Native American Chief
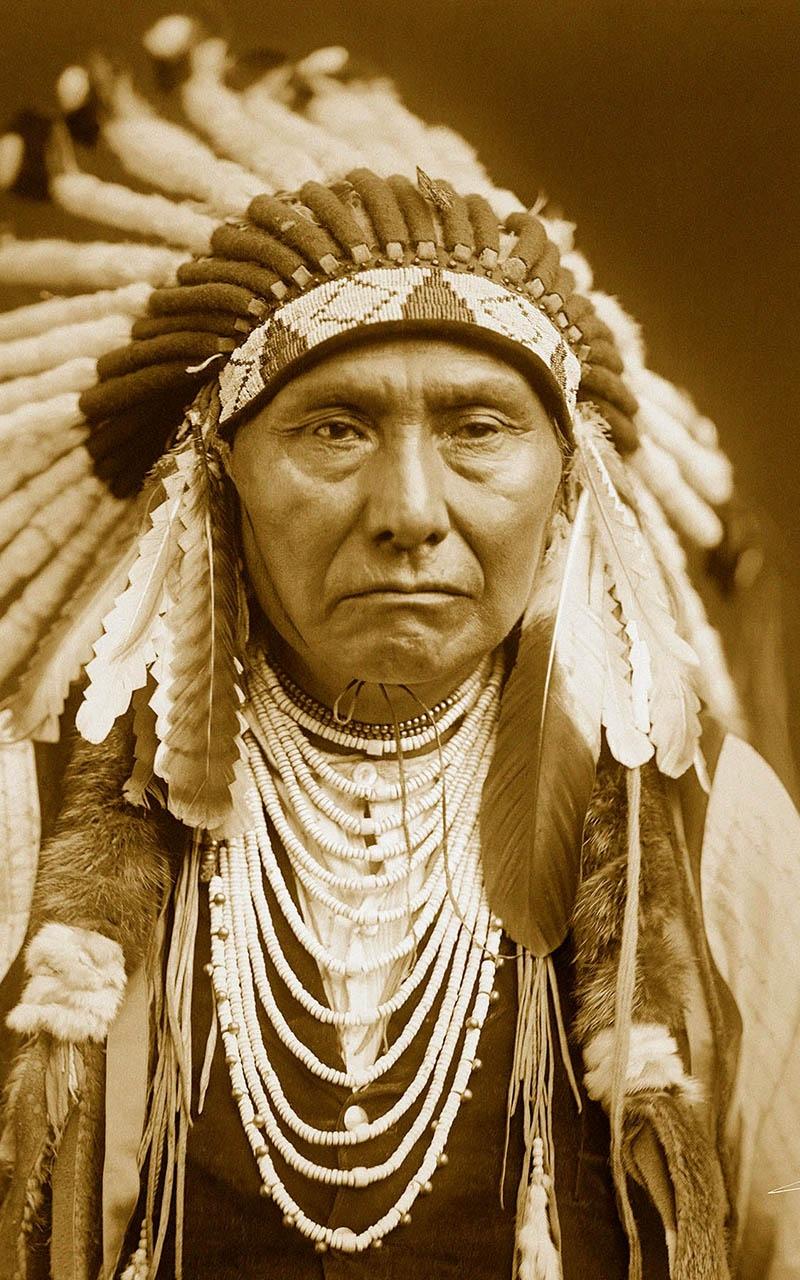

The history and culture of Native Americans are rich and diverse, with countless fascinating stories and traditions that have shaped the fabric of North America. Among the many notable figures, Native American chiefs stand out as leaders, visionaries, and defenders of their communities. This article delves into the world of these influential individuals, exploring their roles, impact, and enduring legacy.
The Role and Significance of Native American Chiefs

Native American chiefs, also known as leaders or headmen, held positions of great importance and responsibility within their tribes. Their roles extended beyond mere political leadership; they were often spiritual and cultural guides, embodying the values, traditions, and knowledge of their people. Chiefs were chosen based on various criteria, including hereditary lineage, bravery in battle, wisdom, and their ability to unite and lead their community.
One of the primary responsibilities of a chief was to ensure the well-being and prosperity of their tribe. This involved making crucial decisions regarding warfare, trade, and diplomacy. Chiefs acted as mediators, resolving conflicts within the tribe and negotiating with other tribes or European settlers. Their leadership skills were pivotal in navigating the complex political landscape, often striking a delicate balance between maintaining tribal autonomy and engaging with external powers.
Spiritual and Cultural Guardians
Native American chiefs were deeply intertwined with the spiritual and cultural practices of their people. They were often regarded as spiritual leaders, responsible for conducting important ceremonies and rituals. Their knowledge of traditional beliefs and practices played a crucial role in preserving and passing down the tribe’s cultural heritage. Chiefs were also storytellers, sharing the tribe’s history, legends, and values, thus ensuring the continuity of their cultural identity.
Additionally, chiefs were key figures in promoting and preserving traditional arts and crafts. They encouraged and supported artisans, ensuring the survival of unique Native American artistic expressions such as pottery, weaving, and beadwork. These artistic traditions not only served as a source of economic livelihood but also as a means of cultural preservation and identity.
Chiefs as Diplomats and Negotiators
In the face of European colonization and the ensuing conflicts, Native American chiefs became pivotal figures in diplomatic relations. They engaged in complex negotiations with colonial powers, often striving to protect their lands, resources, and way of life. Chiefs like Red Cloud of the Oglala Lakota and Chief Joseph of the Nez Perce gained recognition for their strategic diplomacy and resistance against forced relocation and land encroachment.
Their efforts were not without challenges. Native American chiefs had to navigate the intricate web of colonial politics, often facing unequal power dynamics and broken treaties. Despite these obstacles, their diplomatic skills and resilience played a crucial role in shaping the course of history and preserving their people's rights and autonomy.
Famous Native American Chiefs and Their Impact

The annals of Native American history are filled with remarkable chiefs who left an indelible mark on their tribes and the broader world. Here are a few notable examples:
Chief Sitting Bull (Hunkpapa Lakota)
Chief Sitting Bull, born Tatanka Iyotake, was a revered Lakota leader known for his unwavering resistance against the encroachment of European settlers. He played a pivotal role in the victory at the Battle of Little Bighorn, where Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho warriors defeated General George Armstrong Custer’s forces. Sitting Bull’s leadership and spiritual guidance united various tribes, making him a symbol of Native American resistance and cultural pride.
Chief Geronimo (Chiricahua Apache)
Geronimo, born Goyathlay, became an iconic figure in the Apache resistance against Mexican and American encroachment. His fearless raids and escapes earned him a reputation as a formidable warrior. Despite the challenges he faced, Geronimo remained a symbol of Apache resilience and a reminder of the tribe’s unwavering spirit in the face of adversity.
Chief Osceola (Seminole)
Osceola, a prominent figure in the Seminole Wars, led his people in a valiant resistance against the United States’ attempts to remove them from their ancestral lands. His strategic leadership and refusal to sign a treaty that would displace his tribe made him a hero to the Seminole people. Osceola’s legacy continues to inspire Native Americans and highlight the importance of cultural preservation and self-determination.
Chief Pontiac (Odawa)
Pontiac, a renowned Odawa leader, played a crucial role in the Pontiac’s War, a series of conflicts aimed at driving British forces out of the Great Lakes region. His leadership and military strategies united various Native American tribes, making him a symbol of pan-tribal unity and resistance against colonial expansion.
| Chief | Tribe | Notable Achievements |
|---|---|---|
| Sitting Bull | Hunkpapa Lakota | Victory at Little Bighorn, cultural resistance |
| Geronimo | Chiricahua Apache | Apache resistance, legendary warrior |
| Osceola | Seminole | Leadership in Seminole Wars, cultural preservation |
| Pontiac | Odawa | Uniting tribes, Pontiac's War |

The Legacy and Contemporary Relevance
The legacy of Native American chiefs extends far beyond their lifetimes. Their stories and struggles continue to inspire and inform modern Native American communities, serving as a reminder of their rich cultural heritage and the ongoing fight for recognition and justice.
Today, the descendants of these chiefs continue to honor their ancestors' legacies. Many Native American tribes have revived traditional practices, languages, and arts, ensuring the survival and celebration of their unique cultures. Contemporary Native American leaders draw inspiration from their ancestors, advocating for indigenous rights, cultural preservation, and environmental stewardship.
The stories of Native American chiefs also find resonance in popular culture. From literature to film, their narratives have been retold and reimagined, capturing the imagination of audiences worldwide. These depictions, while sometimes controversial, have contributed to a broader understanding and appreciation of Native American history and culture.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Leadership and Resilience
Native American chiefs were more than just leaders; they were guardians of their people’s culture, wisdom, and way of life. Their impact extended beyond their tribes, shaping the course of history and inspiring generations to come. Through their courage, diplomacy, and cultural stewardship, they left an indelible mark on the landscape of North America.
As we reflect on the lives and legacies of these remarkable individuals, we are reminded of the enduring strength and resilience of Native American communities. Their stories serve as a powerful reminder of the importance of cultural preservation, self-determination, and the ongoing struggle for justice and recognition.
What were the key responsibilities of a Native American chief?
+Native American chiefs had diverse responsibilities, including leading their tribes in warfare, trade, and diplomacy. They were also spiritual and cultural guides, preserving and passing down traditional beliefs and practices.
How were Native American chiefs chosen?
+Chiefs were chosen based on various factors, including hereditary lineage, bravery in battle, wisdom, and the ability to unite and lead their community. The selection process varied among different tribes.
What impact did Native American chiefs have on history?
+Native American chiefs played a crucial role in shaping history, particularly during the era of European colonization. Their leadership, resistance, and diplomacy influenced the course of events, often preserving their people’s autonomy and cultural heritage.