Russia On Map

Russia, the largest country in the world by landmass, is a vast and diverse nation that spans across two continents: Europe and Asia. With its immense size and unique geographical position, Russia holds significant geopolitical importance and cultural diversity. This article aims to explore the fascinating aspects of Russia's location, its neighboring countries, and the unique characteristics that make it a key player on the global stage.
The Geography of Russia: A Transcontinental Power
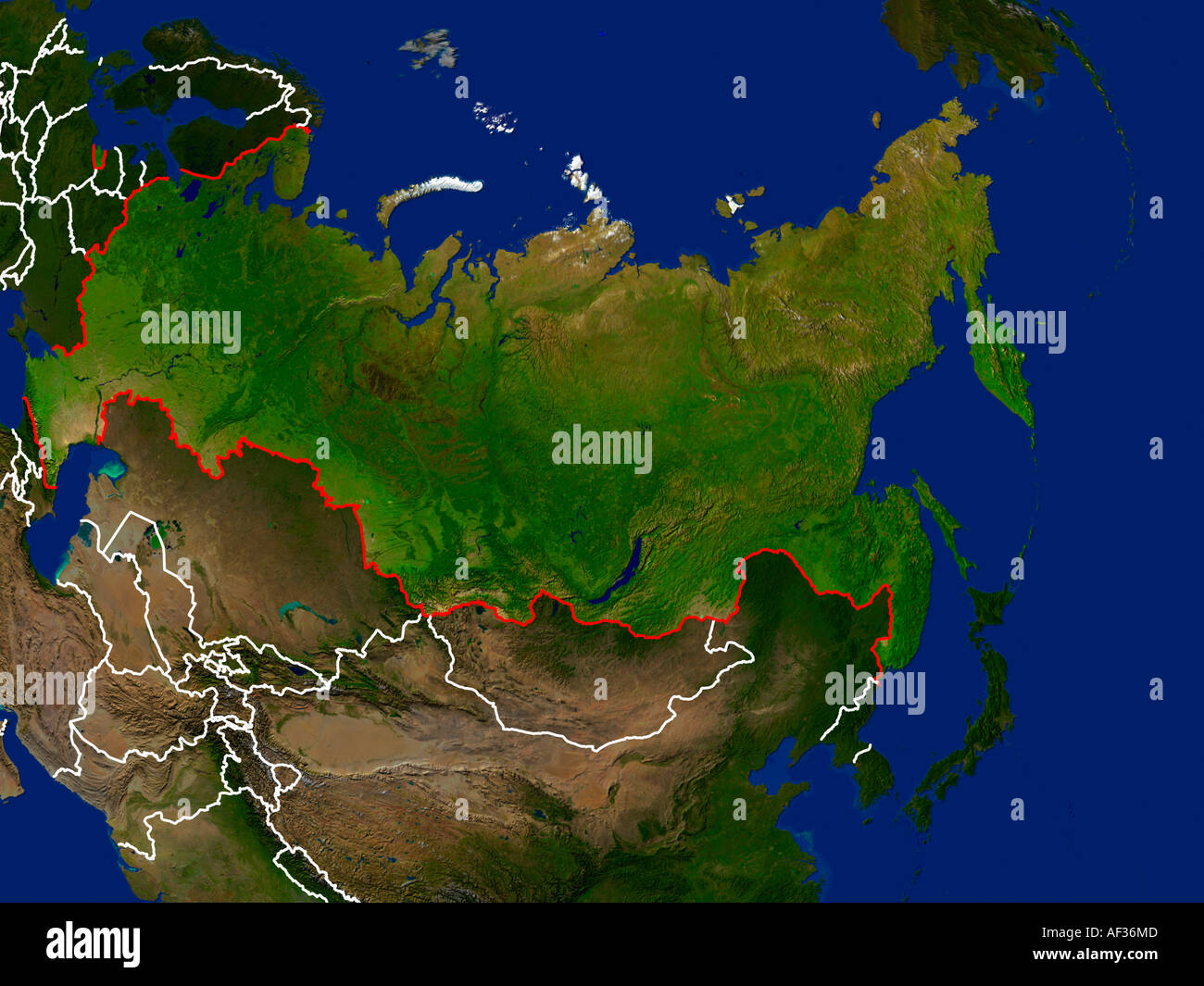
Russia’s geographical expanse is nothing short of extraordinary. Covering an area of approximately 17,098,242 square kilometers, it stretches across the Eastern European and Northern Asian regions. This immense territory is characterized by a wide range of landscapes, from the rugged mountains of the Caucasus and the Ural range to the vast steppes and the vast expanse of the Siberian taiga.
One of the most remarkable features of Russia's geography is its transcontinental nature. While the majority of its territory lies in Asia, it also encompasses a substantial portion of Eastern Europe, making it a unique bridge between two continents. This dual presence allows Russia to exert influence and maintain strategic interests in both regions.
The European part of Russia, known as European Russia, is home to some of the country's most populous cities, including the capital, Moscow. This region is marked by a diverse landscape, including the rolling hills of the Russian Plain and the majestic Volga River, which serves as a vital transportation and trade route.
Russia’s Bordering Countries: A Diverse Neighborhood

Russia shares its borders with an impressive number of countries, each bringing its own cultural and geopolitical dynamics. As of [date of data], Russia borders a total of 14 countries, making it one of the most diverse and complex border regions in the world.
European Bordering Countries
In the European region, Russia shares its borders with several countries, including:
- Norway: Norway’s border with Russia is primarily located in the Arctic region, where the two countries share the barren yet beautiful landscapes of the Arctic tundra.
- Finland: Finland and Russia have a shared border in the northwest, characterized by a mix of forests, lakes, and the iconic Russian-Finnish border zone.
- Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania: These three Baltic states form a contiguous border with Russia, with a history of cultural exchange and political interactions.
- Belarus: Belarus and Russia share a long and complex border, with close economic and political ties due to their membership in the Union State.
- Ukraine: The border between Russia and Ukraine has been a focal point of geopolitical tensions and conflicts in recent years, with the ongoing Russian-Ukrainian war impacting the region.
Asian Bordering Countries
In Asia, Russia’s neighboring countries include:
- China: Russia shares a lengthy border with China, stretching across the vast steppes and mountain ranges of Siberia. The two countries have a complex historical relationship, marked by both cooperation and competition.
- Mongolia: Mongolia and Russia have a shared border in the east, characterized by the rugged beauty of the Mongolian-Russian border zone and the influence of the former Soviet Union.
- Kazakhstan: Kazakhstan and Russia share a long border in the south, with close economic and cultural ties due to their shared Soviet past.
- Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Armenia: These three countries border Russia in the Caucasus region, each with its own unique cultural and historical identity, contributing to the diverse tapestry of the region.
The Impact of Russia’s Geographical Position
Russia’s unique geographical position has had a profound impact on its history, culture, and geopolitical role. Its vast size and diverse landscapes have shaped its identity and influenced its interactions with neighboring countries.
Geopolitical Significance
Russia’s vast territory and strategic location have made it a key player in global politics. Its borders with Europe and Asia give it a unique perspective and influence in both regions. As a result, Russia has often been a pivotal force in international relations, with its decisions and actions having far-reaching consequences.
The country's proximity to key regions, such as the Arctic, the Middle East, and Central Asia, further enhances its geopolitical importance. Russia's role in maintaining stability and managing conflicts in these areas has been a subject of global interest and concern.
Cultural Diversity
Russia’s vast expanse and diverse bordering countries have contributed to its rich cultural heritage. The country is home to a multitude of ethnic groups, languages, and traditions, reflecting the influence of its neighboring regions.
From the vibrant cultures of the Caucasus to the unique traditions of Siberia, Russia's cultural diversity is a testament to its historical interactions and exchanges with its neighboring countries. This diversity has shaped its art, literature, music, and cuisine, making it a fascinating destination for cultural exploration.
Economic Opportunities
Russia’s geographical position also presents significant economic opportunities. Its vast natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, are a major source of wealth and influence. The country’s vast landmass and diverse landscapes offer potential for agriculture, forestry, and other industries.
Additionally, Russia's strategic location as a transit country for trade and transportation between Europe and Asia provides it with a unique advantage. The country serves as a crucial link in the global supply chain, facilitating the movement of goods and services between two of the world's largest economic regions.
Russia’s Border Security and Challenges
With such a vast and diverse border region, Russia faces unique challenges in maintaining border security and managing its interactions with neighboring countries.
Border Security Measures
Russia has implemented a range of border security measures to protect its borders and maintain national security. These measures include:
- Enhanced border patrols and surveillance systems.
- The establishment of border guard forces and specialized units.
- Strict visa and immigration policies to control the movement of people.
- Collaboration with neighboring countries on border management and security initiatives.
Border Disputes and Tensions
Russia’s complex border region has been a source of historical and ongoing disputes and tensions with neighboring countries. Some of the notable border-related issues include:
- The long-standing dispute over the Kuril Islands with Japan.
- Tensions with Ukraine over the annexation of Crimea and the ongoing conflict in the Donbas region.
- Border skirmishes and territorial disputes with neighboring countries, such as Georgia and Azerbaijan.
Managing Border Relations
Despite the challenges, Russia actively engages in diplomatic efforts and regional cooperation to manage its border relations. The country participates in various international organizations and initiatives aimed at promoting stability and resolving border-related issues.
Russia's membership in organizations like the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) and the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) allows it to collaborate with neighboring countries on security, economic, and cultural matters. These platforms provide a platform for dialogue and the peaceful resolution of disputes.
Russia’s Future Prospects and Global Role

As Russia continues to navigate its complex geopolitical landscape, its future prospects and global role remain a subject of much discussion and analysis.
Economic Development and Diversification
Russia has made significant strides in recent years to diversify its economy beyond its traditional reliance on natural resources. The country has invested in sectors such as technology, agriculture, and tourism, aiming to reduce its vulnerability to global commodity price fluctuations.
The development of the Russian Far East, with its vast natural resources and potential for economic growth, is a key focus area. The government has implemented various initiatives and incentives to attract investment and promote sustainable development in this region.
International Relations and Geopolitical Influence
Russia’s international relations and geopolitical influence are shaped by its complex history, cultural heritage, and strategic position. The country has actively engaged in global diplomacy, seeking to assert its role as a major power and protect its national interests.
Russia's relationships with key global players, such as the United States, China, and the European Union, are characterized by a mix of cooperation and competition. The country's involvement in regional organizations and initiatives, such as the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), further demonstrates its desire to shape the global order.
Addressing Border-Related Challenges
As Russia looks to the future, addressing border-related challenges and improving relations with neighboring countries will be crucial. The country has made efforts to enhance border security, combat illegal activities, and improve cross-border cooperation.
Russia's participation in international border management initiatives, such as the Border Security and Management Program (BSMP), demonstrates its commitment to addressing these challenges. By engaging in dialogue and collaboration with neighboring countries, Russia aims to create a more stable and prosperous border region.
Conclusion
Russia’s location on the map is more than just a geographical fact; it is a key factor shaping its identity, culture, and global role. The country’s vast territory, transcontinental nature, and diverse bordering countries have influenced its history, politics, and economy.
As Russia continues to navigate its complex geopolitical landscape, its unique position will remain a critical aspect of its identity and influence. The country's future prospects and global role will be shaped by its ability to manage its borders, engage in constructive international relations, and address the challenges and opportunities presented by its diverse neighborhood.
What is the total length of Russia’s borders with its neighboring countries?
+As of [date of data], Russia’s total border length with its neighboring countries is approximately [total border length in kilometers]. This includes borders with countries like Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine, China, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Armenia.
How has Russia’s history with the Soviet Union influenced its current border situation?
+Russia’s history as a part of the Soviet Union has had a significant impact on its current border situation. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the creation of new independent states, resulting in a complex web of borders and territories. Russia has had to navigate these changes and establish new border agreements with its former Soviet neighbors.
What are some of the key border security challenges faced by Russia?
+Russia faces several border security challenges, including illegal immigration, drug trafficking, and the potential for cross-border terrorism. The country’s vast and diverse border region, combined with its proximity to regions of conflict and instability, presents unique security concerns that require ongoing vigilance and cooperation with neighboring countries.



