Instant Rate Of Change Formula

In the realm of mathematics, the concept of rate of change is a fundamental tool for understanding how quantities evolve over time or in relation to other variables. The instant rate of change, often referred to as the derivative, is a powerful mathematical construct that provides insights into the behavior of functions and their rates of alteration at specific points. This article delves into the instant rate of change formula, exploring its definition, application, and significance in various mathematical and real-world contexts.
Understanding the Instant Rate of Change Formula

The instant rate of change formula, or the derivative formula, is a mathematical expression that calculates the rate at which a function is changing at a specific point. It provides an instantaneous measure of the function’s slope or rate of change at that precise moment. The formula is derived from the concept of limits and is represented as follows:
Instant Rate of Change Formula:
$$ \begin{equation*} \frac{dy}{dx} = \lim_{h \to 0} \frac{f(x + h) - f(x)}{h} \end{equation*} $$
Here's a breakdown of the components:
- dy/dx: This represents the derivative of the function f with respect to x. It signifies the rate of change of the function at a given point x.
- f(x): This is the original function for which we want to find the rate of change.
- h: This is an infinitesimal change in x, which approaches zero as we calculate the limit.
- f(x + h): This represents the value of the function at a point slightly ahead of x, with a small increment of h.
Calculating the Instant Rate of Change

To calculate the instant rate of change, we use the above formula and perform the following steps:
- Choose a function f for which you want to find the rate of change.
- Select a specific point x at which you want to evaluate the rate of change.
- Substitute the function and the point into the formula.
- Calculate the limit as h approaches zero. This can often be done using algebraic manipulation and limit rules.
- The result, dy/dx, represents the rate of change of the function at the chosen point.
Applications of the Instant Rate of Change Formula
The instant rate of change formula has a wide range of applications in mathematics and various scientific and engineering disciplines. Here are some key areas where it is utilized:
1. Calculus and Differential Equations
In calculus, the derivative formula is a fundamental tool for solving differential equations. It allows mathematicians to model and analyze systems that change over time, such as population growth, heat transfer, and fluid dynamics.
2. Physics and Engineering
The concept of instant rate of change is crucial in physics and engineering. It is used to calculate velocities, accelerations, and rates of change in various physical systems. For instance, it can be applied to determine the speed of a moving object at a specific moment or to analyze the rate of reaction in a chemical process.
3. Economics and Finance
In economics and finance, the derivative formula is used to analyze and model economic trends and financial markets. It helps in understanding how variables like supply and demand, interest rates, and stock prices change over time.
4. Optimization Problems
The instant rate of change is also employed in optimization problems, where the goal is to find the maximum or minimum value of a function. By calculating the derivative, one can identify critical points and determine whether they correspond to local maxima, minima, or saddle points.
Real-World Examples
Let’s explore some real-world scenarios where the instant rate of change formula is applied:
1. Velocity of a Car
Consider a car traveling along a straight road. To find its velocity at a specific moment, we can use the derivative of the car’s position function with respect to time. This will give us the rate of change of position, which is the velocity.
2. Growth Rate of a Population
In biology and ecology, the derivative formula is used to determine the growth rate of a population. By modeling the population as a function of time, we can calculate the rate at which the population is changing at any given moment.
3. Price Change in the Stock Market
In finance, the derivative formula can be applied to analyze the rate of change of stock prices. By taking the derivative of the stock price function with respect to time, we can determine the speed at which the stock price is moving, which is crucial for making investment decisions.
Challenges and Advanced Techniques
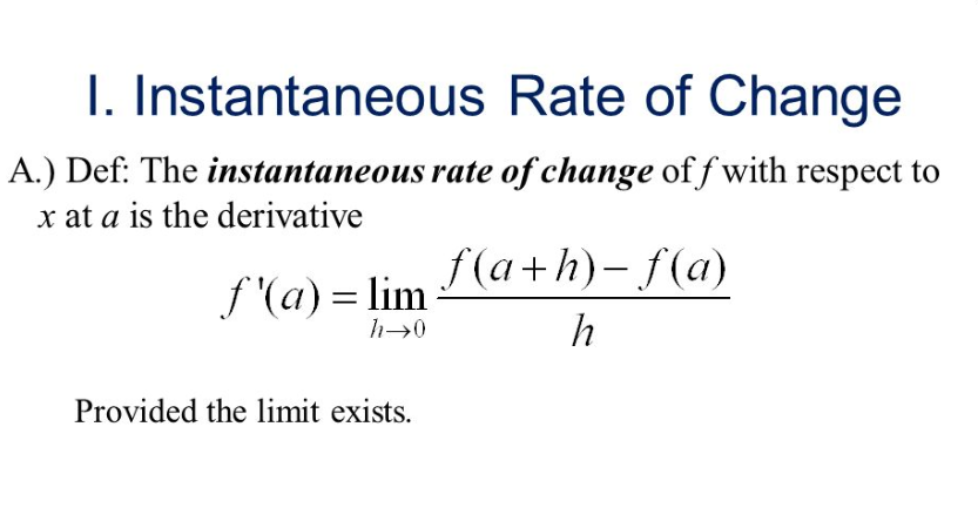
While the instant rate of change formula is a powerful tool, it can present challenges in certain situations. For instance, calculating derivatives for complex functions or functions with discontinuities can be intricate. In such cases, advanced techniques like Taylor series expansions or numerical methods are employed.
Conclusion
The instant rate of change formula, or the derivative formula, is a cornerstone of calculus and mathematical analysis. It provides a means to understand how functions behave at specific points and how they change over time. By applying this formula, mathematicians, scientists, and engineers can model and analyze a vast array of real-world phenomena, making it an indispensable tool in their respective fields.
What is the significance of the instant rate of change formula in calculus?
+The instant rate of change formula, or the derivative formula, is a fundamental tool in calculus. It allows mathematicians to analyze how functions change at specific points, providing insights into the behavior of functions over time. This formula is essential for solving differential equations, modeling physical systems, and understanding the rates of change in various real-world scenarios.
How is the instant rate of change formula used in physics and engineering?
+In physics and engineering, the derivative formula is applied to calculate velocities, accelerations, and rates of change in various systems. For instance, it can be used to determine the speed of a moving object at a specific moment or to analyze the rate of reaction in a chemical process. This formula is a crucial tool for modeling and analyzing physical phenomena.
What are some real-world applications of the instant rate of change formula in economics and finance?
+In economics and finance, the derivative formula is used to analyze and model economic trends and financial markets. It helps in understanding how variables like supply and demand, interest rates, and stock prices change over time. This information is crucial for making informed investment decisions and predicting market behavior.