Unlocking The Instantaneous Rate Of Change: Master The Formulaic Approach
In the realm of mathematics, the concept of instantaneous rate of change stands as a cornerstone, offering a powerful tool to understand the dynamics of various phenomena. This concept, often associated with the derivative, is not merely an abstract mathematical construct but a fundamental principle with wide-ranging applications across diverse fields. From physics and engineering to economics and even biology, the ability to quantify the rate at which a function changes at a specific point holds immense value. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the instantaneous rate of change, exploring its definition, significance, and practical applications, and equip you with the knowledge to master this essential mathematical concept.
Understanding the Instantaneous Rate of Change
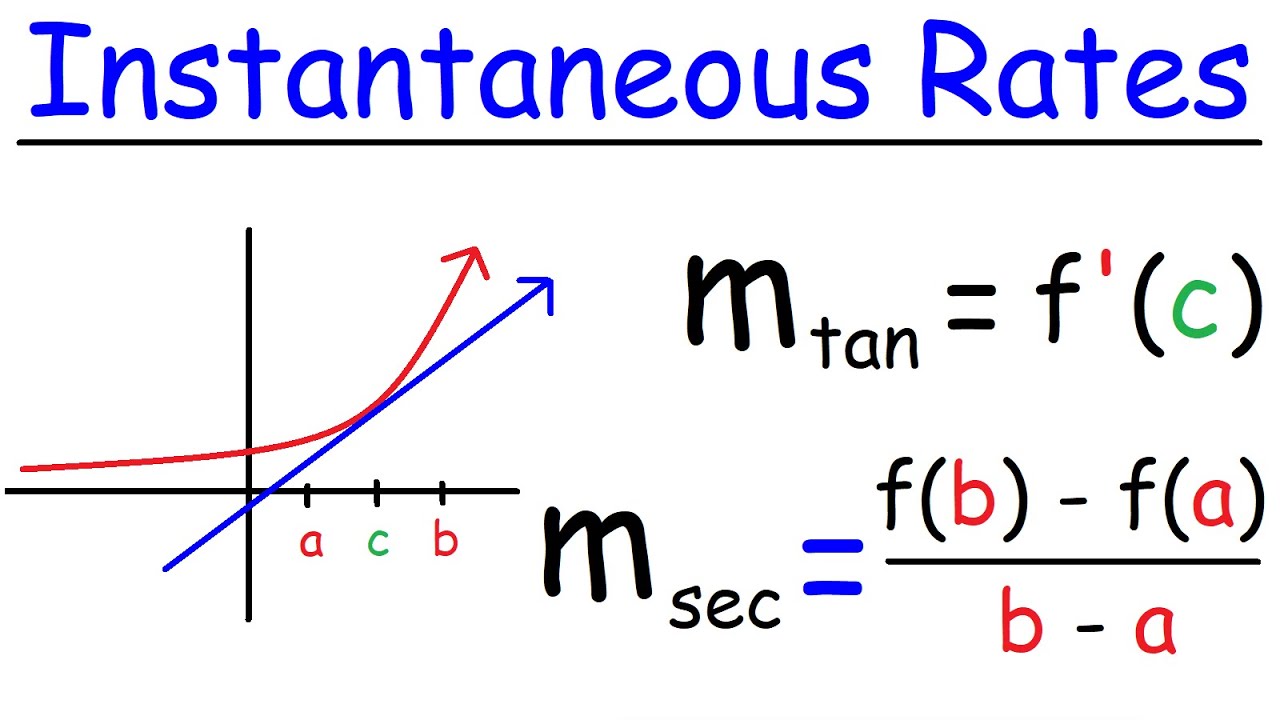
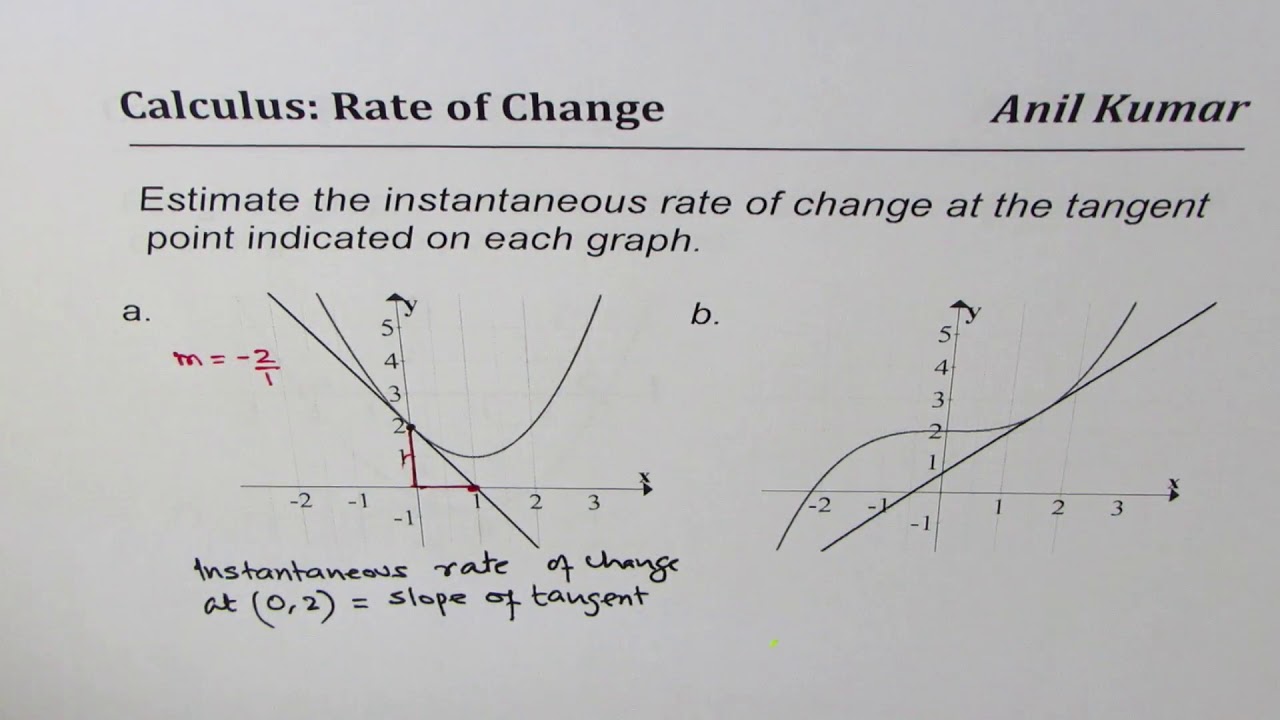
The instantaneous rate of change, also known as the derivative, represents the slope of the tangent line to a function at a specific point. In simpler terms, it measures how quickly a function’s output changes in response to changes in its input. This concept is central to calculus, a branch of mathematics that deals with continuous change. By understanding the instantaneous rate of change, we gain insights into the behavior of functions and can make predictions about their future behavior.
The Derivative: A Mathematical Definition
Mathematically, the derivative of a function f(x) at a point x is defined as the limit of the difference quotient as the change in x approaches zero. This can be expressed as:
f'(x) = limh→0 [(f(x+h) - f(x)) / h]
Here, f'(x) represents the derivative of the function f(x) at point x, and h is an infinitesimal change in x. This definition provides a rigorous framework for calculating the instantaneous rate of change for a wide range of functions.
Visualizing the Instantaneous Rate of Change
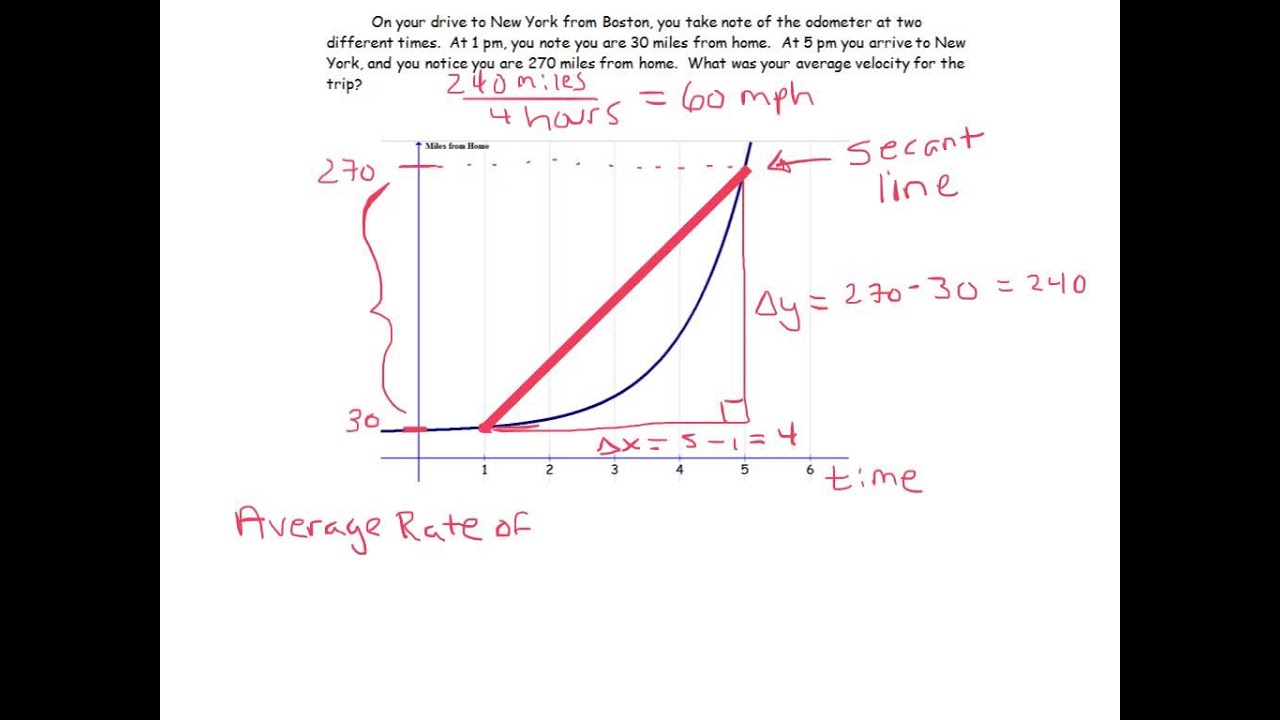
To better understand the concept, let’s consider a simple example. Imagine a car traveling along a straight road. We want to determine the car’s velocity at a specific moment. Velocity, in this context, is the rate of change of the car’s position with respect to time. By taking the derivative of the car’s position function, we can calculate its velocity at any given point. This visualization helps us grasp the concept of the instantaneous rate of change as a measure of how quickly something is changing at a particular instant.
Applications Across Disciplines
The instantaneous rate of change, with its versatile applications, transcends the boundaries of mathematics and finds relevance in numerous fields.
Physics and Engineering
In physics, the derivative is an indispensable tool for describing the behavior of physical systems. For instance, the derivative of position with respect to time gives us velocity, and the derivative of velocity gives us acceleration. This allows physicists and engineers to model and predict the motion of objects, design efficient systems, and solve complex problems in mechanics, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism.
Economics and Finance
The concept of the instantaneous rate of change is equally vital in economics and finance. In economics, derivatives are used to model supply and demand curves, helping economists predict market behavior and make informed policy decisions. In finance, derivatives play a crucial role in risk management and the pricing of complex financial instruments.
Biology and Chemistry
Biologists and chemists also leverage the power of derivatives. In biology, derivatives are used to model population growth, the spread of diseases, and the dynamics of ecosystems. In chemistry, the derivative of a reaction rate with respect to time provides insights into the kinetics of chemical reactions, aiding in the design of efficient chemical processes.
Practical Examples and Real-World Scenarios
To illustrate the practical applications of the instantaneous rate of change, let’s consider a few real-world scenarios.
Optimizing Business Strategies
In the business world, understanding the instantaneous rate of change can be a powerful tool for optimizing strategies. For instance, a company might use derivatives to analyze the rate of change in consumer demand for a particular product. By identifying the inflection points in the demand curve, the company can make informed decisions about production levels, pricing, and marketing campaigns.
Environmental Monitoring and Conservation
Environmental scientists employ derivatives to monitor and study various ecological phenomena. For example, the derivative of a species’ population with respect to time can reveal critical information about its growth rate and the impact of environmental factors. This data is invaluable for conservation efforts and the development of sustainable practices.
Medical Research and Drug Development
In the field of medicine, derivatives play a crucial role in drug development and research. By analyzing the rate of change of a drug’s concentration in the bloodstream, researchers can optimize dosage regimens and minimize side effects. Additionally, derivatives are used to model the progression of diseases, aiding in the development of effective treatment strategies.
Challenges and Limitations
While the instantaneous rate of change is a powerful tool, it is not without its challenges and limitations. One of the primary challenges is the computational complexity involved in calculating derivatives for certain functions. For example, functions with complex or discontinuous behavior can pose significant challenges. Additionally, the concept of the derivative assumes a certain level of smoothness in the function, which may not always be the case in real-world scenarios.
Numerical Methods and Approximations
To address these challenges, mathematicians and scientists often employ numerical methods and approximations. These techniques involve estimating the derivative by using finite differences or other numerical algorithms. While these methods may not provide exact values, they offer practical solutions for dealing with complex functions and real-world data.
Alternative Approaches
In some cases, alternative mathematical approaches may be more suitable than derivatives. For instance, in the field of statistics, the concept of a gradient is often used to analyze the rate of change of a function. The gradient provides a vector-valued measure of the rate of change, which can be particularly useful in multi-dimensional spaces.
Mastering the Formulaic Approach
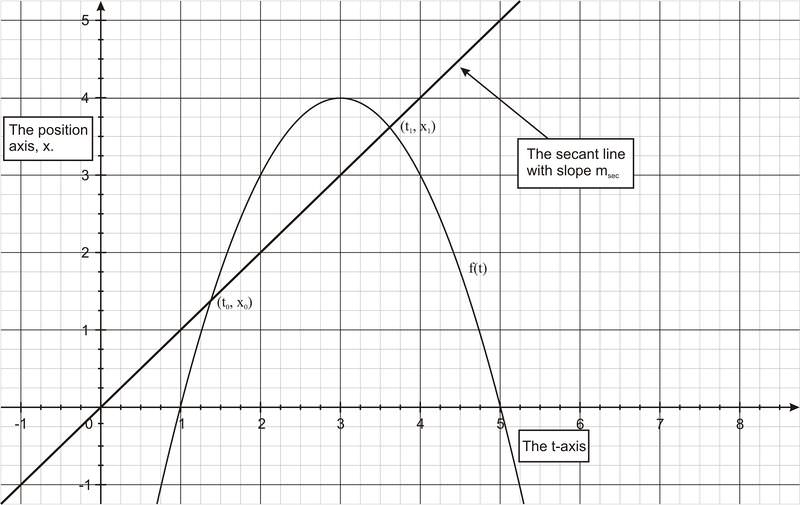
To master the calculation of the instantaneous rate of change, a solid understanding of mathematical principles and a systematic approach are essential. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Identify the Function: Begin by clearly defining the function for which you want to calculate the derivative. Ensure that the function is well-defined and continuous at the point of interest.
- Choose the Appropriate Method: Select the most suitable method for calculating the derivative based on the function's characteristics. Common methods include the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, and chain rule.
- Apply the Derivative Formula: Use the appropriate derivative formula to calculate the derivative. This may involve differentiating each term in the function separately and then combining the results.
- Evaluate at the Given Point: Once you have the derivative, substitute the given point into the derivative expression to find the instantaneous rate of change at that specific point.
- Interpret the Result: Finally, interpret the result in the context of the problem. Understanding the practical implications of the derivative can provide valuable insights into the behavior of the function.
Practice and Real-World Applications
Mastery of the formulaic approach to calculating derivatives comes with practice and exposure to a wide range of real-world applications. Solving diverse problems and exploring the practical implications of derivatives in various fields can enhance your understanding and proficiency.
Conclusion
The instantaneous rate of change, embodied by the derivative, is a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching applications. Its ability to quantify the rate at which a function changes at a specific point makes it an invaluable tool across diverse disciplines. By understanding and mastering the formulaic approach to calculating derivatives, you can unlock a powerful tool for analyzing and predicting the behavior of functions, making informed decisions, and solving complex problems in a wide range of fields.
What is the significance of the instantaneous rate of change in real-world applications?
+The instantaneous rate of change, as measured by the derivative, is crucial in real-world applications as it provides insights into the behavior of functions at specific points. This information is invaluable for making predictions, optimizing strategies, and solving complex problems in fields such as physics, engineering, economics, and biology.
How can I calculate the derivative of a function?
+To calculate the derivative of a function, you can use various derivative rules, such as the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, and chain rule. The choice of rule depends on the specific function and its characteristics. It’s important to practice and become familiar with these rules to efficiently calculate derivatives.
What are some common challenges in calculating derivatives?
+Some common challenges in calculating derivatives include functions with complex or discontinuous behavior, which can make the calculation more intricate. Additionally, functions with multiple variables can require the use of partial derivatives, adding another layer of complexity. However, with practice and a systematic approach, these challenges can be overcome.



