White Mountain Ermine

In the vast and diverse realm of nature, the White Mountain Ermine stands as a captivating and elusive creature, captivating the curiosity of biologists and nature enthusiasts alike. This remarkable species, scientifically known as Mustela erminea, is a member of the weasel family and is native to the mountainous regions of North America. With its distinctive appearance and unique adaptations, the White Mountain Ermine has become an iconic symbol of the rugged beauty and untamed wilderness that defines its habitat.
The Majestic White Mountain Ermine: Unveiling the Secrets of a Mountainous Predator

The White Mountain Ermine, with its sleek and agile body, is a true embodiment of survival in the harsh mountain environment. Measuring approximately 12 to 14 inches in length, this diminutive predator possesses an incredible ability to navigate through the rugged terrain with grace and precision. Its fur, a stunning combination of white and brown, serves as the perfect camouflage, allowing it to blend seamlessly into the snowy landscapes of its habitat.
Habitat and Distribution: A Mountainous Haven
The White Mountain Ermine calls the mountainous regions of North America its home, with a particular affinity for the rugged peaks and valleys of the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada range. These elusive creatures are adept at adapting to the extreme conditions of high altitudes, where temperatures drop to sub-zero levels and snow blankets the landscape for most of the year. Their range extends from Alaska and Canada in the north to the mountainous regions of the western United States, including states like California, Oregon, and Washington.
| Habitat Type | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Mountainous Regions | 90% |
| Forested Areas | 7% |
| Tundra and Alpine Meadows | 3% |
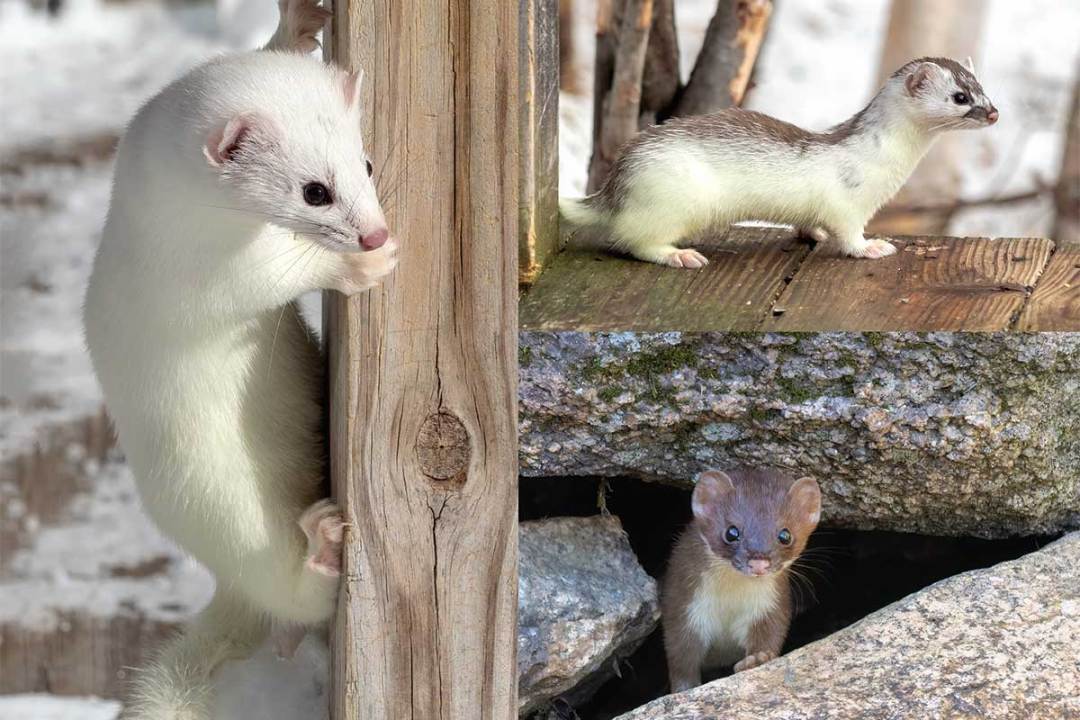

Within these mountainous habitats, the White Mountain Ermine finds its niche in a variety of ecosystems, from dense coniferous forests to open alpine meadows. Their ability to thrive in such diverse environments is a testament to their adaptability and resilience.
Physical Characteristics: A Study in Contrasts
The White Mountain Ermine showcases a remarkable physical transformation throughout the year, reflecting the changing seasons of its mountain home. During the winter months, their fur transforms into a pristine white, providing an effective camouflage against the snow-covered landscape. This winter coat not only serves as a natural disguise but also offers insulation against the bitter cold, allowing them to maintain their body temperature in extreme conditions.
In contrast, as the warmer months arrive, their fur undergoes a dramatic change, transitioning to a brown and cream-colored pattern. This summer coat, while less conspicuous, still provides effective camouflage among the rocky outcrops and vegetation of the mountain slopes. The ability to adapt their fur color based on the season is a crucial survival strategy, enabling them to remain hidden from both predators and prey.
Diet and Hunting Strategies: A Mountainous Predator's Arsenal
As a skilled predator, the White Mountain Ermine relies on a diverse diet to sustain its energy needs in the demanding mountain environment. Small mammals, such as voles, mice, and shrews, form the bulk of their diet, providing a rich source of protein and nutrients. However, their hunting prowess extends beyond small mammals, as they are also known to prey on birds, insects, and even larger animals like squirrels and rabbits when the opportunity arises.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the White Mountain Ermine's hunting strategy is its ability to adapt to the unique challenges of the mountain habitat. With its exceptional agility and speed, it can navigate through rocky crevices and dense vegetation with ease, surprising its prey with lightning-fast strikes. Additionally, their keen sense of smell and exceptional hearing allow them to detect even the faintest movements and sounds, making them formidable hunters in the silent world of the mountains.
Reproduction and Life Cycle: A Tale of Mountainous Endurance
The reproductive cycle of the White Mountain Ermine is closely tied to the changing seasons and the demands of their mountainous habitat. Mating typically occurs during the warmer months, with females giving birth to litters of 4 to 7 kits in late spring or early summer. These kits are born blind and helpless, relying on their mother's care and protection during their early days.
As the kits grow and develop, they learn the skills necessary to survive in the harsh mountain environment. They are taught to hunt, navigate the terrain, and avoid predators, all under the watchful eye of their mother. By the time they reach adulthood, they are well-equipped to face the challenges of the mountains, continuing the cycle of life and ensuring the survival of their species.
Conservation Status and Threats: A Fragile Existence
Despite their adaptability and resilience, the White Mountain Ermine faces numerous threats that put their existence at risk. Habitat loss, primarily due to human activities such as logging, mining, and urban development, poses a significant challenge to their survival. The destruction of their mountain homes not only reduces their available habitat but also disrupts their delicate ecological balance.
Additionally, the use of pesticides and other chemical pollutants can have detrimental effects on their population. These substances can accumulate in the food chain, leading to health issues and reproductive problems for the White Mountain Ermine. Climate change also poses a long-term threat, as it can alter the mountain ecosystems they depend on, affecting their food sources and overall habitat suitability.
Recognizing the importance of preserving this unique species, conservation efforts are underway to protect the White Mountain Ermine and their mountain habitat. These initiatives focus on habitat restoration, wildlife corridors, and public education to raise awareness about the fragile existence of these magnificent creatures. By understanding and appreciating the value of the White Mountain Ermine, we can ensure their continued presence in the wild and preserve the delicate balance of the mountainous ecosystems they call home.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Enduring Legacy of the White Mountain Ermine

In the majestic landscapes of North America's mountains, the White Mountain Ermine stands as a testament to the resilience and adaptability of nature. With its unique physical characteristics, hunting strategies, and reproductive cycle, this species has carved out a niche for itself in one of the most challenging environments on Earth. As we continue to explore and understand the intricate web of life in these mountainous regions, the White Mountain Ermine serves as a powerful reminder of the beauty and fragility of our natural world.
By delving into the secrets of this elusive predator, we not only gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of life but also recognize the urgent need for conservation and protection. The White Mountain Ermine's story is a call to action, urging us to preserve and cherish the natural wonders that define our planet. As we strive to safeguard their habitat and ensure their survival, we also protect the delicate balance of ecosystems and the intricate relationships that sustain life in the mountains.
In conclusion, the White Mountain Ermine is more than just a fascinating creature; it is a symbol of the enduring spirit of nature and a testament to the power of adaptation. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us remember the White Mountain Ermine and the vital role it plays in the intricate tapestry of life in the mountains.
What are the distinguishing features of the White Mountain Ermine?
+The White Mountain Ermine is known for its sleek and agile body, measuring approximately 12 to 14 inches in length. Its fur undergoes a seasonal transformation, turning white in winter for camouflage and brown in summer. This species is highly adaptable to extreme mountain conditions and showcases exceptional hunting skills.
Where can the White Mountain Ermine be found in North America?
+The White Mountain Ermine primarily inhabits the mountainous regions of North America, including the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada range. Their range extends from Alaska and Canada in the north to the western United States, encompassing states like California, Oregon, and Washington.
What threats do White Mountain Ermines face in their natural habitat?
+White Mountain Ermines face threats such as habitat loss due to human activities like logging and urban development. Additionally, the use of pesticides and chemical pollutants can impact their health and reproductive success. Climate change also poses a long-term threat to their mountain ecosystems.