What Do Tubal Ligation Scars Look Like? A Visual Guide.

Tubal ligation, a highly effective form of permanent birth control, is a surgical procedure that involves cutting, sealing, or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent eggs from reaching the uterus. While the procedure itself is relatively straightforward, the resulting scars can vary in appearance and size, depending on the technique used and individual factors. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a visual and informative overview of what tubal ligation scars typically look like, helping individuals understand the potential outcomes and manage their expectations.
Understanding Tubal Ligation and Its Techniques

Tubal ligation, also known as tubal sterilization or tubal occlusion, is a permanent contraceptive method chosen by many women worldwide. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves the following techniques:
Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation
This minimally invasive approach is the most common method. A small incision is made near the navel, and a thin, lighted tube (laparoscope) is inserted to visualize the fallopian tubes. The surgeon then uses small instruments to seal or cut the tubes, leaving a minimal scar.
Minilaparotomy
In this technique, a small incision is made in the abdomen, usually below the belly button. The fallopian tubes are then located and sealed or cut through this incision, resulting in a slightly larger scar than the laparoscopic method.
Hysteroscopic Sterilization
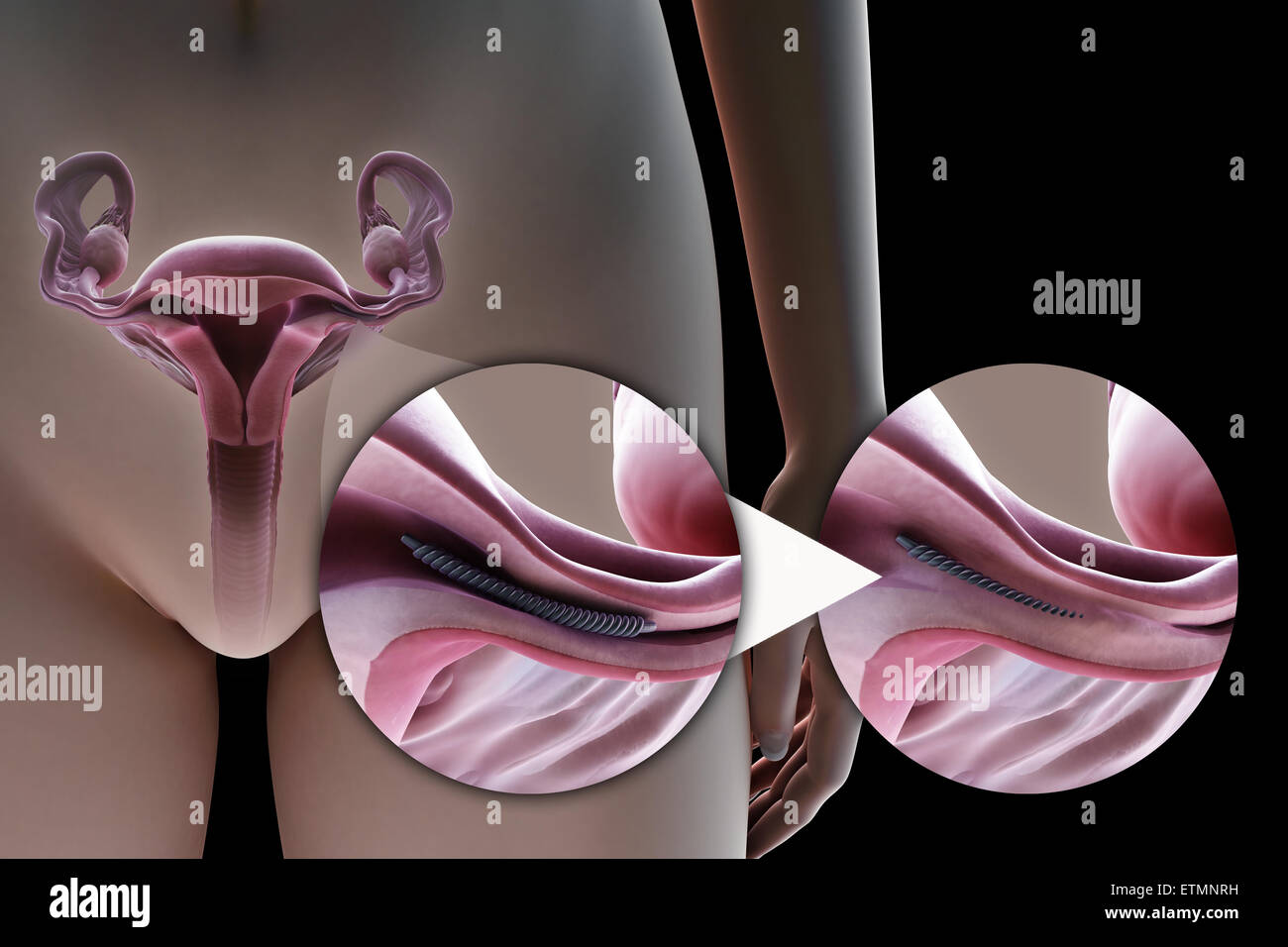
A less invasive option, hysteroscopic sterilization involves inserting a small scope (hysteroscope) through the vagina and cervix to access the uterus. Small implants are then placed in the fallopian tubes, blocking egg passage. This method typically leaves no external scars.
Appearance of Tubal Ligation Scars
The visual characteristics of tubal ligation scars can vary, influenced by factors such as individual healing abilities, the technique employed, and the surgeon’s expertise. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what these scars might look like:
Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation Scars
These scars are usually very small, measuring around 0.5 to 1 centimeter in length. They are often described as thin, straight lines and are typically well-hidden in the natural creases of the skin or near the navel. In most cases, they fade over time and become barely noticeable.
Minilaparotomy Scars
Scars resulting from a minilaparotomy are generally larger than those from laparoscopic procedures. They can range from 1 to 3 centimeters in length and are located in the lower abdomen. While they may be more visible initially, they often fade and flatten over time, especially with proper scar management techniques.
Hysteroscopic Sterilization Scars
This method leaves no visible external scars as the procedure is performed through the vaginal canal. However, some women may experience mild vaginal discomfort or spotting for a short period post-procedure.
Factors Influencing Scar Appearance
Several factors can impact the appearance and healing of tubal ligation scars. Understanding these factors can help individuals prepare for their recovery and manage their expectations:
Skin Type and Tone
Individuals with lighter skin tones may have more noticeable scars initially, but they tend to fade more quickly. Those with darker skin tones may experience less initial visibility but may have scars that fade more slowly.
Incisional Placement
The location of the incision plays a significant role in scar appearance. Incisions made in natural skin creases or folds are less noticeable, while those on flat surfaces may be more visible.
Individual Healing Abilities
Each person’s body heals differently. Some individuals may experience faster healing and minimal scarring, while others may have more pronounced scars that take longer to fade.
Surgeon’s Expertise
An experienced surgeon can minimize the size and visibility of scars by using precise techniques and making incisions in the most favorable locations.
Managing Tubal Ligation Scars
While it’s challenging to eliminate scars entirely, there are strategies to help manage their appearance and promote optimal healing:
Proper Wound Care
Following your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions is crucial. Keep the incision site clean, dry, and covered as recommended. Avoid activities that may strain the incision area, and report any signs of infection or excessive bleeding to your healthcare provider.
Scar Management Products
Over-the-counter or prescription scar management products, such as silicone sheets or gels, can help flatten and fade scars. These products work by providing a protective barrier and promoting collagen production, which can improve the appearance of scars over time.
Massage and Compression
Gently massaging the scar area can help improve circulation and reduce scar tissue buildup. Compression garments or bandages can also provide support and minimize scar tissue formation.
Sun Protection
Exposure to the sun can darken scars and make them more noticeable. Protect your scars from the sun by wearing sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and covering the area with clothing or a scarf when outdoors.
Potential Complications and Long-Term Effects

While tubal ligation is generally safe, like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks. Understanding these potential complications can help individuals make informed decisions and seek prompt medical attention if needed:
Infection
Infection at the incision site is a rare but possible complication. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, or discharge from the incision. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is usually effective.
Bleeding
Minor bleeding or spotting is normal during the healing process. However, excessive bleeding or hematoma (a collection of blood under the skin) may require medical attention.
Pain and Discomfort
Mild to moderate pain and discomfort are common post-procedure. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage these symptoms. If pain persists or becomes severe, consult your healthcare provider.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to the materials used during the procedure, such as surgical gloves or suture materials. Symptoms may include itching, rash, or difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect an allergic reaction.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most individuals recover well from tubal ligation, certain signs and symptoms may indicate a need for prompt medical evaluation. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Fever or chills
- Severe pain or discomfort that doesn't improve with pain medication
- Excessive bleeding or discharge from the incision site
- Redness, swelling, or warmth around the incision that worsens over time
- Nausea, vomiting, or dizziness
Conclusion
Tubal ligation is a safe and effective method of permanent birth control, and understanding the potential appearance of scars can help individuals make informed decisions. While scars may vary in size and visibility, proper wound care, scar management techniques, and patience during the healing process can lead to optimal results. Remember, every individual’s experience is unique, and consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and support throughout the tubal ligation journey.
How long does it take for tubal ligation scars to fade?
+The fading process can vary, but most scars start to fade within a few months. With proper scar management, they can become barely noticeable within a year.
Can tubal ligation scars be removed completely?
+While it’s challenging to eliminate scars entirely, certain cosmetic procedures like laser treatments or surgical scar revisions can help improve their appearance.
Are there any non-surgical alternatives to tubal ligation?
+Yes, non-surgical options include hormonal contraceptives (such as birth control pills or implants) and non-hormonal methods like condoms or diaphragms. It’s essential to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to find the best fit.