What Sickness Is Going Around Right Now

The prevalence and nature of illnesses can vary significantly depending on geographical location, seasonal changes, and other factors. Therefore, it is essential to provide a comprehensive overview of the current health landscape, focusing on the most prominent illnesses circulating in various regions.
Respiratory Infections and the Flu Season

As we transition into the colder months, respiratory infections and influenza (flu) become more prevalent. The flu is a highly contagious viral infection that affects the respiratory system, causing symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. Each year, the flu season varies in timing and severity, with certain strains dominating in different regions.
Currently, health authorities are closely monitoring the circulation of various flu strains, including the influenza A and B viruses. The H3N2 subtype of influenza A has been particularly active in recent years, causing more severe illness, especially among the elderly and individuals with pre-existing health conditions. Additionally, the emergence of new strains, such as the H1N1 pandemic strain in 2009, highlights the importance of staying vigilant and informed about flu activity.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing the spread of respiratory infections and the flu is crucial to protecting public health. Here are some effective strategies:
- Getting an annual flu vaccine is highly recommended, especially for individuals at higher risk of complications, such as the elderly, young children, pregnant women, and those with chronic health conditions.
- Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing with soap and water, using hand sanitizers, and covering coughs and sneezes, helps prevent the transmission of respiratory viruses.
- Avoiding close contact with sick individuals and maintaining physical distance when possible can reduce the risk of infection.
- Staying home when feeling unwell and seeking medical advice if symptoms worsen or persist is essential to prevent further spread.
Treatment for respiratory infections and the flu typically involves managing symptoms and preventing complications. Antiviral medications may be prescribed for severe cases or individuals at high risk. Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers and decongestants, can help alleviate fever, pain, and congestion. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
COVID-19: A Persistent Global Challenge
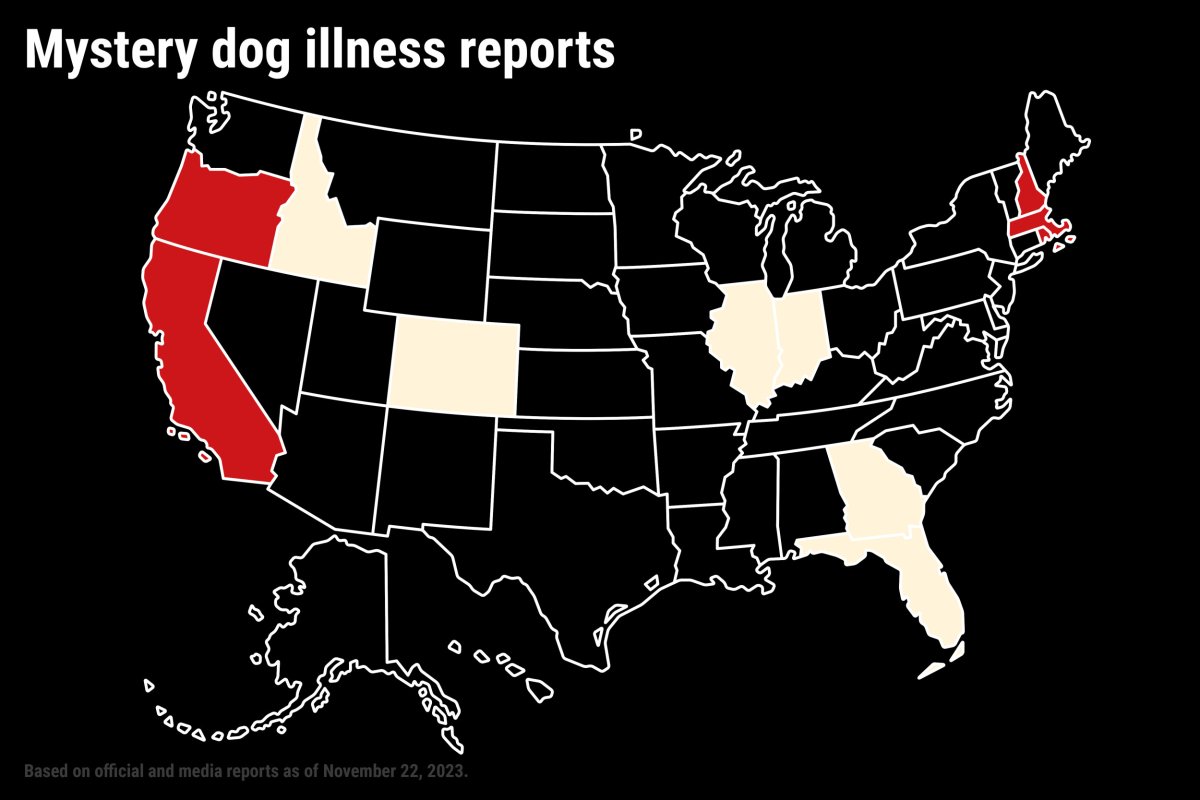
While the world continues to navigate the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, certain regions are experiencing varying levels of transmission and new challenges. The emergence of new variants, such as Omicron and its sublineages, has led to a resurgence of cases and prompted public health authorities to implement enhanced surveillance and mitigation measures.
The Omicron variant, characterized by its high transmissibility and ability to evade immune responses, has resulted in increased infections worldwide. This has put a strain on healthcare systems and led to the implementation of additional public health measures, including booster vaccine doses, mask mandates, and social distancing guidelines.
Vaccination and Booster Doses
Vaccination remains a critical tool in the fight against COVID-19. As new variants emerge, booster doses are recommended to enhance immunity and provide better protection against severe illness and hospitalization. Health authorities emphasize the importance of staying up-to-date with vaccine schedules and booster recommendations to maintain a robust immune response.
The development and distribution of vaccines have significantly reduced the severity and mortality associated with COVID-19. However, the continued circulation of the virus and the emergence of new variants highlight the need for ongoing research, surveillance, and public health interventions to mitigate the impact of the pandemic.
Gastrointestinal Illnesses: A Common Concern
Gastrointestinal illnesses, including viral gastroenteritis (often referred to as “stomach flu”) and foodborne illnesses, are prevalent throughout the year but can become more common during certain seasons. These illnesses are typically caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites and can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Viral gastroenteritis is highly contagious and can spread rapidly in communities, especially in settings like schools, daycare centers, and long-term care facilities. Common viral causes include norovirus, rotavirus, and adenovirus. Outbreaks of gastrointestinal illnesses can have a significant impact on public health and disrupt daily life.
Food Safety and Prevention
Preventing gastrointestinal illnesses often involves practicing good food safety habits. Here are some key measures to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses:
- Properly handle and cook food, especially raw or undercooked meats, poultry, and seafood.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consumption.
- Avoid cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and ready-to-eat foods.
- Maintain good personal hygiene, including regular handwashing before and after food preparation.
- Store food at appropriate temperatures to prevent bacterial growth.
In addition to food safety practices, practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals, can help prevent the spread of gastrointestinal illnesses.
Allergies and Allergic Reactions
Allergies are a common health concern, and certain allergens can be more prevalent during specific seasons. Seasonal allergies, also known as hay fever, are caused by an immune response to airborne allergens such as pollen, mold spores, and grass. Symptoms can include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, and throat irritation.
Allergic reactions can also be triggered by food, medications, insect stings, or other environmental factors. These reactions can range from mild to severe and may require immediate medical attention. Anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction, can cause symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, rapid pulse, and dizziness.
Managing Allergies
Managing allergies often involves a combination of avoidance strategies and medical treatments. Here are some tips for individuals with allergies:
- Identify and avoid known allergens whenever possible.
- Use allergy medications, such as antihistamines and nasal sprays, as recommended by a healthcare professional.
- Consider immunotherapy (allergy shots) for long-term relief from allergy symptoms.
- Keep emergency medications, such as epinephrine auto-injectors, readily available for severe allergic reactions.
- Inform others, such as coworkers, friends, and family, about your allergies to ensure a safe environment.
Consulting an allergist or immunologist can provide specialized care and personalized treatment plans for managing allergies effectively.
The Impact of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as air quality and pollution, can also influence the prevalence of certain illnesses. Poor air quality, especially in urban areas, can exacerbate respiratory conditions and trigger asthma attacks. Additionally, extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and natural disasters, can lead to an increased risk of heat-related illnesses, waterborne diseases, and mental health issues.
Climate change and environmental degradation can also contribute to the emergence and spread of infectious diseases. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the distribution and behavior of disease vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks, leading to the spread of diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease.
Addressing Environmental Health Risks
Addressing environmental health risks requires a multi-faceted approach involving public health initiatives, community engagement, and policy interventions. Here are some key strategies:
- Implementing air quality monitoring and pollution control measures to reduce the impact of air pollution on public health.
- Promoting sustainable practices and reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Strengthening vector control programs to prevent the spread of vector-borne diseases.
- Enhancing disaster preparedness and response plans to address the health impacts of extreme weather events.
- Investing in research and surveillance to better understand the complex interactions between environmental factors and human health.
By addressing environmental health risks, we can work towards creating healthier and more resilient communities, reducing the burden of illness, and improving overall well-being.
The Importance of Staying Informed
In the ever-changing landscape of public health, staying informed about the latest illnesses and health trends is crucial. By being aware of the diseases circulating in your community, you can take proactive measures to protect yourself and your loved ones. Here are some resources to help you stay informed:
- Regularly check reputable health websites and news sources for updates on illness outbreaks and public health advisories.
- Follow local and national health authorities on social media to receive timely notifications and alerts.
- Subscribe to health-focused newsletters or podcasts to stay updated on the latest research and developments.
- Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance based on your specific health needs.
By staying informed and taking preventive measures, we can contribute to a healthier society and reduce the impact of illnesses on our communities.
Conclusion
The illnesses circulating in our communities can vary widely depending on factors such as geography, season, and environmental conditions. From respiratory infections and the flu to COVID-19, gastrointestinal illnesses, allergies, and environmental health risks, staying vigilant and informed is essential for protecting our health and well-being. By practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and adopting healthy habits, we can reduce the spread of illnesses and create a safer and healthier environment for all.
What are some common symptoms of respiratory infections and the flu?
+Common symptoms of respiratory infections and the flu include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, fatigue, and in some cases, difficulty breathing. It’s important to seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or persist.
How long does it take to recover from COVID-19?
+The recovery time for COVID-19 can vary depending on the severity of the illness and individual factors. While some people may experience mild symptoms and recover within a few days, others may have more severe symptoms and require hospitalization. On average, recovery can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks.
What are the main causes of gastrointestinal illnesses?
+Gastrointestinal illnesses are typically caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Common causes include norovirus, rotavirus, E. coli, Salmonella, and Campylobacter. These pathogens can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, or person-to-person contact.