Maximizing Yield: Optimal Techniques For Planting Strawberries
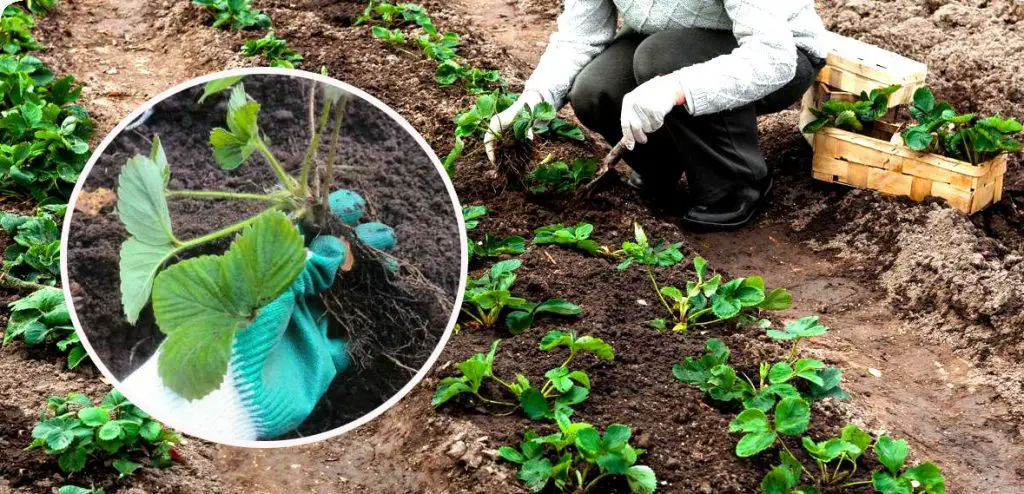

Strawberries are a beloved fruit, cherished for their sweet, juicy flavor and versatility in various culinary creations. For home gardeners and commercial growers alike, maximizing the yield of strawberries is a top priority. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the art of planting strawberries, exploring the optimal techniques that can lead to a bountiful harvest. From selecting the right variety to implementing strategic planting methods, we will uncover the secrets to growing thriving strawberry plants.
Selecting the Right Strawberry Variety
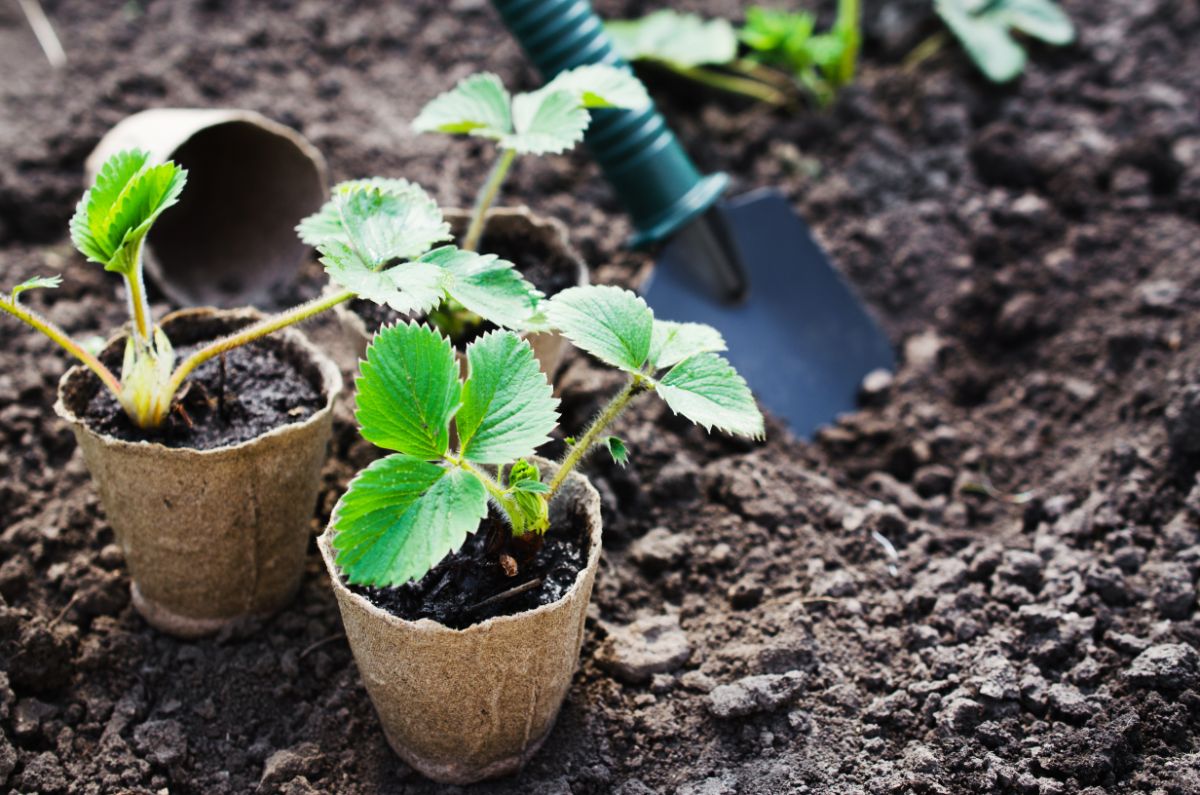

The first step towards maximizing your strawberry yield is choosing the appropriate variety. Different strawberry cultivars have unique characteristics, and selecting the right one for your specific growing conditions and goals is crucial. Here are some key considerations when selecting strawberry varieties:
Climate and Hardiness
Strawberries are generally classified into three main types based on their climate adaptability and hardiness:
- June-bearing Strawberries: These varieties produce a single, large crop of berries in late spring or early summer. They are well-suited for regions with cold winters and are known for their high-quality fruit.
- Everbearing Strawberries: As the name suggests, everbearing strawberries produce two or three smaller harvests throughout the growing season. They are more adaptable to various climates and can tolerate warmer temperatures.
- Day-neutral Strawberries: These varieties can produce fruit continuously throughout the growing season, as long as temperatures remain favorable. Day-neutral strawberries are ideal for extended harvests and are less sensitive to day length.
Taste and Flavor
Strawberry varieties can differ significantly in terms of flavor and sweetness. Some popular choices for exceptional taste include:
- Allstar: Known for its large, firm berries with intense flavor.
- Chandler: Produces exceptionally sweet and aromatic strawberries.
- Albion: A day-neutral variety with excellent flavor and disease resistance.
- Seascape: Renowned for its high sugar content and juicy texture.
Disease Resistance
Disease resistance is a critical factor in strawberry cultivation. Certain varieties are more resilient to common strawberry diseases, such as Verticillium wilt, gray mold, and root rot. Some disease-resistant options include:
- Earliglow: Resistant to Verticillium wilt and gray mold.
- Allstar: Exhibits resistance to several strawberry diseases.
- Tristar: Known for its tolerance to various diseases.
Plant Habit and Growth
Consider the growth habit and vigor of different strawberry varieties. Some varieties are more compact and suitable for smaller spaces, while others can spread and form large mats. Choose a variety that aligns with your garden’s layout and maintenance preferences.
Soil Preparation and Planting Techniques

Proper soil preparation and planting techniques are vital for the successful establishment of strawberry plants. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure optimal growth:
Soil Testing and Amendments
Before planting, conduct a soil test to determine its pH level and nutrient content. Strawberries thrive in slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. If necessary, amend the soil with lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it. Additionally, ensure your soil is rich in organic matter and well-draining.
Choosing the Right Planting Site
Select a sunny location with at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Strawberries prefer well-drained soil and good air circulation to prevent disease. Avoid low-lying areas prone to frost or waterlogging.
Planting Strawberries
Plant strawberry crowns at the appropriate depth, ensuring the roots are covered but the crown (the bud where the leaves emerge) remains above the soil surface. Space the plants 12-18 inches apart in rows, allowing for proper air circulation and growth.
Mulching and Watering
Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, around the strawberry plants to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and maintain a more consistent soil temperature. Water the plants regularly, especially during dry periods, aiming for about 1-2 inches of water per week.
Pruning and Training for Maximum Yield
Pruning and training your strawberry plants can significantly impact their productivity and overall health. Here’s how to do it effectively:
Pruning Techniques
Regularly remove any dead, diseased, or damaged leaves and runners (stolons) from your strawberry plants. This promotes better air circulation and reduces the risk of disease. Additionally, trim back any excessive foliage to allow more sunlight to reach the fruit-bearing parts of the plant.
Training Systems
Consider implementing a training system to maximize the yield and ease of maintenance. Some popular training systems for strawberries include:
- Matted Row System: Allow the strawberry plants to send out runners freely, creating a dense mat of plants. This system is ideal for everbearing and day-neutral varieties.
- Spaced Row System: Control the runners by spacing them evenly along the row. This method is more labor-intensive but can result in larger, higher-quality berries.
- Hilling System: Create small hills or mounds for each strawberry plant, allowing the runners to cascade down the sides. This system improves air circulation and makes harvesting easier.
Fertilization and Nutrient Management
Strawberry plants require a balanced supply of nutrients to thrive and produce abundant fruit. Here’s a guide to proper fertilization and nutrient management:
Fertilizer Selection
Choose a balanced fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10 or 14-14-14. Alternatively, opt for a specialized strawberry fertilizer with a higher potassium content to promote fruit development. Organic options, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can also be used.
Application Timing
Apply fertilizer in early spring, just before new growth begins. Avoid over-fertilizing, as excessive nitrogen can lead to lush foliage at the expense of fruit production. Follow the recommended application rates on the fertilizer package.
Foliar Feeding
Consider foliar feeding your strawberry plants with a liquid fertilizer during the growing season. This method delivers nutrients directly to the leaves, enhancing their absorption and benefiting the overall health of the plant.
Pest and Disease Management

Strawberry plants are susceptible to various pests and diseases, which can significantly impact their yield and quality. Implement the following strategies for effective pest and disease management:
Common Pests
- Slugs and Snails: These pests can cause significant damage to strawberry leaves and fruit. Use organic slug and snail baits or create physical barriers around your plants.
- Aphids: Aphids can transmit viruses and cause distortion of leaves and fruit. Regularly inspect your plants and use insecticidal soap or neem oil to control infestations.
- Spider Mites: These tiny pests can cause yellowing and stunted growth. Keep the plants well-watered and use miticides or insecticidal soaps for severe infestations.
Disease Control
- Gray Mold (Botrytis): This fungal disease can affect both the leaves and fruit. Ensure good air circulation, avoid overhead watering, and remove any infected plant parts.
- Verticillium Wilt: This soil-borne disease causes yellowing and wilting of leaves. Select disease-resistant varieties and practice crop rotation to minimize its impact.
- Root Rot: Waterlogged soil can lead to root rot. Ensure proper drainage and avoid overwatering to prevent this issue.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Care
Proper harvesting and post-harvest care are essential to maintaining the quality and shelf life of your strawberries. Follow these guidelines for successful harvesting and storage:
Harvesting Techniques
Harvest strawberries when they are fully ripe and exhibit a deep red color. Gently twist or cut the stem just above the berry, being careful not to damage the fruit. Regularly inspect your plants and harvest frequently to prevent over-ripening.
Storage and Preservation
Strawberries are highly perishable, so it’s best to consume them soon after harvesting. If you need to store them, keep them in the refrigerator at around 32-36°F (0-2°C). For longer-term preservation, consider freezing, drying, or making jams and jellies.
Maximizing Yield Through Strategic Planting
To optimize your strawberry yield, consider implementing the following strategic planting techniques:
Succession Planting
Plant different strawberry varieties with varying maturity dates to extend your harvest season. This ensures a continuous supply of fresh strawberries throughout the growing season.
Intercropping
Intercropping strawberries with other complementary plants can provide mutual benefits. For example, planting strawberries alongside herbs like thyme or chives can help repel pests and improve overall plant health.
Raised Beds and Containers
Consider growing strawberries in raised beds or containers, especially if your garden soil is less than ideal. This allows for better control over soil quality and drainage, leading to healthier plants and higher yields.
FAQs
What is the best time to plant strawberries?
+The ideal time to plant strawberries varies depending on your climate and the type of strawberries you are growing. Generally, early spring, after the last frost, is the best time for June-bearing strawberries. Everbearing and day-neutral varieties can be planted in early spring or late summer.
How often should I water my strawberry plants?
+Strawberry plants require consistent moisture, especially during the growing season. Aim for about 1-2 inches of water per week, either through rainfall or irrigation. Water deeply and avoid overhead watering to prevent disease.
Can I grow strawberries in containers?
+Absolutely! Growing strawberries in containers is an excellent option, especially for those with limited space. Choose a container with good drainage and fill it with a high-quality potting mix. Ensure the container receives adequate sunlight and water regularly.
How can I protect my strawberry plants from birds and animals?
+To protect your strawberry plants from birds and animals, consider using physical barriers such as bird netting or row covers. These can be placed over the plants to prevent access. Additionally, you can try using scare tactics like reflective tape or decoys to deter pests.
What are some common strawberry diseases and how can I prevent them?
+Common strawberry diseases include gray mold, Verticillium wilt, and root rot. To prevent these diseases, practice good sanitation, remove infected plant parts, and ensure proper air circulation. Avoid overhead watering and consider using fungicides as a preventive measure.
By following these optimal techniques for planting strawberries, you can maximize your yield and enjoy a delicious harvest of fresh, juicy berries. Remember to select the right variety, prepare your soil properly, and implement strategic planting methods to ensure the success of your strawberry garden.