What's The Average Fever Duration? A Quick Guide
Fever is a common ailment that can affect people of all ages, and understanding its duration is crucial for effective management and care. While fever is often a sign of the body's natural response to infection, knowing how long it typically lasts can provide valuable insights for both patients and healthcare professionals. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the average fever duration, the factors that influence it, and the key signs to watch for when assessing the progression of a fever.
Understanding Fever: Definition and Causes

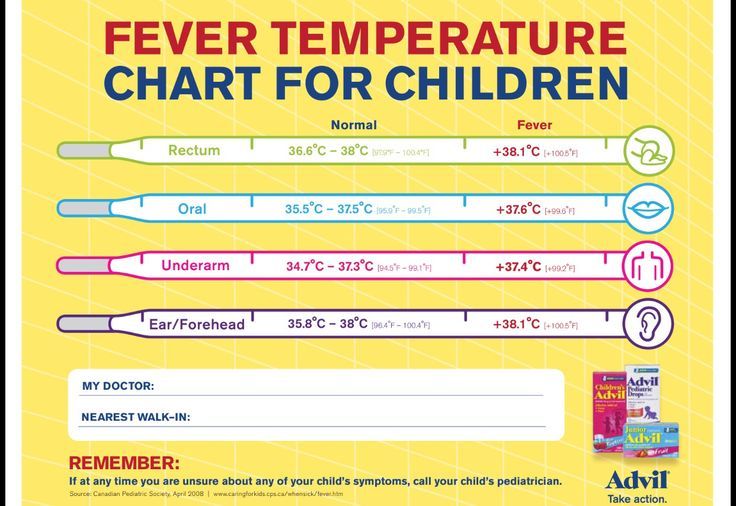
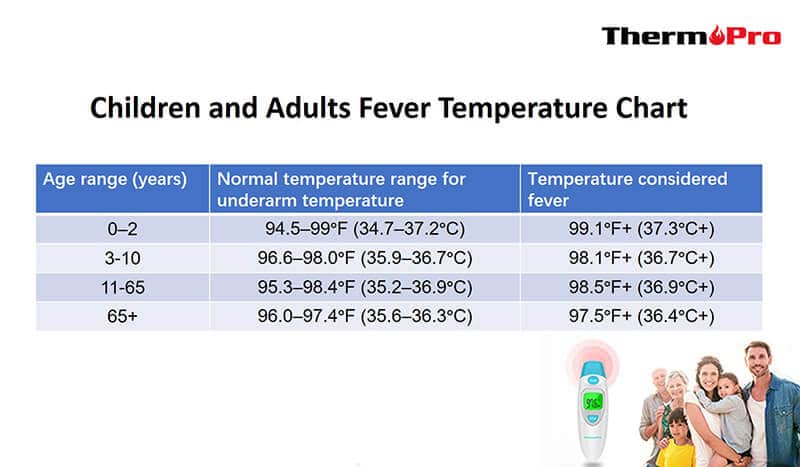
Fever, medically known as pyrexia, is a temporary increase in body temperature above the normal range. It is typically defined as a core body temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or higher. Fever is a common symptom of various illnesses, including infections, inflammatory conditions, and certain medications or treatments.
The body's immune system triggers a fever as a defense mechanism against pathogens. During a fever, the body's temperature rises, creating an inhospitable environment for many microorganisms, which can help fight off infections. However, prolonged or extremely high fevers can have adverse effects and require medical attention.
Average Fever Duration: A General Overview

The average duration of a fever can vary depending on the underlying cause and the individual’s overall health. Here is a breakdown of the typical fever duration for different scenarios:
Viral Infections
Viral infections, such as the common cold, influenza, or viral gastroenteritis, are often associated with fevers. In most cases, these fevers last for 3 to 4 days, with the highest temperatures occurring on the first or second day. The fever tends to resolve as the body’s immune response gains control over the virus.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections, including strep throat, urinary tract infections, or pneumonia, can also cause fevers. The duration of these fevers varies but typically ranges from 2 to 7 days. In some cases, bacterial infections may require medical intervention, such as antibiotics, to resolve the fever and prevent complications.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions, like arthritis or autoimmune disorders, can lead to fever as a symptom. The duration of these fevers can vary widely, from a few days to several weeks or even months. Managing the underlying condition is essential to controlling the fever in these cases.
Medications and Treatments
Certain medications, such as antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs, can cause drug-induced fevers. The duration of these fevers depends on the specific medication and its half-life. In most cases, the fever resolves once the medication is stopped or the body metabolizes it.
Factors Influencing Fever Duration
While the average fever duration provides a general guideline, several factors can influence how long a fever lasts:
Underlying Condition
The specific illness or condition causing the fever plays a significant role in its duration. As mentioned earlier, viral infections tend to have shorter fever durations compared to bacterial infections or inflammatory conditions.
Individual Health Status
A person’s overall health, immune system strength, and age can impact the duration of a fever. Young children and older adults may experience longer fever durations due to their less robust immune systems. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing cancer treatment, may have prolonged fevers.
Treatment and Management
The type of treatment received can also affect fever duration. Antipyretic medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help reduce fever and provide relief. However, it’s essential to note that these medications only manage the symptom and do not treat the underlying cause. Medical interventions, such as antibiotics for bacterial infections, can help resolve fevers more quickly.
Signs to Watch for During a Fever
Monitoring the progression of a fever is crucial to ensure it does not escalate into a more severe condition. Here are some key signs to watch for:
Persistent High Temperatures
If a fever persists for more than 3 days without any signs of improvement, it is essential to seek medical advice. Prolonged high temperatures can indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires medical attention.
Severe Symptoms
Fevers accompanied by severe symptoms, such as persistent vomiting, severe headache, neck stiffness, rash, or difficulty breathing, warrant immediate medical evaluation. These symptoms could indicate a more serious infection or complication.
Dehydration
Fever can lead to increased fluid loss through sweating and increased metabolic rate. It is crucial to monitor for signs of dehydration, such as reduced urine output, dry mouth, and dizziness. Ensuring adequate fluid intake is essential to prevent dehydration during a fever.
Neurological Symptoms
In rare cases, high fevers can trigger neurological symptoms, such as seizures. If a person experiences seizures or exhibits abnormal behavior during a fever, immediate medical care is necessary.
Managing Fever at Home
For mild to moderate fevers, home care measures can help provide comfort and support the body’s natural healing process. Here are some tips for managing fever at home:
Rest and Hydration
Encourage the person with a fever to rest and get plenty of sleep. Adequate rest allows the body to focus its energy on fighting the infection. Additionally, ensure the individual stays well-hydrated by offering cool fluids, such as water, herbal tea, or electrolyte-rich beverages.
Cooling Measures
To help reduce fever and provide comfort, you can use cooling measures such as a cool cloth on the forehead or a lukewarm bath. Avoid using ice or very cold water, as it can cause shivering and further increase body temperature.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Antipyretic medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can be used to reduce fever and relieve associated symptoms like headache or body aches. Follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or questions.
Monitor and Record
Keep a record of the person’s temperature readings and any other relevant symptoms. This information can be valuable when seeking medical advice or tracking the progress of the fever.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most fevers resolve on their own with proper home care, there are situations where medical attention is necessary. Seek immediate medical care if any of the following occur:
- Fever in infants under 3 months of age.
- Fever of 103°F (39.4°C) or higher in children.
- Fever accompanied by severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, persistent vomiting, or seizures.
- Fever that persists for more than 3 days without improvement.
- Fever in individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions.
Conclusion: Fever Management and Awareness
Understanding the average fever duration and the factors that influence it is essential for effective fever management. By recognizing the typical fever durations for different conditions and monitoring for concerning signs, individuals can make informed decisions about when to seek medical care. Remember, while fevers are a common and often self-limiting symptom, prompt medical attention is crucial for severe cases or when in doubt.
What is the highest temperature a fever can reach before it becomes dangerous?
+While a fever is defined as a temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or higher, extremely high temperatures above 40°C (104°F) can be dangerous and require immediate medical attention. Prolonged high fevers can lead to heatstroke, dehydration, and other complications.
Can a fever be a sign of a serious infection?
+Yes, a fever can be a sign of a serious infection, especially if it is accompanied by severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, persistent vomiting, or neurological symptoms. In such cases, immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
How can I tell if my child’s fever is caused by a viral or bacterial infection?
+It can be challenging to differentiate between viral and bacterial infections based on fever alone. However, viral infections often present with additional symptoms like runny nose, cough, and body aches, while bacterial infections may cause more localized symptoms, such as ear pain or urinary discomfort. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause.



