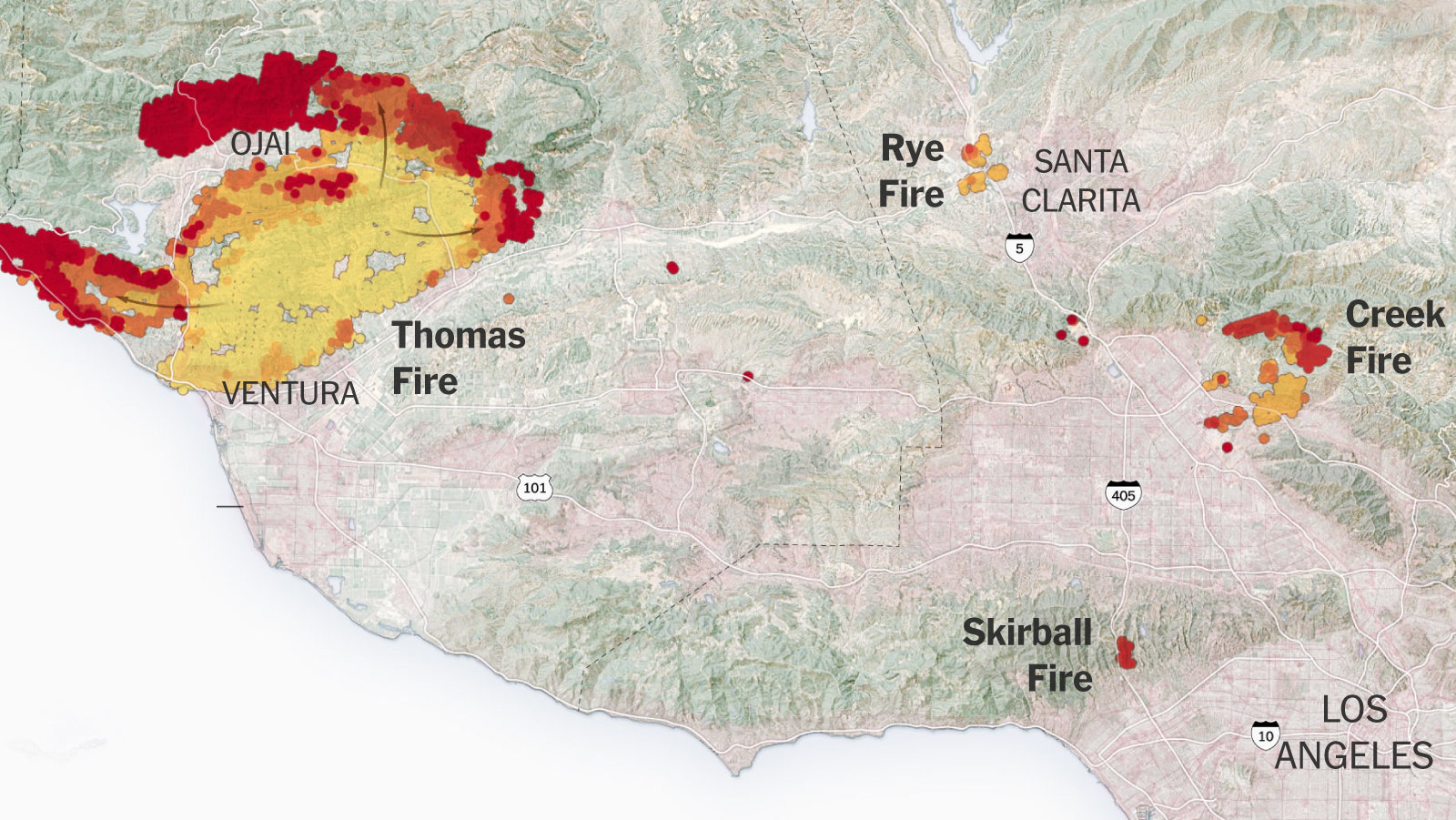
The La Fire, which ignited on August 16, 2020, near the city of Los Angeles, California, left a trail of destruction in its wake. The fire’s origin story is a complex interplay of environmental factors, human activities, and a series of unfortunate events that culminated in a perfect storm of wildfire conditions.
Environmental Factors and Drought Conditions
California had been experiencing a prolonged drought, with exceptionally dry conditions prevailing across the state. The lack of rainfall had left the vegetation parched and highly flammable, creating a tinderbox-like environment. The drought, exacerbated by climate change, had turned the region into a prime target for wildfires.
| Drought Severity | Impact on Wildfire Risk |
|---|---|
| Severe Drought | Increased flammability of vegetation, higher risk of rapid fire spread. |
| Moderate Drought | Elevated fire risk, potential for longer fire seasons. |
Human Activities and Ignitions
While the exact cause of the La Fire remains under investigation, several human activities have been identified as potential ignition sources. These include:
- Arson: Deliberate acts of arson have been linked to several wildfires in California. The La Fire's proximity to urban areas raises concerns about the potential involvement of arsonists.
- Equipment Failures: Malfunctioning machinery, such as power lines or vehicles, can spark wildfires. The region's infrastructure and its proximity to dense vegetation create a high-risk environment.
- Recreational Activities: Campfires, fireworks, and other recreational activities can inadvertently ignite wildfires, especially during dry and windy conditions.
Weather Conditions and Wind Patterns
The La Fire’s rapid spread was influenced by unfavorable weather conditions and strong wind patterns. The Santa Ana winds, known for their intense and dry nature, often fuel wildfires in Southern California. These winds can carry embers over long distances, igniting new fires and rapidly expanding existing ones.
During the La Fire, the Santa Ana winds reached speeds of up to 50 miles per hour, creating a challenging environment for firefighters. The combination of high winds, dry conditions, and abundant fuel sources resulted in an extremely volatile situation.
The Impact and Challenges of the La Fire
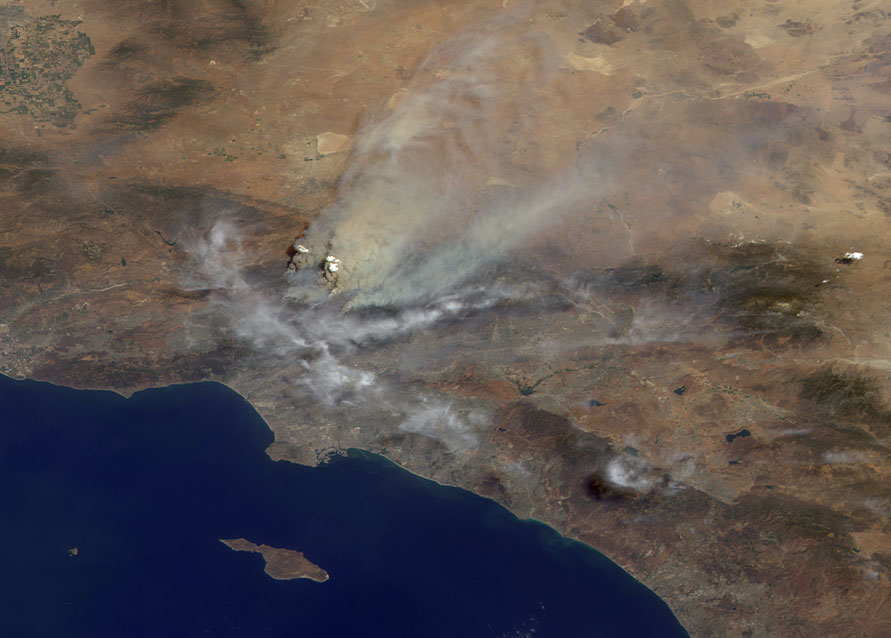

The La Fire’s impact was devastating, resulting in the loss of valuable ecosystems, wildlife habitats, and human lives. The fire’s intense heat and rapid spread made it challenging for emergency responders to contain and control the blaze.
Loss of Property and Evacuations
The La Fire forced the evacuation of thousands of residents as it threatened densely populated areas. Many homes and businesses were destroyed, leaving families displaced and communities in ruins. The economic impact of the fire was significant, with insurance claims and reconstruction efforts straining local resources.
Environmental Damage and Wildlife Impact
The fire’s relentless spread scorched vast areas of wilderness, destroying critical habitats for numerous plant and animal species. The loss of biodiversity and the disruption of ecological balance have long-lasting consequences for the region’s ecosystems.
Challenges Faced by Firefighters
Emergency responders encountered numerous challenges while battling the La Fire. The extreme fire behavior, characterized by intense heat and erratic wind patterns, made it difficult to establish effective firebreaks. The fire’s rapid spread and unpredictable nature required firefighters to adapt their strategies on the fly.
Additionally, the fire's proximity to urban areas and the need to protect lives and property added complexity to the response efforts. Firefighters had to balance the need for aggressive suppression tactics with the safety of residents and the preservation of critical infrastructure.
Lessons Learned and Future Implications
The La Fire serves as a stark reminder of the importance of proactive wildfire management and the need for continuous improvement in our response capabilities. Several key lessons can be drawn from this catastrophic event:
- Wildfire Prevention: Emphasizing the importance of wildfire prevention measures, such as fuel reduction, prescribed burns, and public education, can help mitigate the risk of future fires.
- Early Detection and Rapid Response: Investing in advanced fire detection systems and improving response times can significantly impact the success of fire suppression efforts.
- Community Engagement: Engaging local communities in wildfire preparedness and response planning can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to more effective collaboration during emergencies.
- Climate Change Adaptation: As climate change continues to impact wildfire behavior, adapting our strategies and infrastructure to accommodate changing conditions is crucial.
The Role of Technology in Wildfire Management
Advancements in technology offer promising solutions for enhancing wildfire management. Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras can provide real-time data on fire behavior and help identify hotspots. Additionally, satellite imagery and advanced weather modeling can aid in predicting fire spread and informing tactical decisions.
Collaborative Efforts and Research
Addressing the complex challenges posed by wildfires requires a collaborative approach involving various stakeholders, including government agencies, research institutions, and community organizations. By pooling resources and expertise, we can develop more effective wildfire management strategies and improve our overall resilience.
Ongoing research in wildfire behavior, climate change impacts, and innovative suppression techniques is crucial for staying ahead of the curve. Investing in scientific studies and technology development can lead to breakthroughs that will benefit wildfire-prone regions worldwide.
Conclusion
The La Fire stands as a somber reminder of the destructive power of wildfires and the urgent need for enhanced wildfire management. By understanding the factors that contributed to this catastrophic event, we can take proactive steps to mitigate future risks and build more resilient communities. Through a combination of prevention, early detection, community engagement, and technological advancements, we can work towards a future where wildfires are better managed and their impacts are minimized.
What can individuals do to prepare for wildfires in their area?
+Individuals can take several proactive measures to prepare for wildfires. These include creating a defensible space around their homes by removing flammable materials, having an emergency plan and supplies ready, staying informed about local fire conditions, and following evacuation orders promptly. Regular maintenance of homes and properties, such as cleaning gutters and trimming vegetation, can also reduce the risk of fire spread.
How can communities come together to support wildfire recovery efforts?
+Communities can play a vital role in supporting wildfire recovery by organizing fundraising events, donating to reputable charities, volunteering time and resources, and offering emotional support to those affected. Additionally, community-led initiatives can focus on rebuilding infrastructure, replanting vegetation, and providing long-term assistance to those who lost their homes or businesses.
What are some innovative technologies being developed to combat wildfires?
+Innovative technologies are being developed to enhance wildfire detection, suppression, and management. This includes advanced drones with thermal imaging capabilities, artificial intelligence-powered fire behavior prediction models, and autonomous firefighting robots. These technologies, combined with improved data analytics and communication systems, offer promising solutions for more effective wildfire response and mitigation.