Michigan Tornado History: Uncovering The Path Of Destruction
The Great Lakes State, Michigan, is not typically associated with tornadoes, but these powerful storms have left their mark on the region's history. While tornadoes are more common in the Great Plains and Southeast regions of the United States, Michigan has experienced its fair share of these destructive forces of nature. This article delves into the path of destruction left by tornadoes in Michigan, exploring their impact, frequency, and the measures taken to mitigate their effects.
The Frequency and Impact of Tornadoes in Michigan

Michigan's unique geographical location, with its proximity to the Great Lakes, plays a role in the formation of tornadoes. The state experiences a range of weather conditions, including warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and cooler air from the Great Lakes, creating an environment conducive to tornado development. While tornadoes can occur throughout the year, the peak season is typically from May to August, with June being the most active month.
The impact of tornadoes in Michigan can be devastating. These powerful storms can cause significant damage to property, infrastructure, and natural environments. They can uproot trees, destroy buildings, and leave a trail of destruction in their wake. The human cost can also be high, with injuries and, in some cases, loss of life. It is essential to understand the historical patterns and characteristics of tornadoes in Michigan to better prepare and protect the state's residents and infrastructure.
Notable Tornado Events in Michigan's History
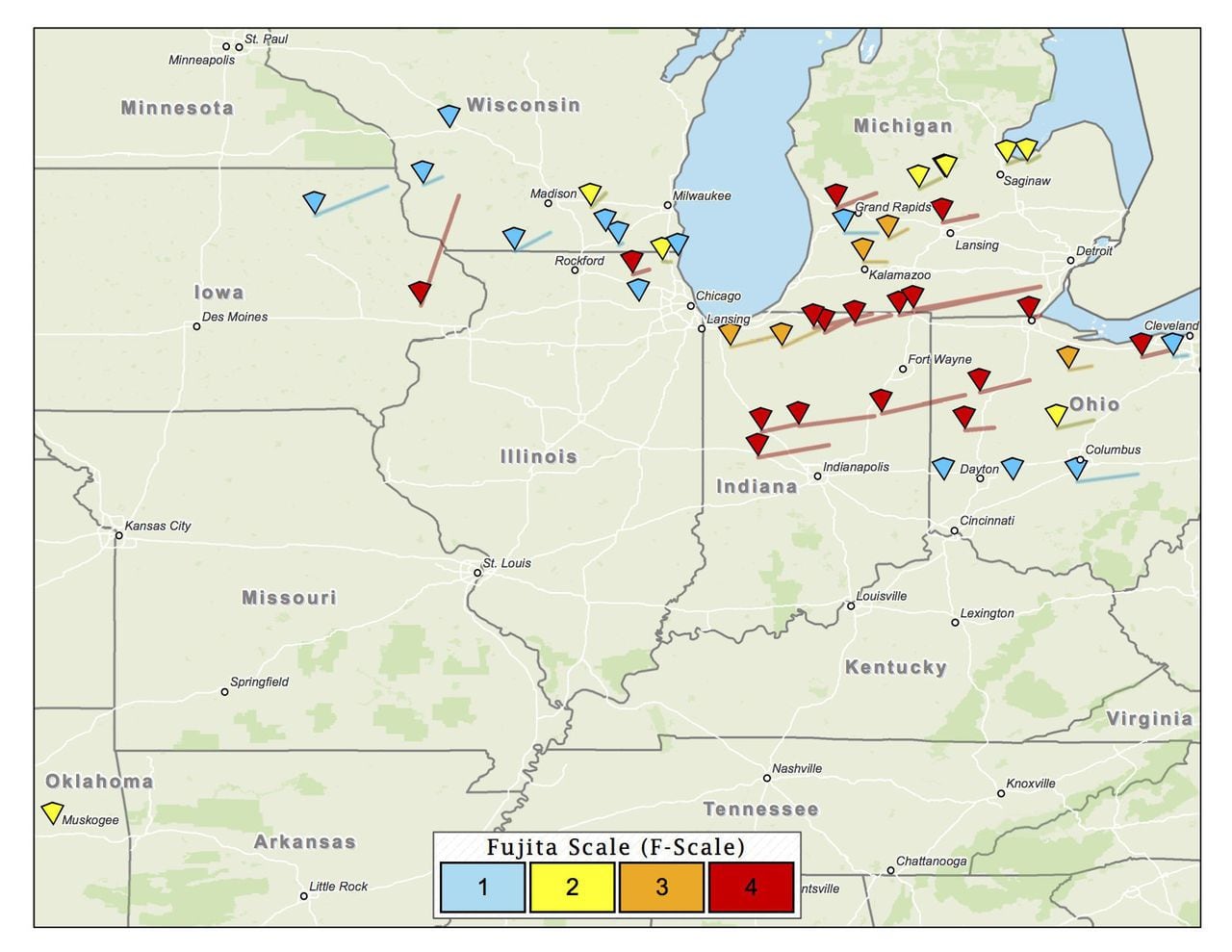
Michigan's tornado history is dotted with notable events that have left an indelible mark on the state. One of the most significant tornado outbreaks occurred on June 8, 1953, when a series of tornadoes struck the southern part of the state. This outbreak, known as the Flint-Beecher Tornado, resulted in 116 fatalities and over 800 injuries. The tornado, classified as an F5 on the Fujita scale, caused widespread devastation, destroying entire neighborhoods and businesses.
Another significant tornado event took place on April 11, 1965, when a tornado swept through the city of Berkley, a suburb of Detroit. The Berkley Tornado, classified as an F4, caused extensive damage to homes and businesses, resulting in numerous injuries and one fatality. This tornado highlighted the vulnerability of urban areas to the destructive forces of nature.
More recently, on June 22, 2015, a supercell thunderstorm spawned a tornado that touched down in the city of Dexter, located in Washtenaw County. The tornado, rated an EF1, caused significant damage to homes and businesses, uprooting trees and damaging power lines. This event served as a reminder that tornadoes can occur even in regions not typically associated with severe weather.
These are just a few examples of the many tornado events that have impacted Michigan. Each storm leaves its unique mark, shaping the state's history and prompting efforts to enhance preparedness and resilience.
Understanding the Path of Destruction: Tornado Tracking and Analysis

To better understand the impact and frequency of tornadoes in Michigan, meteorologists and researchers employ various tracking and analysis techniques. By studying historical data, weather patterns, and storm behavior, they can identify trends and develop strategies to mitigate the risks associated with these powerful storms.
The Role of Doppler Radar and Storm Chasers
Doppler radar technology plays a crucial role in tornado tracking and forecasting. This advanced radar system can detect the rotation and intensity of storms, providing valuable information to meteorologists and emergency management officials. By monitoring the radar data, they can issue timely warnings and alerts to the public, helping them take appropriate precautions.
In addition to radar technology, storm chasers play a vital role in gathering real-time data and observations during tornado events. These dedicated individuals venture into the path of storms, documenting their behavior and providing valuable insights to researchers and meteorologists. Their firsthand accounts and visual evidence contribute to a deeper understanding of tornado formation and behavior.
Historical Data Analysis and Tornado Trends
By analyzing historical tornado data, researchers can identify patterns and trends that help them predict the likelihood of future tornado events. This data includes information on the frequency, intensity, and path of tornadoes, as well as the geographical areas most prone to these storms. By studying these trends, meteorologists can improve their forecasting models and provide more accurate tornado warnings.
One notable trend in Michigan's tornado history is the impact of the Great Lakes on tornado formation. The warm, moist air from the lakes can provide the necessary ingredients for tornado development, particularly during the summer months. Understanding this relationship is crucial for meteorologists to issue timely warnings and for residents to be aware of the potential risks.
Tornado Safety and Preparedness in Michigan
Given the potential for tornado activity in Michigan, it is essential for residents and businesses to be prepared and take appropriate safety measures. Tornado safety and preparedness involve a combination of education, planning, and access to reliable information.
Community Education and Awareness
Community education and awareness are critical components of tornado safety. Local authorities, emergency management agencies, and weather experts play a vital role in disseminating information and raising awareness about tornado risks and safety measures. This includes conducting public awareness campaigns, providing educational resources, and offering training sessions on tornado preparedness.
One effective way to enhance community awareness is through the use of social media and digital platforms. By leveraging these channels, authorities can quickly disseminate tornado warnings, provide real-time updates, and share important safety information. Social media platforms also serve as a valuable tool for residents to stay informed and connected during severe weather events.
Tornado Safety Drills and Emergency Plans
Regular tornado safety drills and the development of comprehensive emergency plans are essential for ensuring the safety of residents and minimizing the impact of tornadoes. These drills simulate tornado scenarios, allowing individuals and communities to practice their response and evacuation plans. By participating in these drills, residents can familiarize themselves with safe locations, such as basements or interior rooms on the lowest level, and learn the proper actions to take during a tornado.
Emergency plans should be developed in collaboration with local authorities, emergency management agencies, and weather experts. These plans should outline the steps to be taken before, during, and after a tornado event, including communication protocols, evacuation procedures, and the establishment of emergency shelters. By having a well-rehearsed plan in place, communities can respond quickly and efficiently to tornado threats.
The Importance of Tornado Sirens and Alerts
Tornado sirens and alerts are crucial for providing timely warnings to residents and businesses. These systems, typically activated by local authorities or emergency management agencies, emit a loud, distinctive sound to alert the public of an impending tornado. Sirens are especially important in rural areas or locations where other forms of communication may be less reliable.
In addition to sirens, residents should familiarize themselves with other tornado alert systems, such as weather radios and mobile alerts. Weather radios, tuned to National Weather Service frequencies, provide continuous weather updates and can issue alerts for severe weather, including tornadoes. Mobile alerts, sent directly to smartphones, can also provide real-time warnings, ensuring that residents are informed even when they are away from home.
Michigan's Tornado Resilience: Infrastructure and Mitigation Efforts
In the face of the destructive power of tornadoes, Michigan has taken significant steps to enhance its resilience and mitigate the impact of these storms. These efforts involve a combination of infrastructure improvements, building codes, and community engagement.
Tornado-Resistant Infrastructure and Building Codes
Michigan has implemented building codes and regulations aimed at increasing the resilience of structures to tornado damage. These codes dictate the use of reinforced materials, proper anchoring, and other measures to ensure that buildings can withstand high winds and flying debris. By adhering to these codes, architects, engineers, and builders can construct tornado-resistant infrastructure, minimizing the potential for catastrophic damage.
In addition to building codes, Michigan has also invested in infrastructure improvements to enhance tornado resilience. This includes the installation of tornado shelters in public buildings, schools, and other critical facilities. These shelters provide a safe haven for individuals during tornado events, offering protection from flying debris and high winds. By having access to these shelters, communities can reduce the risk of injuries and fatalities during severe weather.
Community Engagement and Tornado Preparedness Programs
Community engagement plays a vital role in tornado preparedness and resilience. Michigan has implemented various programs and initiatives to involve residents in the process of enhancing their community's readiness for tornado events. These programs often include educational workshops, community meetings, and the distribution of tornado safety kits.
One successful example of community engagement is the StormReady program, initiated by the National Weather Service. This program provides communities with the tools and resources needed to improve their severe weather preparedness. By participating in the StormReady program, Michigan communities can access training, resources, and recognition for their efforts in enhancing tornado safety.
Collaborative Efforts and Research Initiatives
Michigan's efforts to enhance tornado resilience are not limited to local initiatives. The state actively collaborates with federal agencies, research institutions, and meteorologists to stay at the forefront of tornado research and mitigation strategies. These collaborative efforts involve the sharing of data, the development of advanced forecasting models, and the implementation of innovative technologies to improve tornado detection and warning systems.
Research initiatives, such as the National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL) and the Storm Prediction Center (SPC), play a crucial role in advancing tornado research and improving forecasting capabilities. By partnering with these organizations, Michigan can access the latest advancements in tornado science and incorporate them into its tornado preparedness and response strategies.
Looking Ahead: Future Implications and Continued Preparedness

As Michigan continues to experience the impact of tornadoes, it is essential to remain vigilant and proactive in preparedness efforts. The state's history of tornado events serves as a reminder of the importance of ongoing research, community engagement, and infrastructure improvements.
Climate Change and Its Impact on Tornado Activity
The potential impact of climate change on tornado activity is a growing area of concern. As the climate continues to warm, some researchers suggest that the frequency and intensity of tornadoes may increase. Understanding the relationship between climate change and tornado activity is crucial for meteorologists and policymakers to develop effective adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Michigan, along with other states, is actively monitoring and studying the potential impacts of climate change on tornado behavior. By staying abreast of the latest research and adapting preparedness strategies accordingly, the state can ensure that its residents and infrastructure are well-equipped to handle future tornado events.
Continuing Education and Awareness Campaigns
Maintaining a high level of tornado awareness and education is essential for the long-term safety and resilience of Michigan's communities. Ongoing education campaigns, public awareness initiatives, and community outreach programs can help ensure that residents remain informed about tornado risks and safety measures.
These campaigns can take various forms, including public service announcements, social media campaigns, and community events. By leveraging multiple channels and engaging with diverse audiences, Michigan can reach a wider range of residents and ensure that tornado safety information is accessible to all.
Tornado Research and Technology Advancements
The field of tornado research is constantly evolving, with advancements in technology and scientific understanding. Michigan can benefit from these advancements by staying engaged with the latest research and technologies. This includes exploring new methods of tornado detection, such as advanced radar systems and drone technology, as well as improved forecasting models and warning systems.
By investing in tornado research and technology, Michigan can enhance its ability to detect and warn residents of impending tornado events. This, in turn, can lead to more effective emergency response and a reduced impact on communities.
Collaborative Efforts for a Safer Future
The path to a safer and more resilient future in the face of tornadoes requires a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders. This includes local and state governments, emergency management agencies, meteorologists, researchers, and community members. By working together, these groups can share knowledge, resources, and best practices to enhance tornado preparedness and response capabilities.
Michigan has already established strong collaborative relationships with federal agencies and research institutions. By continuing to foster these partnerships and exploring new collaborations, the state can stay at the forefront of tornado research and preparedness, ensuring the safety and well-being of its residents.
Conclusion: Michigan's Journey Towards Tornado Resilience
Michigan's history with tornadoes is a reminder of the destructive power of nature and the importance of preparedness and resilience. Through a combination of historical analysis, community engagement, and technological advancements, the state has made significant strides in mitigating the impact of tornadoes. However, the journey towards tornado resilience is an ongoing process, requiring continuous learning, adaptation, and collaboration.
As Michigan continues to navigate the path of destruction left by tornadoes, it serves as an example for other regions facing similar challenges. By sharing its experiences, best practices, and lessons learned, Michigan can contribute to a broader understanding of tornado behavior and preparedness, ultimately saving lives and reducing the impact of these powerful storms.
What is the average number of tornadoes that occur in Michigan each year?
+On average, Michigan experiences around 16 tornadoes per year. However, this number can vary significantly from year to year, with some years seeing a higher frequency of tornadoes.
Are there any regions in Michigan that are more prone to tornadoes than others?
+While tornadoes can occur anywhere in Michigan, certain regions are statistically more prone to tornado activity. The southern and central parts of the state, particularly the Flint-Tri-Cities area, have historically experienced a higher frequency of tornadoes.
What should I do if a tornado warning is issued in my area?
+If a tornado warning is issued, it is crucial to take immediate action to ensure your safety. Move to a safe location, such as a basement or an interior room on the lowest level of a sturdy building. Stay away from windows and exterior walls, and if possible, seek shelter under a sturdy piece of furniture. Remember to stay informed and follow the instructions provided by local authorities.