Premature Infant Care: Nurturing Your Baby's Growth And Milestones

Premature birth is a common occurrence, with approximately 10% of babies born prematurely worldwide. This early arrival can present unique challenges for both the infant and their parents, as premature babies often require specialized care to support their growth and development. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of premature infant care, exploring the various aspects that contribute to their healthy growth and the achievement of important milestones.
Understanding Premature Birth and Its Challenges

A premature birth is defined as the birth of an infant before 37 weeks of gestation. These tiny bundles of joy, often referred to as “preemies,” face a range of medical and developmental challenges due to their underdeveloped organs and systems. The earlier a baby is born, the more critical their condition and the greater the need for specialized care.
The challenges associated with premature birth can be daunting, but with the right support and medical interventions, many of these challenges can be overcome. Here, we will explore the key aspects of premature infant care, providing parents and caregivers with the knowledge and tools they need to nurture their baby's growth and watch them reach important milestones.
The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)

For many premature infants, their journey begins in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). The NICU is a highly specialized unit within a hospital that provides intensive care for newborns who require advanced medical attention. Here, a team of healthcare professionals, including neonatologists, nurses, and respiratory therapists, work together to ensure the baby’s well-being.
In the NICU, premature infants receive round-the-clock monitoring and care. This includes regular check-ups, vital sign monitoring, and specialized treatments to address any medical conditions or complications. The NICU environment is designed to be as comforting and nurturing as possible, with low lighting, soft sounds, and a focus on creating a calm and stress-free atmosphere for the infants.
Medical Interventions in the NICU
The medical interventions provided in the NICU are tailored to the individual needs of each premature infant. These interventions may include:
- Respiratory Support: Many premature infants require assistance with breathing due to underdeveloped lungs. This can involve the use of oxygen therapy, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), or mechanical ventilation to support their respiratory system.
- Nutrition and Feeding: Premature babies often have difficulty feeding due to their small size and underdeveloped digestive systems. Specialized feeding methods, such as tube feeding or the use of fortified breast milk or formula, are employed to ensure they receive adequate nutrition.
- Temperature Regulation: Maintaining a stable body temperature is crucial for premature infants. Incubators or radiant warmers are used to provide a controlled environment, ensuring the baby's body temperature remains within a safe range.
- Blood Transfusions: In some cases, premature infants may require blood transfusions to address anemia or other blood-related conditions.
- Phototherapy: Phototherapy is a common treatment for jaundice, a condition that affects many premature babies. It involves the use of special lights to break down bilirubin, a substance that can cause jaundice.
The NICU team works closely with parents to keep them informed about their baby's progress and the various treatments being administered. This collaboration is essential for creating a supportive and nurturing environment for the infant's growth and development.
The Role of Parents and Caregivers
While the NICU provides essential medical care, the role of parents and caregivers is equally vital in a premature infant’s journey. Here are some key ways in which parents and caregivers can contribute to their baby’s growth and development:
Bonding and Skin-to-Skin Contact
Bonding with their baby is an important aspect of care for parents of premature infants. Skin-to-skin contact, also known as “kangaroo care,” has been shown to have numerous benefits for both the infant and the parent. This practice involves holding the baby against the parent’s bare chest, allowing for close physical contact and promoting bonding.
Kangaroo care has been associated with improved weight gain, better temperature regulation, and enhanced brain development in premature infants. It also provides a sense of comfort and security for the baby, reducing stress and promoting a sense of well-being. Parents are encouraged to spend as much time as possible engaging in kangaroo care, as it can have a positive impact on their baby's overall health and development.
Feeding and Nutrition
Feeding a premature infant can be a delicate process, as their nutritional needs are unique. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in ensuring their baby receives the proper nutrition to support their growth. Here are some key considerations:
- Breast Milk: Breast milk is highly recommended for premature infants, as it provides essential nutrients and antibodies that support their immune system. If breastfeeding is not possible, donor breast milk or specialized formula designed for premature babies can be used.
- Tube Feeding: In cases where a premature infant is unable to feed orally, tube feeding may be necessary. This involves delivering breast milk or formula directly into the baby's stomach through a feeding tube. The NICU team will provide guidance and support for parents on how to manage tube feeding at home.
- Fortified Milk: Premature infants often require additional calories and nutrients to support their growth. Fortified breast milk or formula can be used to meet these needs. The NICU team will work with parents to determine the appropriate fortification and feeding schedule for their baby.
Parent Education and Support
Navigating the world of premature infant care can be overwhelming for parents. The NICU team plays a crucial role in providing education and support to help parents understand their baby’s condition and the various aspects of their care. This includes:
- Medical Education: Parents are given information about their baby's medical condition, including any complications or treatments required. This empowers them to make informed decisions and participate actively in their baby's care.
- Feeding and Nutrition Guidance: The NICU team provides guidance on feeding techniques, including breastfeeding, bottle-feeding, and tube feeding. They also offer advice on proper positioning and burping techniques to ensure the baby receives adequate nutrition.
- Developmental Milestones: Parents are educated about the typical developmental milestones for premature infants, such as rolling over, sitting up, and crawling. This helps them track their baby's progress and identify any areas that may require additional support or intervention.
- Emotional Support: The NICU team understands the emotional challenges that come with having a premature infant. They provide support and resources to help parents cope with the stress and anxiety that may arise during their baby's NICU stay.
Transitioning Home
As a premature infant’s condition improves and they meet certain medical criteria, the transition from the NICU to home becomes a possibility. This transition can be both exciting and daunting for parents, as it marks a new chapter in their baby’s care journey.
Preparing for Home
Before a premature infant is discharged from the NICU, the medical team ensures that they are stable and ready for the transition to home care. This involves assessing the baby’s medical condition, ensuring they are gaining weight appropriately, and confirming that any necessary medical equipment or supplies are in place.
Parents and caregivers are provided with comprehensive discharge instructions, which outline the specific care requirements for their baby at home. This may include information on feeding schedules, medication administration, and any special instructions related to the baby's medical condition.
Post-Discharge Care
Once home, the focus shifts to providing a nurturing and supportive environment for the premature infant’s continued growth and development. Here are some key aspects of post-discharge care:
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with the baby's pediatrician or neonatologist are crucial to monitor their progress and address any concerns. These appointments may include growth assessments, developmental screenings, and evaluations of any ongoing medical conditions.
- Feeding and Nutrition: Continuing to provide appropriate nutrition is essential for the baby's growth. Parents should follow the feeding plan outlined by the NICU team, ensuring their baby receives the necessary calories and nutrients. This may involve a combination of breastfeeding, bottle-feeding, or specialized formula.
- Monitoring for Complications: Premature infants are at a higher risk for certain medical complications, such as respiratory issues, infections, or developmental delays. Parents should be vigilant in monitoring their baby for any signs of illness or developmental concerns and seek medical attention promptly if needed.
- Creating a Nurturing Environment: Providing a calm and stimulating environment is important for the baby's overall well-being. This includes ensuring a safe sleeping environment, engaging in interactive play, and promoting bonding through skin-to-skin contact and responsive caregiving.
Long-Term Outcomes and Support
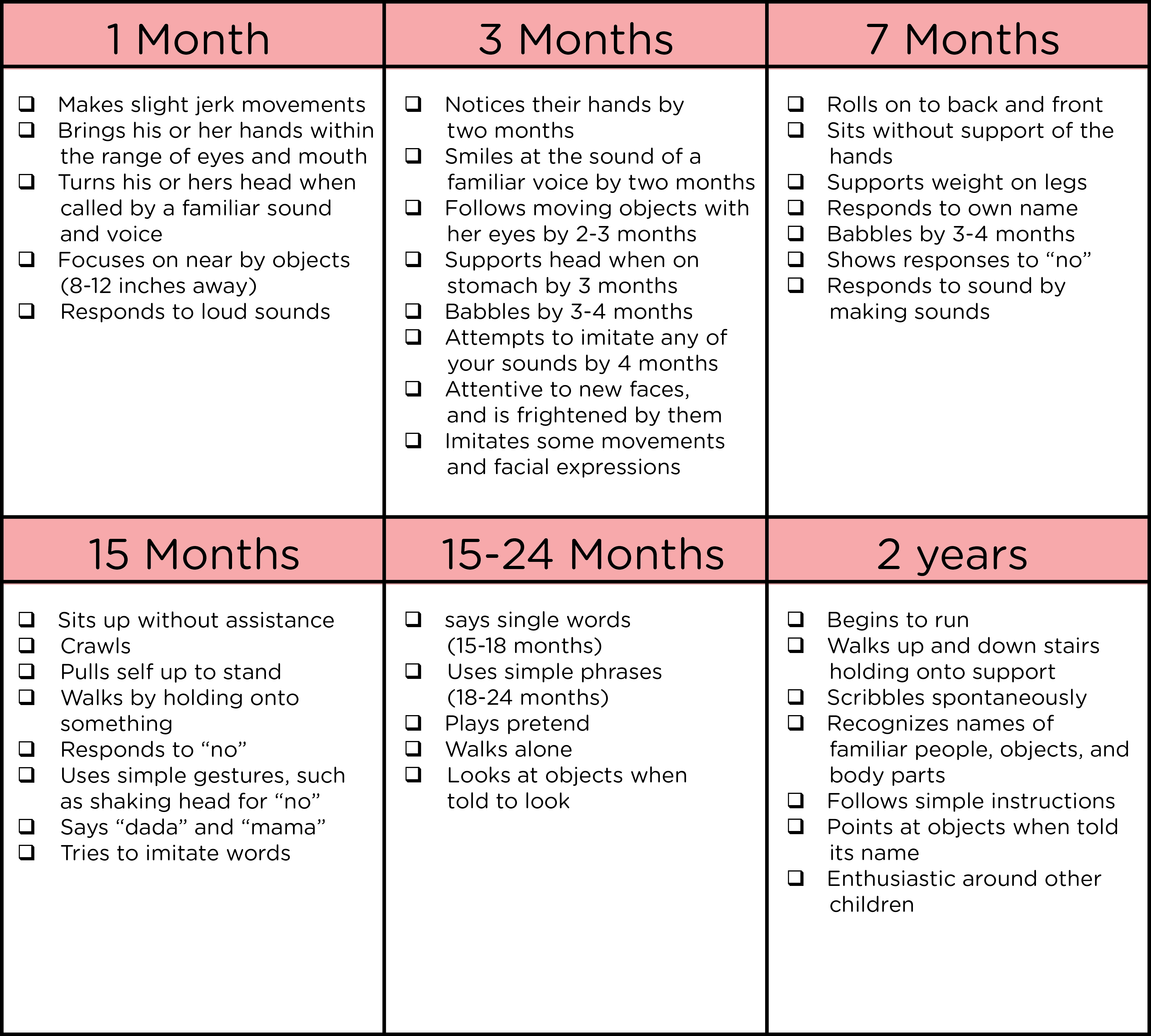
As premature infants grow and develop, their long-term outcomes become a primary focus. While many premature babies go on to lead healthy and fulfilling lives, some may face ongoing challenges or require additional support. Here, we explore the long-term outlook for premature infants and the resources available to support their continued growth and development.
Developmental Milestones and Delays
Premature infants often reach developmental milestones at a slower pace compared to full-term babies. This is due to the underdevelopment of their nervous system and the challenges they faced during their early weeks or months of life. It is important for parents and caregivers to understand that reaching milestones may take longer for premature infants, and patience is key.
The NICU team, in collaboration with early intervention programs and developmental specialists, can provide guidance and support to help premature infants reach their developmental milestones. This may involve therapy services, such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy, to address any delays or challenges the baby may be experiencing.
Long-Term Medical Conditions
Some premature infants may develop long-term medical conditions as a result of their early birth. These conditions can vary widely and may include respiratory issues, such as asthma or chronic lung disease, as well as neurological conditions, such as cerebral palsy or developmental delays.
For parents and caregivers, it is crucial to be aware of these potential long-term conditions and to seek appropriate medical care and support. Regular follow-up appointments with specialists, such as pulmonologists, neurologists, or developmental pediatricians, can help monitor and manage these conditions effectively.
Support Groups and Resources
Having a premature infant can be a challenging and emotional journey for parents and caregivers. Support groups and resources can provide a valuable source of comfort, information, and guidance. Here are some options to consider:
- Premature Infant Support Groups: Local or online support groups can connect parents with others who have experienced premature birth. These groups provide a safe space to share experiences, seek advice, and find emotional support.
- Premature Infant Associations: National or regional associations dedicated to premature infant care can offer a wealth of resources, including educational materials, support programs, and access to specialized services.
- Therapy and Counseling: Seeking therapy or counseling can be beneficial for parents and caregivers who are navigating the emotional challenges of having a premature infant. Therapists can provide support and strategies to cope with stress, anxiety, and any emotional difficulties that may arise.
Conclusion
Caring for a premature infant is a journey filled with challenges and triumphs. With the right medical care, parental involvement, and support, premature babies can thrive and reach their full potential. This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth look at the various aspects of premature infant care, from the NICU to the transition home and long-term outcomes.
As parents and caregivers embark on this journey, it is important to remember that each premature infant is unique, and their care should be tailored to their individual needs. With patience, love, and the support of healthcare professionals, premature infants can overcome the obstacles of their early birth and grow into healthy and happy individuals.
What are the common signs of premature labor?
+Common signs of premature labor include regular contractions, vaginal bleeding or spotting, a persistent low, dull backache, and a feeling of pelvic pressure. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
How can I support my premature infant’s feeding and nutrition at home?
+To support your premature infant’s feeding and nutrition at home, follow the feeding plan provided by the NICU team. Ensure your baby receives the recommended amount of breast milk or formula, and monitor their weight gain regularly. Seek guidance from healthcare professionals if you have any concerns or need assistance with feeding techniques.
What are some common developmental milestones for premature infants?
+Common developmental milestones for premature infants include head control, sitting up independently, crawling, and walking. It’s important to remember that premature infants may reach these milestones at a slower pace compared to full-term babies. Regular developmental screenings and early intervention programs can provide support and guidance.