How Long Does An Earthquake Last

The duration of an earthquake is a complex aspect of seismology that often sparks curiosity and concern among the public. While the intense shaking and potential damage caused by earthquakes are well-known, understanding the factors that influence their duration is crucial for preparedness and safety. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of earthquake duration, exploring the various factors that contribute to it and shedding light on the science behind this natural phenomenon.
The Complexity of Earthquake Duration

Contrary to popular belief, earthquakes do not have a fixed duration. The length of an earthquake can vary significantly, ranging from a few seconds to several minutes, and even, in rare cases, hours. This variability is influenced by a multitude of factors, each playing a unique role in the seismic process.
The Role of Tectonic Forces
Earthquakes are primarily the result of tectonic forces acting along fault lines. When these forces build up, they cause stress to accumulate within the Earth’s crust. Eventually, this stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, leading to a sudden release of energy in the form of seismic waves. The duration of an earthquake is directly related to the amount of energy released during this process.
Larger earthquakes, often referred to as megathrust earthquakes, occur along subduction zones where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another. These events can last for several minutes due to the extensive area of fault rupture and the significant energy release. For instance, the 2011 Tohoku earthquake in Japan, a magnitude 9.0 event, lasted approximately six minutes.
| Earthquake | Duration (Minutes) |
|---|---|
| 2011 Tohoku Earthquake | 6 |
| 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake | 10 |
| 1960 Great Chilean Earthquake | 10 |

Fault Characteristics and Rupture Style
The characteristics of the fault itself play a significant role in determining the duration of an earthquake. Faults can be categorized as either strike-slip, where blocks of rock slide past each other horizontally, or dip-slip, where one block moves vertically over another. The orientation and structure of the fault influence the ease with which it can rupture, thus affecting the duration of the earthquake.
Additionally, the style of rupture can vary. Some earthquakes feature a single rupture along a fault, while others may involve multiple ruptures, a phenomenon known as "pulse-like" behavior. These pulse-like earthquakes can exhibit a stop-and-go pattern, resulting in a longer overall duration.
Seismic Waves and Ground Shaking
The duration of an earthquake is also influenced by the type and speed of seismic waves generated. There are two primary types of waves: body waves and surface waves. Body waves, which include primary (P) waves and secondary (S) waves, travel through the Earth’s interior, while surface waves travel along the Earth’s surface. Surface waves, particularly the Love and Rayleigh waves, can cause the most intense ground shaking and are often responsible for the majority of earthquake damage.
The duration of ground shaking is not solely determined by the duration of the earthquake itself. The seismic waves can continue to propagate and cause shaking for some time after the initial rupture. This post-earthquake shaking can last for several minutes to hours, depending on the size and location of the earthquake.
Depth of the Earthquake Focus
The depth at which an earthquake originates, known as the focus or hypocenter, can impact its duration. Earthquakes that occur at shallow depths (less than 70 km) tend to have shorter durations compared to those that occur at greater depths. This is because the energy released at shallow depths dissipates more quickly due to the proximity to the Earth’s surface.
The Impact of Magnitude and Intensity

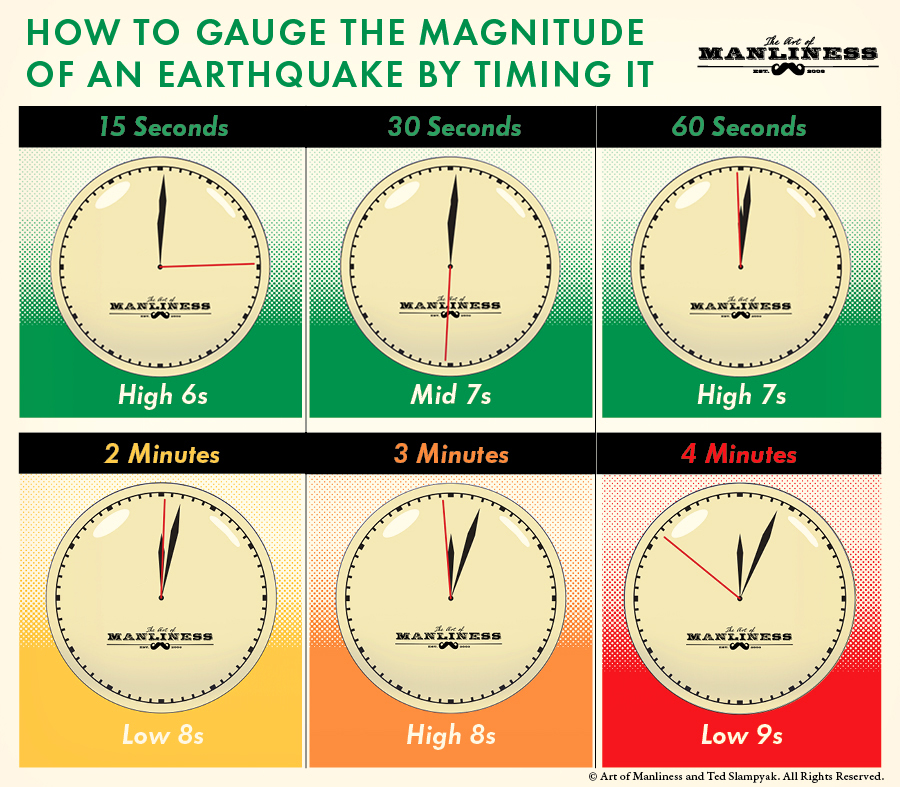
The magnitude of an earthquake, measured on the moment magnitude scale (MMS), is a crucial factor in determining its duration. Larger magnitude earthquakes generally last longer due to the extensive energy release. For instance, a magnitude 7.0 earthquake may last around 20-30 seconds, while a magnitude 9.0 earthquake, like the aforementioned Tohoku event, can persist for several minutes.
However, it's important to note that the duration of an earthquake is not solely dependent on its magnitude. The intensity of shaking experienced at a specific location is also a factor. Intensity is measured on the Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) scale, which considers the effects of an earthquake on people, structures, and the natural environment. An earthquake of a given magnitude may have a longer perceived duration if it occurs closer to populated areas, as the ground shaking will be more intense and potentially more damaging.
Understanding Aftershocks and Their Duration
Aftershocks are a common occurrence following a significant earthquake. They are smaller earthquakes that occur in the same region as the mainshock and are a result of the readjustment of the Earth’s crust after the initial disturbance. Aftershocks can persist for days, weeks, or even months after the main event, and their duration is influenced by the same factors as the main earthquake.
The frequency and duration of aftershocks can provide valuable insights into the underlying tectonic processes. Scientists use aftershock data to study fault behavior, assess the potential for future earthquakes, and improve earthquake forecasting models.
Real-World Examples: Earthquakes and Their Durations
To illustrate the range of earthquake durations, let’s examine a few notable events:
- 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and Tsunami: This magnitude 9.1 earthquake, which triggered a devastating tsunami, lasted approximately 10 minutes.
- 1960 Great Chilean Earthquake: One of the largest earthquakes ever recorded, with a magnitude of 9.5, lasted for about 10 minutes.
- 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake: A magnitude 6.9 earthquake that struck the San Francisco Bay Area lasted around 15 seconds.
- 2010 Haiti Earthquake: This magnitude 7.0 earthquake, which caused widespread destruction in Haiti, lasted approximately 30-40 seconds.
Mitigating the Impact: Preparedness and Response
Understanding the duration of earthquakes is crucial for effective preparedness and response strategies. While the exact duration of an earthquake cannot be predicted, seismic monitoring and early warning systems can provide valuable advance notice, allowing individuals and communities to take protective actions.
Educating the public about earthquake safety measures, such as drop, cover, and hold on, can significantly reduce the risk of injury during an earthquake. Additionally, implementing building codes that consider the potential duration of earthquakes is essential for constructing resilient structures.
Future Implications and Research
The study of earthquake duration is an active area of research, with scientists continually refining their understanding of this complex phenomenon. Advancements in seismic monitoring technology, such as the deployment of dense arrays of seismometers, are providing more detailed data on earthquake processes, including duration.
Furthermore, the integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques is enhancing our ability to analyze large datasets and identify patterns in earthquake behavior. These advancements hold the potential to improve earthquake forecasting and early warning systems, ultimately saving lives and minimizing the impact of these natural disasters.
What is the longest recorded duration of an earthquake?
+The longest recorded duration of an earthquake is approximately 10 minutes. This was observed during the 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and Tsunami, which had a magnitude of 9.1.
Can an earthquake last for hours?
+While rare, earthquakes can last for hours, especially in the case of very large magnitude events. These long-duration earthquakes are typically associated with extensive fault ruptures and complex seismic processes.
How does the depth of an earthquake affect its duration?
+Earthquakes that occur at shallow depths tend to have shorter durations compared to those at greater depths. This is because the energy released at shallow depths dissipates more quickly due to the proximity to the Earth’s surface.



