Root Mean Square Velocity
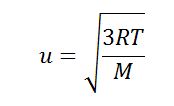
In the vast field of thermodynamics, a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of matter and energy, the concept of root mean square velocity holds significant importance. This measurement provides valuable insights into the kinetic energy and behavior of particles within a gas, offering a deeper understanding of their motion and interactions. As we delve into the intricacies of this topic, we will explore its definition, significance, and applications, shedding light on its role in various scientific and industrial processes.
Understanding Root Mean Square Velocity
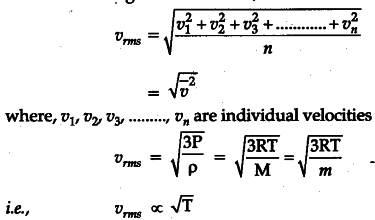
Root mean square velocity, often denoted as urms, is a statistical measure used to describe the average velocity of particles in a gas. It provides a way to quantify the kinetic energy of these particles, which is a fundamental aspect of thermodynamics. By calculating the root mean square velocity, scientists and engineers can gain insights into the motion and behavior of gases under different conditions.
The formula for calculating root mean square velocity is as follows:
urms = √(3RT / M)
Where:
- urms is the root mean square velocity.
- R is the universal gas constant, approximately equal to 8.314 J/(mol·K)
- T is the temperature of the gas in Kelvin (K)
- M is the molar mass of the gas in kilograms per mole (kg/mol)
This formula highlights the relationship between the root mean square velocity, temperature, and molar mass of a gas. By manipulating these variables, we can understand how changes in temperature or the nature of the gas affect the velocity of its particles.
Significance and Applications

Root mean square velocity finds extensive applications in various scientific and industrial domains. Its significance lies in its ability to provide insights into the kinetic energy of gas particles, which is crucial for understanding and predicting their behavior.
Gas Laws and Thermodynamics
In the realm of gas laws and thermodynamics, root mean square velocity plays a pivotal role. It helps in understanding the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature in gases. By considering the root mean square velocity, scientists can derive and explain the behavior of gases under different conditions, such as during adiabatic processes or when subjected to changes in temperature and pressure.
Diffusion and Gas Transport
The concept of root mean square velocity is instrumental in understanding diffusion and gas transport phenomena. It aids in predicting the rate at which gases diffuse through different materials, which is essential in fields like environmental science, chemistry, and material science. By analyzing the root mean square velocity, researchers can design more efficient gas separation processes and optimize the performance of gas-based technologies.
Chemical Reactions and Kinetics
In the context of chemical reactions, root mean square velocity provides valuable insights into the kinetics of reactions involving gases. It helps in determining the rate at which gas molecules collide and react, influencing the overall reaction rate. By considering the root mean square velocity, chemists and engineers can design more efficient reaction systems and optimize reaction conditions.
Engineering and Industrial Processes
Root mean square velocity finds practical applications in various engineering and industrial processes. In combustion engines, for instance, understanding the root mean square velocity of fuel and air molecules is crucial for optimizing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions. Similarly, in chemical plants and refineries, accurate calculations of root mean square velocity are essential for designing and operating equipment effectively.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the practical implications of root mean square velocity, let’s explore a few real-world examples and case studies:
Combustion Engines
In the automotive industry, engineers strive to optimize the performance of combustion engines. By analyzing the root mean square velocity of fuel and air molecules, they can fine-tune the combustion process. For instance, increasing the root mean square velocity of fuel molecules can lead to more efficient combustion, resulting in better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Gas Separation Technologies
Gas separation is a critical process in various industries, including petrochemicals and environmental engineering. By understanding the root mean square velocity of different gas molecules, researchers can design more efficient separation techniques. For example, in gas purification processes, the root mean square velocity of impurities can be used to optimize the performance of membrane-based separation systems.
Chemical Reactors
Chemical reactors are essential in the production of various chemicals and materials. By considering the root mean square velocity of reactant molecules, engineers can design reactors that maximize the rate of chemical reactions. This optimization leads to more efficient and cost-effective production processes, reducing energy consumption and waste generation.
Challenges and Future Directions
While root mean square velocity provides valuable insights, there are challenges associated with its application. One of the primary challenges is the accurate measurement of root mean square velocity, especially in complex systems or at extreme conditions. Researchers are continually working on developing advanced measurement techniques and models to address these challenges.
Looking ahead, the future of root mean square velocity research holds promising prospects. With advancements in computational power and simulation techniques, scientists can now model and predict the behavior of gases with greater accuracy. This opens up new avenues for exploring the applications of root mean square velocity in emerging fields such as nanotechnology, energy storage, and climate science.
Conclusion
In conclusion, root mean square velocity is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics that provides a deeper understanding of the kinetic energy and behavior of gas particles. Its applications span across various scientific and industrial domains, from gas laws and thermodynamics to chemical reactions and engineering processes. By harnessing the insights provided by root mean square velocity, scientists and engineers can optimize processes, improve efficiency, and drive innovation in numerous fields.
How does root mean square velocity differ from average velocity?
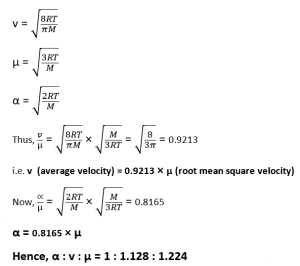
+Root mean square velocity (urms) and average velocity are related but distinct concepts. Average velocity represents the mean velocity of all particles in a gas, while root mean square velocity focuses on the kinetic energy of these particles. urms is calculated using the square root of the average of the squares of individual particle velocities, making it a measure of the average kinetic energy of the gas.
What factors influence the root mean square velocity of a gas?
+The root mean square velocity of a gas is influenced by temperature and molar mass. As temperature increases, so does the root mean square velocity, indicating higher kinetic energy of particles. Additionally, gases with lower molar mass tend to have higher root mean square velocities compared to those with higher molar mass, as reflected in the formula urms = √(3RT / M)
How is root mean square velocity used in real-world applications?
+Root mean square velocity finds practical applications in various industries. In combustion engines, it helps optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. In gas separation technologies, it aids in designing efficient separation systems. Chemical reactors use root mean square velocity to maximize reaction rates, leading to more efficient production processes.