What Are Little Green Bugs? Identifying And Eliminating Pests

In the world of gardening and pest control, the term "little green bugs" is a broad description often used to refer to a variety of small, green-colored insects that can cause damage to plants. These tiny invaders can be a nuisance for both amateur and experienced gardeners, and identifying and managing them effectively is crucial for maintaining a healthy garden ecosystem. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on these common pests, providing an in-depth understanding of their characteristics, impact, and management strategies.
Unveiling the Little Green Bugs: Common Species and Their Traits

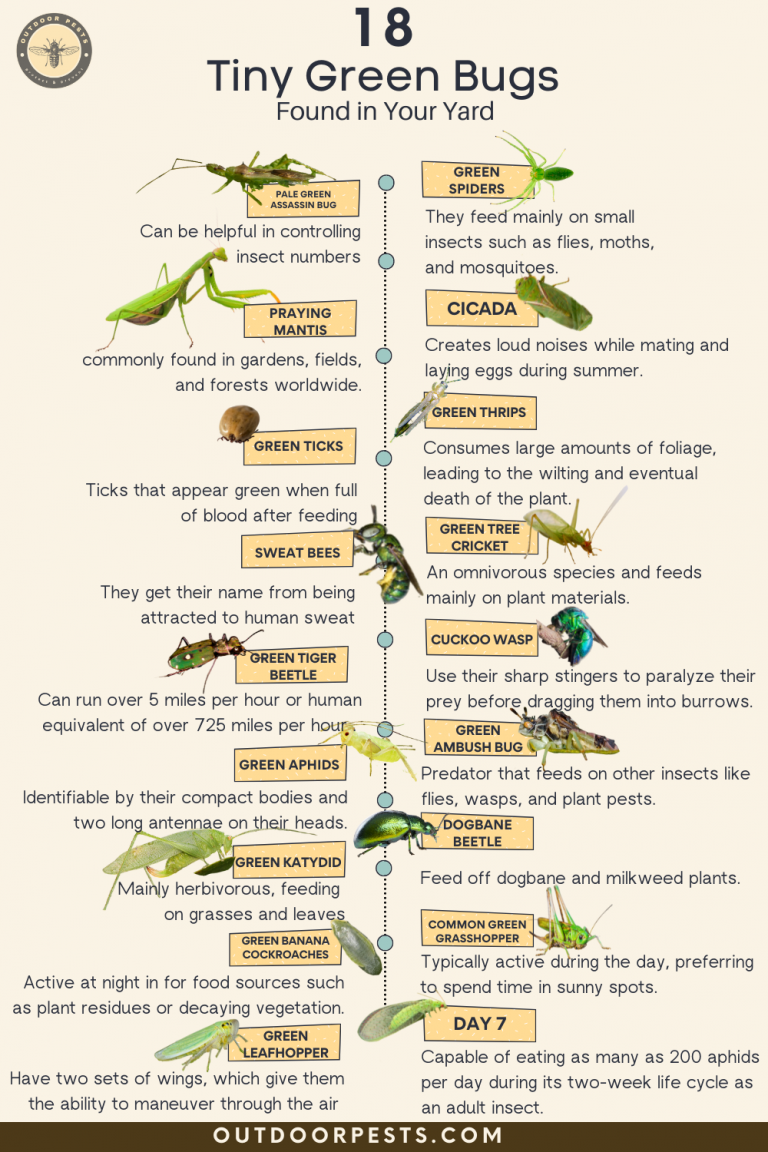
The term “little green bugs” encompasses a range of insect species, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. Some of the most common green-hued pests found in gardens include:
Aphids
Aphids, often referred to as plant lice, are one of the most prevalent green pests. They are typically small, pear-shaped insects with long antennae and a pair of cornicles (tube-like structures) at the end of their abdomen. Aphids feed on plant sap, causing leaves to curl, distort, or turn yellow. They also excrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which can attract other pests and promote the growth of sooty mold.
Mealybugs
Mealybugs are soft-bodied insects that resemble small pieces of cotton or lint. They are often found in clusters on the stems, leaves, and fruits of plants. Like aphids, mealybugs feed on plant sap, leading to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced plant vigor. They also produce honeydew, which can create an ideal environment for fungal diseases.
Thrips
Thrips are tiny, slender insects with fringed wings. They are known for their rapid movement and can be difficult to spot due to their small size. Thrips feed on plant tissues, causing silvering or scarring of leaves, flowers, and fruits. Their feeding can also lead to the transmission of plant diseases.
Whiteflies
Despite their name, whiteflies are often green or yellow in color. They are small, winged insects that resemble tiny moths. Whiteflies feed on plant sap, causing yellowing leaves and stunted growth. They also produce honeydew, which can lead to sooty mold growth.
Scale Insects
Scale insects are small, immobile pests that resemble scales or bumps on plant stems and leaves. They have a waxy or cottony appearance and feed on plant sap. Scale insects can cause yellowing, wilting, and dieback of infested plants.
Impact of Little Green Bugs on Plants
The presence of little green bugs can have significant impacts on plant health and productivity. These pests can cause direct damage to plants by feeding on their sap, tissues, or roots, leading to a range of symptoms, including:
- Leaf curling, distortion, or yellowing
- Stunted plant growth
- Reduced fruit or flower production
- Silvering or scarring of leaves and flowers
- Transmission of plant diseases
Additionally, the honeydew produced by aphids, mealybugs, and whiteflies can attract ants and promote the growth of sooty mold, further impacting plant health and aesthetics.
Integrated Pest Management Strategies for Little Green Bugs
Managing little green bugs effectively requires an integrated approach that combines various control methods. Here are some strategies to consider:
Cultural Control
Implementing good cultural practices can help prevent and manage pest populations. This includes:
- Regularly inspecting plants for early signs of pest infestation
- Removing infested plant parts or entire plants to prevent further spread
- Practicing crop rotation to disrupt pest life cycles
- Maintaining proper plant spacing to promote air circulation and reduce pest habitat
Biological Control
Introducing natural enemies of little green bugs can help control their populations. Some beneficial insects and organisms that prey on these pests include:
- Ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on aphids and other soft-bodied insects
- Parasitic wasps, which lay their eggs inside mealybugs and scale insects
- Predatory mites, which feed on thrips and other small pests
- Fungus gnats, which can help control root-feeding pests
Physical Control
Physical methods can be effective for managing little green bugs, especially when used in combination with other control strategies. Some physical control methods include:
- Hosing down plants with a strong stream of water to dislodge pests
- Using sticky traps or barriers to capture and prevent pest movement
- Hand-picking or pruning infested plant parts
- Covering plants with row covers to exclude pests
Chemical Control
In severe infestations, chemical control may be necessary. However, it’s important to use pesticides selectively and responsibly to minimize their impact on beneficial insects and the environment. Consider the following:
- Choose pesticides specifically labeled for the target pest and plant type
- Follow label instructions carefully, paying attention to application rates and timing
- Consider using organic or least-toxic pesticides, such as insecticidal soaps or neem oil
- Monitor pest populations after treatment to assess the effectiveness of the control measure
Preventing Little Green Bug Infestations
Prevention is key to effective pest management. Here are some proactive measures to help prevent little green bug infestations:
- Start with healthy, pest-free plants from reputable sources
- Quarantine new plants before introducing them to your garden
- Maintain good garden hygiene by removing plant debris and weeds
- Provide optimal growing conditions for plants, including proper watering, fertilizing, and pruning
- Encourage biodiversity in your garden to attract beneficial insects and promote natural pest control
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Pest Management

Managing little green bugs requires a holistic approach that considers the complex interactions between pests, plants, and the environment. By implementing a combination of cultural, biological, physical, and chemical control strategies, gardeners can effectively manage these pests and maintain a healthy, thriving garden ecosystem. Regular monitoring, early detection, and proactive management are key to successful pest control.
How can I identify little green bugs on my plants?
+Look for small, green-colored insects on the leaves, stems, or flowers of your plants. Common little green bugs include aphids, mealybugs, thrips, whiteflies, and scale insects. They may have distinctive shapes or behaviors, such as the pear-shaped aphids or the cotton-like appearance of mealybugs. Inspect both the upper and lower surfaces of leaves, as well as the stems and buds, for any signs of pest activity.
What are the signs of a little green bug infestation?
+Signs of a little green bug infestation can include distorted or curled leaves, yellowing foliage, stunted plant growth, and the presence of honeydew (a sticky substance) on plant surfaces. You may also notice ants crawling on the plants, as they are attracted to the honeydew produced by some pests like aphids and mealybugs.
How can I naturally control little green bugs in my garden?
+Natural control methods for little green bugs include releasing beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on pests. You can also use organic pesticides such as neem oil or insecticidal soap. Physical methods like hosing down plants with water or using sticky traps can also help manage pest populations. Additionally, maintaining good garden hygiene and practicing crop rotation can disrupt pest life cycles.