Latin America Map Unveiled: Explore The Continent's Rich Geography
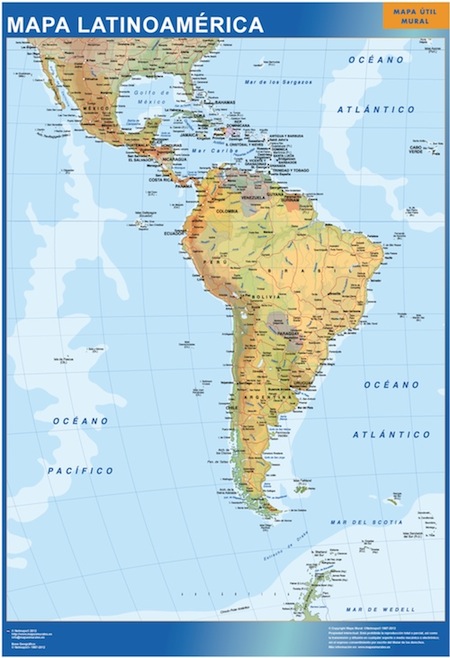
Latin America, a vibrant and diverse region, presents a captivating geographical landscape that invites exploration and discovery. With its vast expanse spanning from the vibrant Caribbean islands to the majestic Andes and the lush Amazon rainforest, the continent offers a tapestry of natural wonders and cultural richness. This article aims to delve into the intricate details of Latin America's geography, offering an in-depth exploration of its diverse landscapes, unique ecosystems, and the cultural significance that shapes this extraordinary part of the world.
A Journey Through Latin America’s Diverse Landscapes

Latin America’s geographical diversity is nothing short of remarkable, boasting a wide array of landscapes that range from rugged mountain ranges to expansive deserts, lush rainforests, and pristine coastal regions. Each of these landscapes contributes to the continent’s rich biodiversity and cultural heritage, making it a captivating destination for exploration and study.
The Majestic Andes: A Mountainous Marvel
The Andes, a formidable mountain range stretching along the western coast of South America, is a geological wonder that dominates the landscape of several countries, including Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela. With its highest peak, Mount Aconcagua, towering at 6,960.8 meters (22,837 feet) above sea level, the Andes is the longest continental mountain range in the world, stretching over 7,000 kilometers (4,350 miles) in length.
The Andes is a region of immense natural beauty, characterized by its snow-capped peaks, deep valleys, and high-altitude lakes. It is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, from the arid deserts of the Atacama in Chile to the lush cloud forests of the Ecuadorian Andes. The mountain range also plays a significant role in the region's cultural heritage, with many indigenous communities calling the Andes home and preserving their ancient traditions and way of life.
| Country | Andes Mountain Range |
|---|---|
| Argentina | Aconcagua (6,960.8 m) |
| Bolivia | Illimani (6,438 m) |
| Chile | Ojos del Salado (6,893 m) |
| Colombia | Cristóbal Colón (5,775 m) |
| Ecuador | Chimborazo (6,263 m) |
| Peru | Huascarán (6,768 m) |
| Venezuela | Pico Bolívar (5,007 m) |
The Amazon Rainforest: A Biological Hotspot
The Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” is a vast and pristine ecosystem that spans across several Latin American countries, including Brazil, Peru, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. Covering an area of approximately 5.5 million square kilometers (2.1 million square miles), the Amazon is the largest tropical rainforest in the world, accounting for over half of the planet’s remaining rainforests.
The Amazon is a biological hotspot, teeming with an incredible diversity of plant and animal life. It is estimated to contain over 30% of the world's species, with new species being discovered regularly. The rainforest plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate and is a vital carbon sink, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. Its intricate network of rivers, including the mighty Amazon River, is home to an abundance of aquatic life, making it a crucial ecosystem for the planet's biodiversity.
| Country | Amazon Rainforest Area |
|---|---|
| Brazil | 49% of the Amazon |
| Peru | 13% of the Amazon |
| Colombia | 10% of the Amazon |
| Venezuela | 6% of the Amazon |
| Ecuador | 1% of the Amazon |
| Bolivia | 11% of the Amazon |
| Guyana | 3% of the Amazon |
| Suriname | 3% of the Amazon |
| French Guiana | 3% of the Amazon |
The Caribbean: A Tropical Paradise
The Caribbean region, consisting of a vast archipelago of islands, is a tropical paradise known for its stunning beaches, crystal-clear waters, and vibrant culture. This region encompasses countries such as Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Haiti, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, and many smaller island nations. The Caribbean is a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world with its beautiful scenery, vibrant music, and rich cultural heritage.
The Caribbean islands are characterized by their diverse landscapes, ranging from mountainous interiors to lush rainforests and picturesque coastlines. The region is also known for its unique blend of African, European, and indigenous influences, which have shaped its culture, cuisine, and music. The Caribbean's warm climate and natural beauty make it an ideal destination for those seeking a tropical escape.
| Island/Country | Notable Features |
|---|---|
| Cuba | Vibrant culture, music, and architecture |
| Dominican Republic | Stunning beaches, colonial architecture |
| Haiti | Rich history, vibrant art scene |
| Jamaica | Reggae music, beautiful beaches |
| Puerto Rico | Breathtaking nature, vibrant nightlife |
| Bahamas | Stunning pink sand beaches |
| Barbados | White sand beaches, diverse marine life |
| Belize | Coral reefs, ancient Mayan ruins |
| Cayman Islands | Scuba diving, vibrant coral reefs |
Latin America’s Cultural Significance

Latin America’s geography is intricately linked to its cultural identity, with its diverse landscapes serving as a backdrop for a rich tapestry of traditions, customs, and artistic expressions. The region’s indigenous populations, African descendants, and European influences have all contributed to a unique cultural melting pot that is both diverse and unified.
Indigenous Heritage and Cultural Diversity
Latin America is home to a vast array of indigenous communities, each with its own distinct culture, language, and way of life. From the ancient civilizations of the Maya, Inca, and Aztec to the diverse tribal groups in the Amazon rainforest, the region’s indigenous heritage is a testament to the resilience and richness of its cultural tapestry. Many indigenous communities have preserved their traditional practices, such as agriculture, handicrafts, and spiritual beliefs, which continue to shape the region’s cultural identity.
European Influences and Colonial Heritage
The arrival of European colonizers in the 15th and 16th centuries brought significant changes to Latin America’s cultural landscape. The Spanish, Portuguese, and French colonizers introduced their languages, religions, and architectural styles, which have left an indelible mark on the region. The colonial era also saw the establishment of cities, such as Lima, Mexico City, and Buenos Aires, which became centers of cultural exchange and fusion, blending European and indigenous influences.
The Power of Music and Dance
Music and dance are integral to Latin American culture, serving as powerful expressions of identity and community. From the vibrant rhythms of salsa and merengue to the soulful melodies of tango and bossa nova, Latin American music has captivated audiences worldwide. Dance, too, plays a vital role, with genres like samba, flamenco, and rumba showcasing the region’s passion and creativity. These artistic expressions not only entertain but also preserve and celebrate the diverse cultural heritage of Latin America.
Conclusion: A Continent of Endless Discovery
Latin America’s geography is a testament to the beauty and diversity of our planet. From the majestic Andes to the lush Amazon rainforest and the vibrant Caribbean, the continent offers a wealth of natural wonders and cultural richness. As we explore and uncover the intricacies of this remarkable region, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness between geography, culture, and the human experience. Latin America’s geography is not just a collection of landscapes and ecosystems; it is a living, breathing entity that shapes and is shaped by the people who call it home.
As we continue to explore and appreciate Latin America's rich geography, we must also recognize the importance of conservation and sustainable practices. The continent's natural wonders are fragile and face numerous threats, including deforestation, climate change, and habitat destruction. It is our collective responsibility to protect and preserve these unique ecosystems and the cultural heritage they embody for future generations.
In conclusion, Latin America's geography is a journey of endless discovery, a tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and traditions that inspire and enrich our lives. By exploring and celebrating this extraordinary continent, we not only gain a deeper understanding of the world but also foster a sense of appreciation and respect for the beauty and diversity that surrounds us.
What is the largest country in Latin America by land area?
+Brazil is the largest country in Latin America, covering an area of approximately 8.5 million square kilometers (3.3 million square miles). It is home to a diverse range of landscapes, including the Amazon rainforest, the Pantanal wetlands, and the rugged terrain of the Brazilian Highlands.
Which country in Latin America has the longest coastline?
+Chile has the longest coastline in Latin America, stretching over 4,000 kilometers (2,500 miles) along the Pacific Ocean. Its coastline is characterized by stunning fjords, picturesque islands, and the majestic Andes mountain range in the background.
What is the highest point in Latin America?
+The highest point in Latin America is Mount Aconcagua, located in Argentina. It stands at an impressive height of 6,960.8 meters (22,837 feet) above sea level, making it the highest peak in the Western Hemisphere.



