Japanese Beetle Traps: A Comprehensive Guide To Success

Japanese beetles are a notorious pest for gardeners and farmers alike, causing significant damage to a wide range of plants and crops. Their voracious appetite and ability to multiply rapidly make them a challenging adversary. To effectively manage these pests, it is crucial to employ a comprehensive strategy, and one of the key components is the use of Japanese beetle traps. In this expert guide, we will delve into the world of Japanese beetle traps, exploring their types, placement, and effectiveness, as well as offering valuable insights and strategies to maximize their success.
Understanding the Japanese Beetle
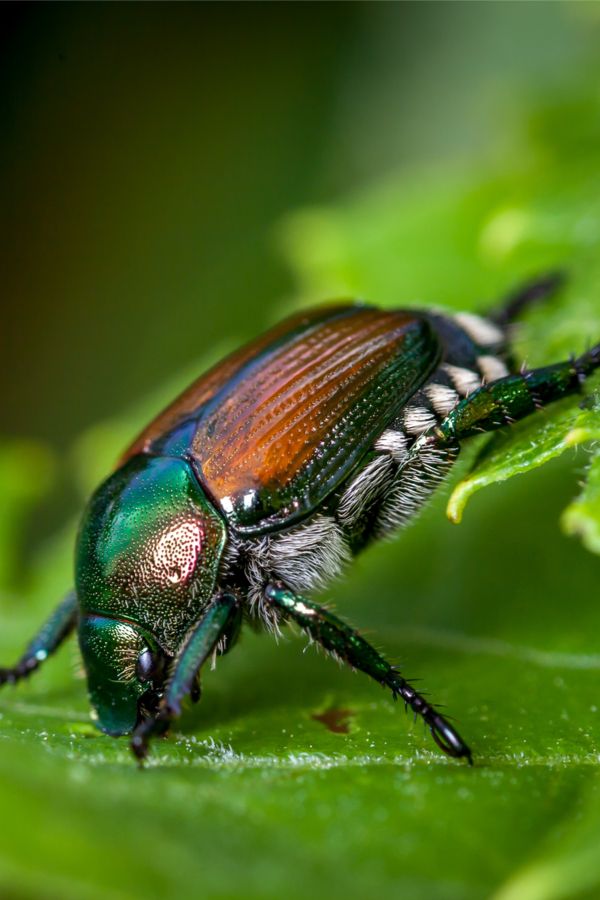

Before we dive into the world of traps, let's familiarize ourselves with the enemy. The Japanese beetle, Popillia japonica, is a small, metallic-green insect native to Japan. It was first discovered in the United States in 1916 and has since become a widespread and destructive pest across the country. These beetles are known for their diverse dietary preferences, feasting on over 300 species of plants, including roses, grapes, and various fruit trees.
Japanese beetles have a unique life cycle, with adults emerging from the soil in late spring or early summer. They are most active during the day, especially on warm, sunny days. The females lay their eggs in the soil, and the larvae, known as grubs, feed on the roots of grasses and other plants, causing further damage to lawns and gardens. Understanding this life cycle is crucial for effective trap placement and timing.
The Role of Traps in Pest Management

In the realm of pest control, traps play a vital role in monitoring and managing populations. For Japanese beetles, traps serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they provide an early warning system, allowing gardeners and farmers to detect the presence of these pests before significant damage occurs. Secondly, traps can help reduce the overall population, preventing further spread and minimizing the impact on crops and plants.
Additionally, traps offer a non-toxic and environmentally friendly approach to pest management. By capturing adult beetles, traps disrupt the reproductive cycle, reducing the number of eggs laid and, consequently, the population of grubs in the soil. This integrated pest management (IPM) approach is especially beneficial for organic growers and those seeking sustainable solutions.
Types of Japanese Beetle Traps
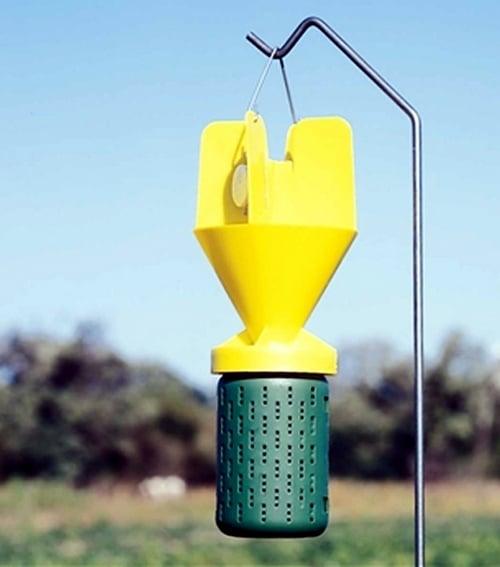
When it comes to Japanese beetle traps, there are several types available on the market, each with its own unique design and features. The most common types include:
Bag Traps
Bag traps are a popular choice for their simplicity and effectiveness. They consist of a mesh bag or net, often with a lure attached, which attracts the beetles. As the beetles enter the bag, they become trapped and cannot escape. Bag traps are easy to set up and can be hung from trees, posts, or other structures. They are particularly useful for small-scale gardens and residential areas.
Jar Traps
Jar traps, also known as container traps, are another effective option. These traps consist of a jar or container with a lid that has a small opening. The lure is placed inside the jar, and as the beetles enter through the opening, they become trapped. Jar traps are versatile and can be placed on the ground, hung from structures, or even buried partially in the soil. They are suitable for both residential and commercial use.
Net Traps
Net traps, or funnel traps, are designed to capture beetles as they fly towards the lure. These traps consist of a net or mesh funnel that leads into a collection chamber. As the beetles enter the funnel, they are guided into the chamber, where they become trapped. Net traps are often used in larger areas, such as orchards or vineyards, where a more extensive trapping system is required.
Lure Options
An essential component of Japanese beetle traps is the lure. Lures are substances that attract the beetles, enticing them to enter the trap. There are two primary types of lures used in Japanese beetle traps:
- Sex Pheromones: Sex pheromones are chemicals released by female Japanese beetles to attract males. These pheromones are highly effective in luring adult beetles to the trap. Commercially available pheromone lures are often used in combination with other attractants to maximize their effectiveness.
- Food-Based Lures: Food-based lures mimic the scent of the beetles' favorite food sources, such as flowers or fruit. These lures are particularly attractive to both male and female beetles. Examples of food-based lures include geranium oil, rose oil, and synthetic attractants that mimic the scent of damaged plants.
Trap Placement and Timing
The success of Japanese beetle traps heavily relies on proper placement and timing. Here are some expert tips to optimize your trap setup:
Placement
When placing your traps, consider the following factors:
- Wind Direction: Position your traps upwind of your plants or crops. This ensures that the scent of the lure is carried towards the beetles, increasing the chances of them finding the trap.
- Sunlight Exposure: Japanese beetles are most active during the day, so choose a location that receives ample sunlight. Avoid placing traps in shaded areas, as this may reduce their effectiveness.
- Distance from Plants: While it may be tempting to place traps directly next to your prized plants, exercise caution. Traps can sometimes attract more beetles than they capture, leading to increased damage. Aim to place traps at least 30 feet away from vulnerable plants to avoid this issue.
Timing
Timing is crucial when it comes to Japanese beetle traps. Here are some key considerations:
- Early Detection: Set up your traps as early as possible in the season, preferably before the adult beetles emerge. This allows you to monitor their presence and take action before significant damage occurs.
- Peak Activity: Japanese beetles are most active during the summer months, typically from late June to early August. Ensure your traps are in place during this period to maximize their effectiveness.
- Replacement and Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain your traps. Replace lures as needed, as their effectiveness may diminish over time. Clean and empty the traps to prevent the buildup of dead beetles, which can reduce their attractiveness.
Maximizing Trap Effectiveness

To ensure the success of your Japanese beetle traps, consider the following strategies:
Use Multiple Traps
Deploying multiple traps in your garden or farm can increase the chances of capturing beetles. Space the traps evenly throughout the area, ensuring they are not too close to each other. This strategy helps cover a larger area and reduces the likelihood of beetles bypassing the traps.
Combine Traps with Other Control Methods
While traps are an effective tool, they should be used in conjunction with other pest management techniques. Consider implementing cultural practices, such as crop rotation, sanitation, and proper irrigation, to further reduce the beetle population. Additionally, biological control methods, such as introducing natural predators or beneficial nematodes, can complement the use of traps.
Targeted Placement
Strategically place your traps near areas where Japanese beetles are known to congregate. This could include flower beds, rose gardens, or fruit trees. By targeting these hotspots, you can maximize the trap's effectiveness and capture a larger number of beetles.
Rotate Lures
To prevent beetles from becoming accustomed to a particular lure, consider rotating between different lure types. For example, you can use a sex pheromone lure for a few weeks, followed by a food-based lure, and then switch back. This helps maintain the beetles' interest and prevents them from developing resistance.
Performance Analysis and Results
When it comes to evaluating the performance of Japanese beetle traps, several factors come into play. Here's a breakdown of what to consider:
Capture Rate
The capture rate refers to the number of beetles trapped over a specific period. While this metric is important, it should be interpreted with caution. A high capture rate may indicate a successful trap, but it could also mean a high population of beetles in the area. Conversely, a low capture rate may not necessarily mean the trap is ineffective, as it could simply reflect a lower beetle population.
Trap Efficiency
Trap efficiency takes into account the ratio of beetles captured to the total number of beetles in the area. This metric provides a more accurate assessment of the trap's effectiveness. A high trap efficiency indicates that the trap is successfully capturing a significant proportion of the beetle population.
Impact on Population
The ultimate goal of using Japanese beetle traps is to reduce the overall population and minimize damage to plants. To assess the impact, consider the following:
- Monitor the damage caused by beetles before and after trap deployment.
- Compare the beetle population in areas with and without traps.
- Evaluate the health and vigor of plants in treated areas.
Long-Term Effectiveness
To ensure the long-term success of your trap strategy, consider the following factors:
- Regularly monitor and maintain your traps to ensure they remain effective.
- Rotate and replace lures to prevent beetles from becoming accustomed to a single attractant.
- Combine trap use with other pest management practices for a comprehensive approach.
Expert Insights and Tips
Here are some valuable insights and tips from industry experts to enhance your Japanese beetle trap strategy:
Conclusion
Japanese beetle traps are a valuable tool in the arsenal of pest management strategies. By understanding the types of traps available, their placement and timing, and implementing expert tips, you can effectively manage and reduce the impact of these destructive pests. Remember, a comprehensive approach, combining traps with other control methods, is key to long-term success. With the right knowledge and strategies, you can protect your plants and crops from the voracious appetite of Japanese beetles.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I check and empty my Japanese beetle traps?
+It is recommended to check and empty your traps at least once a week, especially during the peak activity period of the beetles. Regular maintenance ensures that the traps remain effective and do not become overwhelmed with captured beetles.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can I use Japanese beetle traps as a standalone pest control method?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>While traps are an effective tool, they are most successful when used in conjunction with other pest management practices. Combining traps with cultural, biological, and chemical control methods can provide a comprehensive and sustainable approach to managing Japanese beetle populations.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any natural predators that can help control Japanese beetles?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, certain natural predators can help keep Japanese beetle populations in check. Birds, such as starlings and robins, are known to feed on adult beetles. Additionally, parasitic wasps and flies can help control the beetle population by attacking the larvae stage.</p>
</div>
</div>