Polyatomic Ions Chart: Your Comprehensive Reference Companion

Polyatomic ions, also known as molecular ions, are charged species composed of multiple atoms that act as a single unit. These ions play a crucial role in various chemical processes and are essential for understanding the behavior of compounds in different environments. In this comprehensive reference companion, we present a detailed chart of polyatomic ions, providing you with a valuable resource for your studies and research.
The World of Polyatomic Ions: An Introduction

Polyatomic ions are a fascinating aspect of chemistry, offering a glimpse into the intricate world of molecular structures and their associated charges. These ions, often formed by the combination of two or more atoms, exhibit unique properties and are integral to the study of inorganic and organic chemistry.
One of the key characteristics of polyatomic ions is their ability to stabilize compounds and influence their reactivity. The charge carried by these ions can significantly impact the overall charge and stability of a molecule, making them crucial players in various chemical reactions and equilibrium systems.
Additionally, polyatomic ions are prevalent in biological systems, where they contribute to the functioning of enzymes, the transport of ions across cell membranes, and the regulation of pH levels. Understanding the behavior and properties of these ions is therefore essential not only for chemists but also for biologists and medical professionals.
The Polyatomic Ions Chart: A Comprehensive Overview
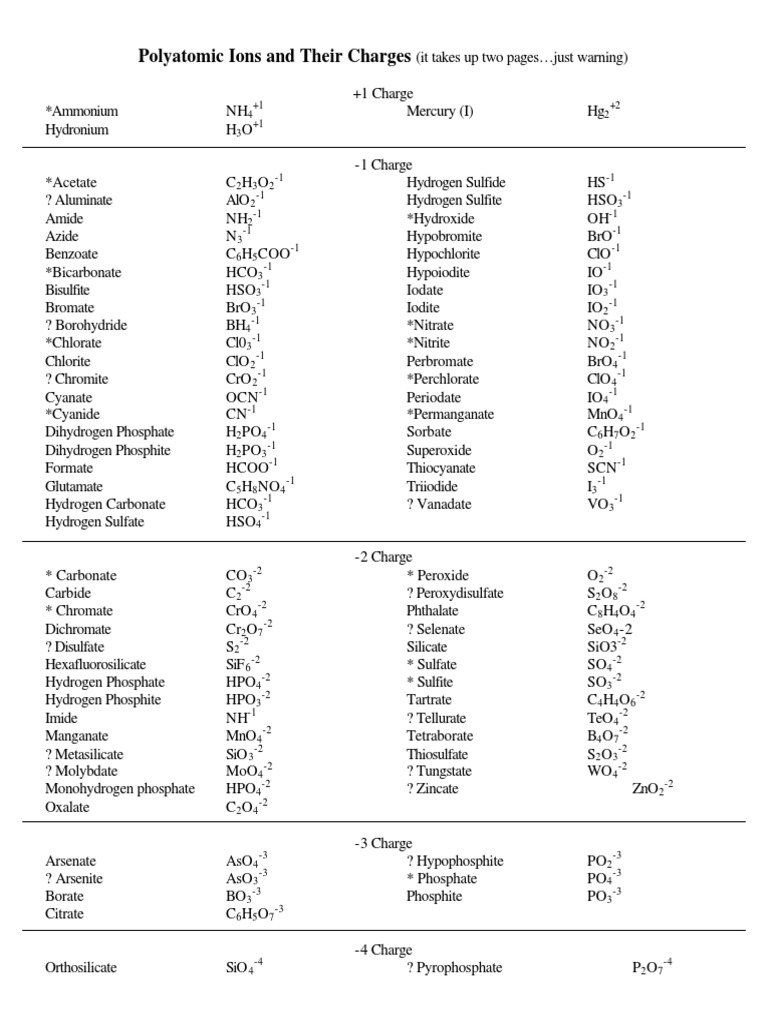
Our polyatomic ions chart aims to provide a comprehensive and user-friendly reference for students, researchers, and professionals alike. It includes a wide range of polyatomic ions, covering both common and less frequently encountered species. Each ion is presented with its chemical formula, name, charge, and a brief description of its properties and occurrences.
The chart is organized systematically, with ions categorized based on their chemical composition and structural similarities. This organization allows for easy navigation and comparison, making it an invaluable tool for quick reference and in-depth study.
Furthermore, we have included additional information and resources within the chart to enhance your understanding. This includes links to relevant articles, research papers, and online databases, providing you with further insights and opportunities for exploration.
Key Features of the Polyatomic Ions Chart
- Comprehensive Coverage: Our chart includes a wide range of polyatomic ions, from common ions like sulfate (\mathrm{SO_4^{2-}}) to more specialized ions such as thiocyanate (\mathrm{SCN^-}). This ensures that you have access to a diverse array of ions, catering to various educational and research needs.
- Detailed Information: Each ion is accompanied by detailed information, including its chemical formula, name, charge, and a concise description of its properties. This information is presented in a clear and concise manner, making it easy to understand and reference.
- Structural Insights: We provide visual representations of the molecular structures of select polyatomic ions. These structures offer a deeper understanding of the arrangement of atoms within the ion and how they contribute to its overall charge and behavior.
- Application Examples: To illustrate the practical significance of polyatomic ions, we have included real-world examples of their applications. From their role in analytical chemistry to their presence in biological systems, these examples showcase the diverse and critical roles polyatomic ions play.
- Interactive Features: Our chart is designed with interactivity in mind. Users can hover over or click on specific ions to reveal additional details, including links to external resources and further reading materials. This interactive element enhances the learning experience and encourages exploration.
Exploring the Polyatomic Ions Chart: A Step-by-Step Guide
To make the most of our polyatomic ions chart, we recommend the following step-by-step approach:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Structure: Start by exploring the overall layout and organization of the chart. Understand how ions are categorized and grouped, and familiarize yourself with the key sections and their contents.
- Search for Specific Ions: Use the search function or navigate through the categories to find specific polyatomic ions of interest. Whether you are looking for a particular ion or exploring a new category, our chart provides easy access to the information you need.
- Study Ion Properties: Dive deeper into the properties of individual ions. Examine their chemical formulas, charges, and descriptions to gain a comprehensive understanding of their characteristics. Pay attention to any unique or notable features mentioned.
- Explore Structural Representations: For select ions, we provide visual representations of their molecular structures. Take the time to study these structures, as they offer valuable insights into the arrangement of atoms and the resulting ion's behavior.
- Apply Your Knowledge: Apply the knowledge gained from the chart to real-world scenarios. Consider the applications and examples provided, and think about how polyatomic ions contribute to various chemical and biological processes. This practical application will reinforce your understanding.
- Utilize Interactive Features: Engage with the interactive elements of the chart. Hover over or click on ions to reveal additional details and resources. These features provide a dynamic learning experience and allow you to explore further beyond the basic information presented.
- Stay Updated: Our polyatomic ions chart is regularly updated to include the latest discoveries and advancements in the field. Stay tuned for new additions, updates, and improvements to ensure you have access to the most current and accurate information.
Real-World Applications of Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions are not merely theoretical concepts; they have numerous practical applications across various fields. Here are some examples of how polyatomic ions are utilized in real-world scenarios:
Analytical Chemistry
In analytical chemistry, polyatomic ions are essential for the identification and quantification of various compounds. Techniques such as mass spectrometry and ion chromatography rely on the unique properties of polyatomic ions to analyze complex mixtures and determine the presence and concentration of specific ions.
Environmental Science
Polyatomic ions play a significant role in environmental science, particularly in the study of water quality and pollution. Ions like nitrate (\mathrm{NO_3^-}) and phosphate (\mathrm{PO_4^{3-}}) are commonly monitored to assess the health of aquatic ecosystems and identify potential sources of pollution.
Biology and Medicine
In biological systems, polyatomic ions are involved in a multitude of processes. For example, ions such as chloride (\mathrm{Cl^-}) and bicarbonate (\mathrm{HCO_3^-}) are crucial for maintaining the pH balance in the body. Additionally, polyatomic ions like calcium (\mathrm{Ca^{2+}}) and magnesium (\mathrm{Mg^{2+}}) are essential for muscle function and enzyme activity.
Materials Science
Polyatomic ions are also utilized in materials science, particularly in the development of new materials with specific properties. For instance, the incorporation of polyatomic ions into polymers can enhance their electrical conductivity or improve their mechanical strength.
Conclusion: A Valuable Resource for Your Journey

Our polyatomic ions chart is designed to be a trusted companion on your journey through the world of chemistry. Whether you are a student studying the fundamentals of chemical bonding or a researcher exploring the intricacies of molecular structures, this chart will provide you with the information and insights you need.
With its comprehensive coverage, detailed information, and interactive features, our chart offers a unique and engaging learning experience. We hope it becomes an indispensable tool in your studies, research, and professional endeavors, helping you unlock the secrets of polyatomic ions and their fascinating role in the chemical universe.
What are the most common polyatomic ions and their charges?
+Some of the most common polyatomic ions include sulfate (\mathrm{SO_4^{2-}}) with a charge of -2, nitrate (\mathrm{NO_3^-}) with a charge of -1, and ammonium (\mathrm{NH_4^+}) with a charge of +1. These ions are frequently encountered in various chemical compounds and reactions.
How do polyatomic ions contribute to the stability of compounds?
+Polyatomic ions can stabilize compounds by forming ionic bonds with other ions or atoms. The charge of the polyatomic ion can help neutralize the overall charge of the compound, leading to a more stable molecular structure. This stabilization is particularly important in the formation of salts and other ionic compounds.
What are some practical applications of polyatomic ions in everyday life?
+Polyatomic ions have numerous practical applications. For example, the chloride ion (\mathrm{Cl^-}) is essential for the proper functioning of our digestive system, and the bicarbonate ion (\mathrm{HCO_3^-}) helps regulate the pH of our blood. Additionally, polyatomic ions are used in various industrial processes, such as water treatment and the production of fertilizers.



