Water Density Insights: Unlocking The Power Of 62.4 Lb/Ft³
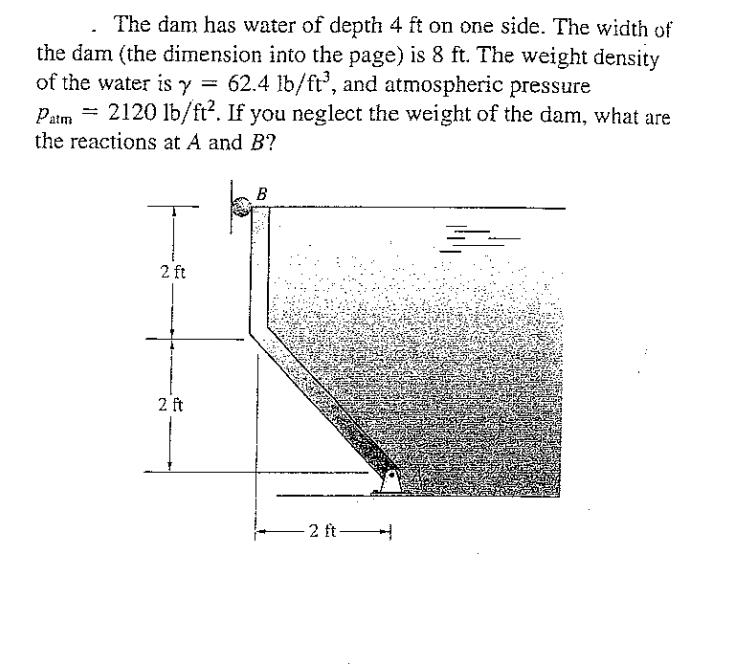
Water, a ubiquitous substance on our planet, possesses a fascinating property that often goes unnoticed: its density. At a remarkable 62.4 lb/ft³, water's density is a key factor that influences various natural phenomena and has significant implications across different scientific disciplines. In this article, we delve into the world of water density, exploring its intricacies, real-world applications, and the profound impact it has on our understanding of the natural world.
The Intricacies of Water Density
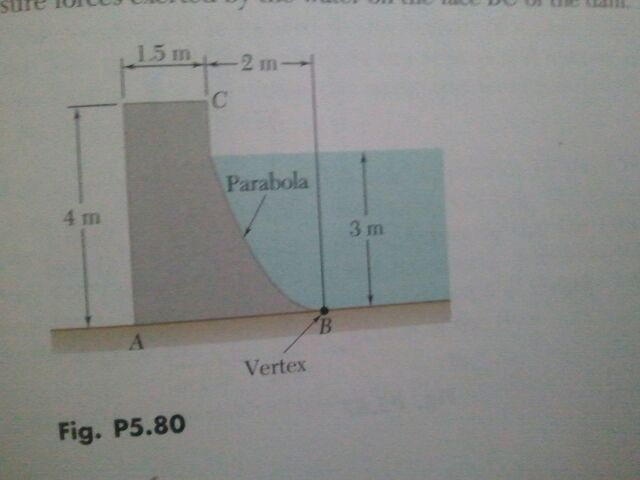
Water’s density, denoted as 62.4 lb/ft³, is a fundamental property that defines its mass per unit volume. This seemingly simple metric holds a wealth of information about the behavior and characteristics of water. The density of water is not constant; it varies with temperature and pressure, a phenomenon that has intrigued scientists for centuries.
One of the most remarkable aspects of water density is its behavior as temperature changes. As water cools, its density increases until it reaches its maximum density at approximately 39.2°F (4°C). This is a crucial factor in the formation of ice, as water's unique density behavior allows it to expand and become less dense as it freezes, forming ice that floats on top of liquid water. This property is essential for the survival of aquatic life, as it prevents bodies of water from freezing solid, creating a protective layer of ice that insulates the water below.
Furthermore, water's density is influenced by its salinity. The addition of salt or other dissolved substances can significantly alter water's density. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in the study of oceans and seas, where variations in salinity create density-driven currents and influence the distribution of marine life. Understanding the relationship between salinity and density is crucial for oceanographers and marine biologists alike.
Real-World Applications of Water Density
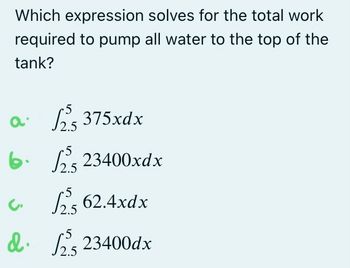
The concept of water density extends far beyond theoretical discussions, finding practical applications in various fields.
Hydraulic Engineering
In the realm of hydraulic engineering, water density plays a pivotal role in the design and operation of water infrastructure. Engineers must consider the density of water when designing dams, canals, and irrigation systems. The accurate calculation of water pressure and flow rates depends on understanding water’s density, ensuring the safe and efficient management of water resources.
Marine Navigation
For mariners and naval architects, water density is a critical factor in the design and navigation of ships and submarines. The density of seawater can vary significantly with depth and location, affecting a vessel’s buoyancy and stability. By accounting for water density, naval engineers can optimize the design of vessels to navigate through different aquatic environments safely.
Environmental Science
Environmental scientists utilize water density to study and monitor the health of aquatic ecosystems. Changes in water density can indicate alterations in water quality, such as pollution or the presence of harmful substances. By tracking density variations, scientists can identify potential environmental threats and implement mitigation strategies to protect fragile ecosystems.
Water Density in Action: Case Studies
To illustrate the practical implications of water density, let’s explore a few real-world case studies.
The Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef, an iconic marine ecosystem off the coast of Australia, is a prime example of how water density influences marine life. The reef’s diverse array of coral species relies on specific water density conditions for their survival. Any changes in water density, whether due to climate change or pollution, can disrupt the delicate balance of the reef ecosystem, impacting the health of corals and the entire marine food chain.
The Dead Sea
The Dead Sea, located between Israel and Jordan, is known for its extremely high salinity and density. With a salinity level over ten times that of the ocean, the Dead Sea has a density of approximately 124 lb/ft³, making it one of the saltiest bodies of water on Earth. This high density allows bathers to float effortlessly on the surface, creating a unique recreational experience. However, the Dead Sea’s density also poses challenges for researchers studying its unique microbial life, as they must account for the extreme conditions when conducting experiments.
Hydroelectric Power Generation
Hydroelectric power plants rely on the potential energy stored in water to generate electricity. The density of water is a critical factor in determining the efficiency of these power plants. By utilizing the weight and density of water, hydroelectric dams can harness the power of flowing water to generate clean and renewable energy. Understanding water density allows engineers to optimize the design and operation of these power plants, ensuring maximum energy output.
Future Implications and Research Directions
As our understanding of water density deepens, new avenues of research and innovation emerge. Scientists and engineers are exploring the following directions to unlock the full potential of water density.
Desalination Technologies
With the increasing demand for fresh water, researchers are developing advanced desalination technologies to convert seawater into potable water. Understanding the density-related challenges of desalination, such as the formation of salt crystals and the efficiency of reverse osmosis processes, is crucial for the development of sustainable and cost-effective desalination methods.
Water Quality Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of water quality is essential for maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems and ensuring safe drinking water supplies. By developing innovative sensors and monitoring systems that can accurately measure water density, scientists can detect subtle changes in water quality and respond promptly to potential contamination events.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on water density, particularly in the oceans. Rising sea temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can alter the density of seawater, affecting marine life and ocean circulation patterns. Research into the effects of climate change on water density is crucial for predicting and mitigating potential ecological disruptions.
Advanced Hydraulic Systems
The development of advanced hydraulic systems, such as those used in renewable energy technologies and space exploration, requires a deep understanding of water density. By harnessing the power of water’s density, engineers can design more efficient and sustainable hydraulic systems, contributing to the transition towards a greener and more sustainable future.
| Water Density Fact | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum Density | Water reaches its maximum density at approximately 39.2°F (4°C) |
| Salinity Impact | The addition of salt or dissolved substances can significantly alter water's density |
| Freezing Behavior | Water expands and becomes less dense as it freezes, allowing ice to float |

What factors influence water density?
+Water density is primarily influenced by temperature and salinity. As water cools, its density increases until it reaches its maximum density at approximately 39.2°F (4°C). Salinity, or the concentration of dissolved substances in water, can also significantly impact water’s density, particularly in marine environments.
How does water density affect marine life?
+Water density plays a crucial role in the distribution and survival of marine life. Changes in water density can affect the buoyancy and migration patterns of marine organisms. For example, variations in salinity and temperature can create density-driven currents, influencing the movement and behavior of fish and other aquatic species.
What are the challenges of desalination in relation to water density?
+Desalination, the process of removing salt from seawater to produce fresh water, faces challenges related to water density. The high density of seawater can lead to the formation of salt crystals, which can clog filters and reduce the efficiency of desalination processes. Understanding and overcoming these density-related challenges is crucial for the development of sustainable and cost-effective desalination technologies.



