Sds Safety Data Sheets: Your Comprehensive Guide
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are an essential component of workplace health and safety practices, providing critical information on the properties and potential hazards of various substances. These documents are designed to inform and educate workers about the substances they may encounter, helping to prevent accidents, injuries, and exposure to harmful materials. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of SDS, exploring their purpose, structure, and the vital role they play in maintaining a safe and compliant work environment.
Understanding the Purpose of Safety Data Sheets

Safety Data Sheets serve as a comprehensive resource for anyone working with or around potentially hazardous substances. They are an integral part of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS), an international initiative aimed at standardizing chemical hazard communication. The primary objectives of SDS include:
- Hazard Communication: SDS provide detailed information on the physical, chemical, and toxicological properties of substances, helping workers understand the potential risks associated with their use.
- Safety Measures: These documents outline the necessary precautions, protective measures, and emergency procedures to follow when handling or storing the substance.
- Compliance: SDS ensure that employers and employees comply with relevant health and safety regulations, reducing the likelihood of legal issues and penalties.
- Worker Training: By providing accessible and detailed information, SDS contribute to effective worker training, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their safety.
The Structure of a Safety Data Sheet

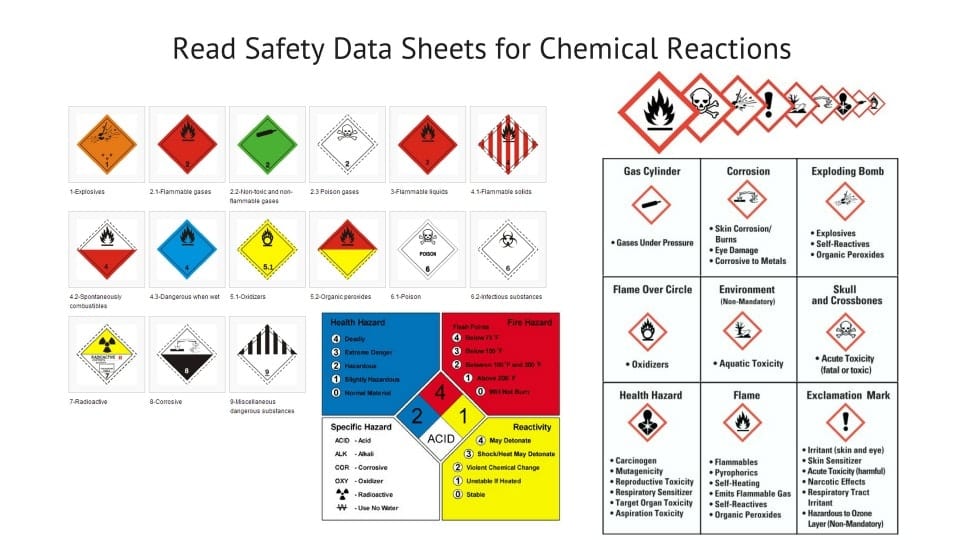
Safety Data Sheets follow a standardized format, ensuring consistency and ease of use. The 16-section structure is as follows:
- Identification: Provides basic information about the substance, including its name, manufacturer, and contact details.
- Hazard(s) Identification: Details the potential hazards associated with the substance, including its classification and labeling elements.
- Composition/Information on Ingredients: Lists the chemical composition of the substance, including any impurities or stabilizing additives.
- First-Aid Measures: Offers guidance on immediate actions to take in case of exposure or injury, covering inhalation, skin contact, eye contact, and ingestion.
- Fire-Fighting Measures: Provides information on the appropriate fire-fighting methods and equipment to use in case of a fire involving the substance.
- Accidental Release Measures: Outlines the steps to take in the event of a spill, leak, or release of the substance, including containment and cleanup procedures.
- Handling and Storage: Offers guidance on the safe handling and storage of the substance, including any specific requirements or precautions.
- Exposure Controls/Personal Protection: Identifies the exposure limits and provides recommendations for personal protective equipment (PPE) to be used when handling the substance.
- Physical and Chemical Properties: Describes the physical and chemical characteristics of the substance, such as appearance, odor, solubility, and stability.
- Stability and Reactivity: Discusses the stability of the substance under different conditions and any potential hazardous reactions it may undergo.
- Toxicological Information: Provides detailed information on the toxicological properties of the substance, including acute and chronic effects, LD50/LC50 values, and potential health effects.
- Ecological Information: Offers guidance on the environmental impact of the substance, including its potential ecological toxicity and any necessary precautions for disposal.
- Disposal Considerations: Provides information on the proper disposal methods and any regulatory requirements for the substance.
- Transport Information: Includes the UN number, proper shipping name, and any special precautions for transporting the substance.
- Regulatory Information: Lists the relevant regulations and directives applicable to the substance, including any specific requirements or restrictions.
- Other Information: Provides additional information, such as the date of preparation or last revision of the SDS, and any relevant references or sources.
The Importance of SDS in Workplace Safety
Safety Data Sheets play a crucial role in ensuring a safe and healthy workplace environment. Here are some key reasons why SDS are essential:
- Risk Assessment: SDS provide the necessary information for employers and safety professionals to conduct comprehensive risk assessments, identifying potential hazards and implementing appropriate control measures.
- Worker Training: By providing detailed and accessible information, SDS contribute to effective worker training programs, ensuring that employees understand the risks associated with the substances they work with and the necessary precautions to take.
- Emergency Response: In the event of an accident or emergency, SDS serve as a critical resource, offering guidance on first-aid measures, fire-fighting procedures, and spill response, helping to minimize the impact of the incident.
- Regulatory Compliance: SDS ensure that employers meet their legal obligations under various health and safety regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
- Environmental Protection: SDS provide valuable information on the environmental impact of substances, helping to prevent pollution and promote sustainable practices.
Implementing an Effective SDS Management System
To maximize the benefits of Safety Data Sheets, it is essential to implement a well-organized and efficient SDS management system. Here are some key considerations:
- Centralized Repository: Establish a centralized digital repository for SDS, ensuring easy access and retrieval for all relevant personnel.
- Regular Updates: Stay up-to-date with the latest SDS revisions and ensure that all substances in your workplace have current and accurate SDS.
- Training and Awareness: Provide comprehensive training to employees on the importance of SDS, how to access and use them, and the necessary actions to take based on the information provided.
- Hazard Communication Program: Integrate SDS into a comprehensive hazard communication program, ensuring that all aspects of chemical safety, including labeling, training, and emergency response, are covered.
- Supplier Collaboration: Work closely with suppliers to ensure that accurate and up-to-date SDS are provided for all substances supplied to your workplace.
Conclusion: Empowering Workplace Safety with SDS

Safety Data Sheets are a vital tool in promoting workplace safety and compliance. By providing comprehensive information on the properties and hazards of substances, SDS empower workers to make informed decisions and take necessary precautions. Implementing an effective SDS management system ensures that your workplace remains compliant, safe, and well-prepared for any potential chemical-related incidents. Remember, a well-informed and prepared workforce is the key to a successful and sustainable safety culture.
FAQs
What is the Globally Harmonized System (GHS)?
+The Globally Harmonized System (GHS) is an international initiative aimed at standardizing the classification and labeling of chemicals. It provides a consistent framework for communicating chemical hazards, ensuring that information is easily understood by workers worldwide.
Are Safety Data Sheets mandatory for all substances?
+Yes, Safety Data Sheets are mandatory for all substances that meet the criteria for classification as hazardous under the GHS. This includes substances that are classified as flammable, corrosive, toxic, or pose other health or environmental hazards.
How often should Safety Data Sheets be updated?
+Safety Data Sheets should be updated whenever new information becomes available, such as changes in the substance’s composition, new scientific research, or regulatory updates. It is recommended to review and update SDS at least annually to ensure they remain accurate and up-to-date.