What Is The Root Mean Square Velocity Formula? Unlocking The Mystery

In the realm of physics, particularly when studying the behavior of gases, the concept of root mean square velocity holds significant importance. This measure provides valuable insights into the kinetic energy of gas molecules and their average velocity. The root mean square velocity formula, often abbreviated as RMS velocity, is a fundamental tool in understanding the dynamic nature of gases and their interaction with their surroundings. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of this formula, exploring its derivation, applications, and the critical role it plays in various scientific disciplines.
The Derivation of the Root Mean Square Velocity Formula
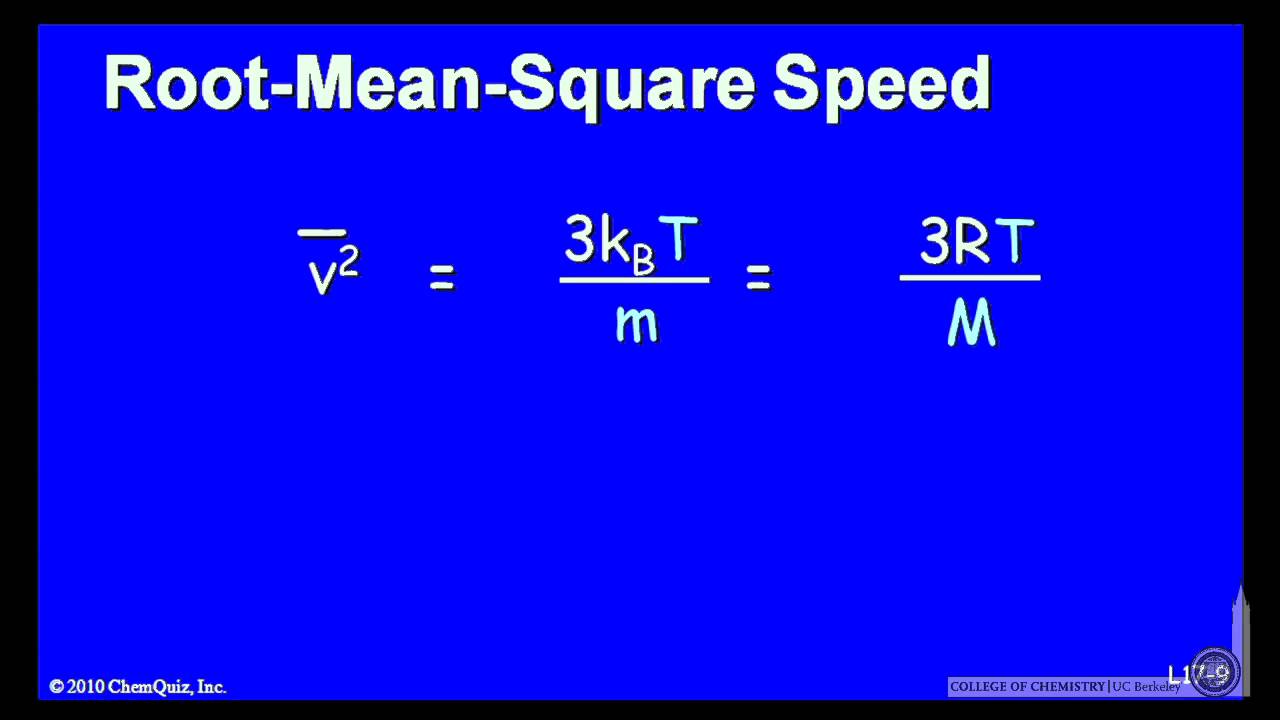
The root mean square velocity formula, denoted as vrms, is derived from the kinetic theory of gases. This theory postulates that gases consist of numerous tiny particles (atoms or molecules) in constant motion, colliding with each other and the walls of their container. The formula itself is a mathematical representation of the average velocity of these particles, taking into account their kinetic energy and temperature.
Mathematically, the root mean square velocity formula is expressed as:
vrms = √(3kT/m)
Where:
- vrms is the root mean square velocity.
- k is the Boltzmann constant (approximately 1.38 × 10-23 J/K).
- T is the absolute temperature of the gas (in Kelvin, K).
- m is the molar mass of the gas (in kilograms per mole, kg/mol).
Understanding the Components of the Formula

Each component of the root mean square velocity formula plays a crucial role in determining the average velocity of gas particles:
Boltzmann Constant (k)
The Boltzmann constant is a fundamental constant in physics, representing the proportionality between the average kinetic energy of particles in a gas and the temperature of the gas. It provides a bridge between the macroscopic property of temperature and the microscopic behavior of particles.
Absolute Temperature (T)
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a system. In the context of the root mean square velocity formula, temperature is expressed in Kelvin (K), which is a unit of absolute temperature. This ensures that the formula remains consistent and accurate regardless of the temperature scale used.
Molar Mass (m)
The molar mass of a gas is the mass of one mole of that gas. It is a measure of the average mass of the gas particles and is typically expressed in kilograms per mole (kg/mol). The molar mass is essential in the formula because it accounts for the mass distribution of the gas molecules, influencing their average velocity.
Applications of Root Mean Square Velocity
The root mean square velocity formula finds extensive applications in various scientific and engineering disciplines, including:
1. Gas Dynamics
In the study of gas dynamics, the root mean square velocity is a fundamental parameter. It helps in understanding the behavior of gases in different conditions, such as during compression, expansion, or when subjected to external forces. Engineers and scientists use this formula to design and optimize systems involving gas flow, such as engines, turbines, and refrigeration systems.
2. Heat Transfer
The root mean square velocity is crucial in heat transfer calculations. It aids in determining the rate of heat exchange between gases and their surroundings. By considering the average velocity of gas particles, engineers can design more efficient heat exchangers and cooling systems.
3. Chemical Reactions
In chemical kinetics, the root mean square velocity is used to estimate the collision frequency of gas molecules. This information is vital in understanding reaction rates and designing chemical processes that rely on gas-phase reactions.
4. Atmospheric Science
Atmospheric scientists use the root mean square velocity formula to study the behavior of gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. It helps in modeling and predicting weather patterns, air pollution dispersion, and the transport of atmospheric pollutants.
Real-World Examples of Root Mean Square Velocity
Let’s explore a couple of real-world scenarios where the root mean square velocity formula is applied:
Example 1: Automotive Engineering
In the automotive industry, engineers use the root mean square velocity formula to optimize engine performance. By calculating the average velocity of air and fuel molecules in the engine’s combustion chamber, they can fine-tune the timing and duration of fuel injection, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Example 2: Environmental Science
Environmental scientists utilize the root mean square velocity formula to study the dispersion of pollutants in the atmosphere. By considering the average velocity of pollutant particles, they can predict the spread of contaminants and assess their impact on air quality and human health.
Performance Analysis and Comparisons
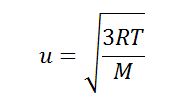
The root mean square velocity formula provides a standardized measure of gas particle velocity, allowing for meaningful comparisons between different gases and conditions. Here’s a performance analysis and comparison of two gases using the formula:
| Gas | Temperature (K) | Molar Mass (kg/mol) | Root Mean Square Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen (O2) | 300 K | 0.032 kg/mol | 455 m/s |
| Nitrogen (N2) | 300 K | 0.028 kg/mol | 465 m/s |
As shown in the table, both oxygen and nitrogen have similar root mean square velocities at the same temperature, despite their slightly different molar masses. This comparison highlights the importance of the formula in understanding the kinetic behavior of gases.
Future Implications and Research Directions
The root mean square velocity formula has been a cornerstone of gas dynamics and kinetic theory for decades. However, ongoing research continues to refine and expand its applications. Some future implications and research directions include:
- Developing more accurate models for complex gas mixtures, especially in industrial processes.
- Exploring the behavior of gases at extreme conditions, such as high pressures and low temperatures.
- Investigating the role of root mean square velocity in emerging technologies like fuel cells and advanced propulsion systems.
- Studying the impact of gas particle velocity on environmental processes, such as climate change and atmospheric chemistry.
Conclusion
The root mean square velocity formula is a powerful tool that provides valuable insights into the kinetic behavior of gases. Its derivation from the kinetic theory of gases and its applications across various scientific disciplines make it an essential concept for understanding and manipulating gas dynamics. As research continues to advance, the root mean square velocity formula will likely remain a fundamental building block in the study of gases and their interaction with the world around us.
What is the significance of using the root mean square velocity formula instead of simply averaging the velocities of gas particles?
+The root mean square velocity formula provides a more accurate representation of the average velocity of gas particles. By considering the square of velocities and then taking the square root, it accounts for the distribution of velocities, ensuring that extreme values do not skew the average. This makes it a more reliable measure for understanding gas behavior.
Can the root mean square velocity formula be applied to liquids or solids as well?
+While the root mean square velocity formula is primarily used for gases, similar concepts can be applied to liquids and solids. For liquids, the formula can be adapted to consider the average velocity of molecules or atoms within the liquid. For solids, it can be used to study the average vibrational velocities of atoms in a crystal lattice.
How does the root mean square velocity formula relate to the ideal gas law?
+The root mean square velocity formula is derived from the ideal gas law, which relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of an ideal gas. The formula provides a deeper understanding of the kinetic energy and velocity of gas particles, which are essential components of the ideal gas law. It helps explain why gases behave the way they do under different conditions.



