What Does A Positive Tb Test Look Like
Tuberculosis (TB) is a highly contagious bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs, but can also impact other parts of the body. The diagnosis of TB involves various tests, and a positive TB test result is a crucial indicator of the presence of the disease. In this article, we will delve into the details of what a positive TB test looks like, its implications, and the subsequent steps that follow.
Understanding the TB Test

The TB test, also known as the tuberculin skin test or the Mantoux test, is a widely used diagnostic tool to detect the presence of tuberculosis. It involves injecting a small amount of a substance called tuberculin into the skin, which is a purified protein derivative (PPD) derived from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. The test is designed to trigger an immune response in individuals who have been exposed to the bacteria.
Interpreting a Positive TB Test

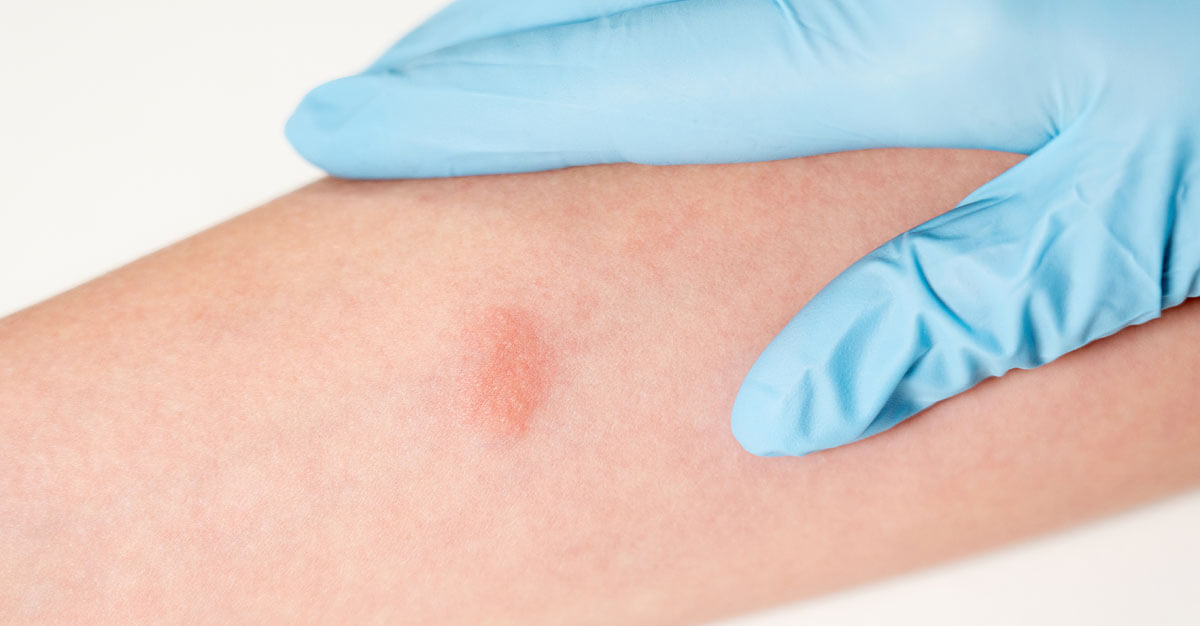
A positive TB test indicates that the individual has been infected with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. The interpretation of the test result is based on the size of the induration or swelling at the injection site. Here’s how a positive TB test is typically interpreted:
Induration Size
The size of the induration is measured in millimeters (mm) and is considered positive based on the following criteria:
- Recent Infection or High-Risk Individuals: For individuals with a high risk of TB exposure or those who have recently been exposed, an induration of 5 mm or more is considered a positive result.
- Low-Risk Individuals: In individuals with no known risk factors for TB, an induration of 10 mm or more is generally considered positive.
- Individuals with a Previous Positive Test: If an individual has had a previous positive TB test, an induration of 15 mm or more is considered a positive result.
Induration Characteristics
Apart from the size, the characteristics of the induration also play a role in interpreting the test result. A positive TB test typically exhibits the following features:
- Palpable Swelling: A positive TB test often results in a raised, palpable swelling at the injection site.
- Firm Consistency: The induration is usually firm to the touch, indicating an immune response.
- Redness or Erythema: Some individuals may also experience mild redness or erythema around the injection site.
Causes of a Positive TB Test
A positive TB test can have several causes, including:
Active Tuberculosis
A positive TB test is a strong indicator of active tuberculosis. In this case, the individual is likely to experience symptoms such as persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. Further diagnostic tests, such as chest X-rays and sputum cultures, are usually performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the infection.
Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI)
A positive TB test can also indicate latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). In LTBI, the individual has been infected with the bacteria but does not have active disease and does not exhibit any symptoms. However, there is a risk of developing active TB in the future. Individuals with LTBI are typically prescribed a course of preventive medication to reduce the risk of progression to active disease.
Previous TB Infection or Vaccination
A positive TB test can also result from a previous infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis or from vaccination with the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine. The BCG vaccine, which is used in some countries to prevent severe forms of TB in children, can cause a positive TB test result years after vaccination.
Next Steps After a Positive TB Test
A positive TB test is not a definitive diagnosis of active tuberculosis. Further evaluation is necessary to determine the extent of the infection and the appropriate course of action. Here are the typical steps that follow a positive TB test:
Clinical Evaluation
The individual with a positive TB test will undergo a thorough clinical evaluation. This includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and assessment of symptoms. The healthcare provider will inquire about any recent travel to high-risk areas, exposure to infected individuals, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions that may impact TB treatment.
Diagnostic Tests
To confirm the presence of active TB, additional diagnostic tests are usually performed. These may include:
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can help identify abnormalities in the lungs, such as cavities or infiltrates, which are characteristic of active TB.
- Sputum Culture: Sputum samples are collected and sent for laboratory analysis to detect the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. This test helps confirm the diagnosis and determine the drug susceptibility of the bacteria.
- GeneXpert MTB/RIF Assay: This rapid molecular test can detect the presence of TB bacteria and identify resistance to the antibiotic rifampicin, which is commonly used in TB treatment.
Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of TB depend on the results of the diagnostic tests and the individual’s overall health. Here are the general approaches:
- Active Tuberculosis: Individuals with active TB are usually treated with a combination of antibiotics for a prolonged period, typically lasting 6 to 9 months. The treatment aims to kill the bacteria and prevent the spread of the disease.
- Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI): For individuals with LTBI, a course of preventive medication, typically isoniazid (INH), is prescribed for 6 to 9 months. This treatment reduces the risk of developing active TB in the future.
- Close Contacts and High-Risk Individuals: In cases where an individual has a positive TB test but no signs of active disease, close contacts and high-risk individuals may also be evaluated and offered preventive treatment to reduce the risk of TB transmission.
Prevention and Control of Tuberculosis

Tuberculosis is a global health concern, and preventing its spread is crucial. Here are some key strategies for TB prevention and control:
Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection of TB through regular screening and prompt treatment of active cases is essential to prevent the spread of the disease. This includes implementing effective contact tracing and ensuring access to healthcare services for vulnerable populations.
Vaccination
The BCG vaccine, while not 100% effective, is still recommended in high-risk areas and for individuals with a high risk of TB exposure. It provides some protection against severe forms of TB, particularly in children.
Infection Control Measures
Implementing strict infection control measures in healthcare settings and public spaces is vital to prevent the transmission of TB. This includes proper ventilation, isolation of infected individuals, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by healthcare workers.
Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a crucial role in controlling TB. These initiatives include education and awareness campaigns, strengthening healthcare infrastructure, and ensuring access to affordable and effective TB treatment.
Conclusion
A positive TB test is a significant indicator of tuberculosis infection, whether it is active TB or latent TB. Understanding the implications of a positive test result and taking the necessary steps for further evaluation and treatment is crucial. With early detection, proper management, and effective public health measures, the spread of tuberculosis can be controlled, and the global burden of this infectious disease can be reduced.
What should I do if I have a positive TB test result?
+If you have a positive TB test result, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They will guide you through the next steps, which may include further diagnostic tests and treatment options. Follow their advice and complete the recommended course of treatment to ensure the best possible outcome.
Are there any risks associated with a positive TB test?
+A positive TB test indicates the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, which can lead to active tuberculosis if left untreated. However, with early detection and appropriate treatment, the risks can be minimized. It is important to follow the recommended treatment plan to prevent the spread of the disease and protect your own health.
Can a positive TB test result from the BCG vaccine?
+Yes, the BCG vaccine can cause a positive TB test result. The vaccine contains a weakened strain of Mycobacterium bovis, which is similar to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. This can lead to a positive reaction on the TB test. However, it is important to note that the BCG vaccine does not cause active TB and is used to prevent severe forms of the disease.



